How to use computed properties and listeners in Vue3
Computed properties
We know that some data in data can be displayed directly through interpolation syntax in the template, but in some cases, we may need to perform some transformations on the data before displaying it, or we need to Combining multiple data for display
Using expressions in templates can be very convenient, but they are originally designed for simple operations. Putting too much logic in the template will make the template It is too heavy and difficult to maintain, and if it is used in multiple places, there will be a lot of duplicate code
So we hope to separate the business logic and UI interface. One way is to extract the logic into a method, but this approach has the following disadvantages
All the data usage process will become a method call
Multiple acquisitions Data needs to call the method multiple times to execute the corresponding logic without caching
In fact, For any complex logic that contains responsive data, you should use calculated properties
<div id="app">
<!-- 计算属性的使用和普通状态的使用方式是一致的 -->
<h3>{{ fullname }}</h3>
</div>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
firstname: 'Klaus',
lastname: 'Wang'
}
},
computed: {
fullname() {
return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname
}
}
}).mount('#app')Cache
Computed properties will be cached based on their dependencies. When the data does not change, calculated properties do not need to be recalculated
But if When the dependent data changes, the calculated properties will still be recalculated when used
And the interface will be re-rendered using the latest calculated property values
getters and setters
Computed properties In most cases, only one getter method is needed, so we will write the calculated properties directly as a function
<div id="app">
<!-- 计算属性的使用和普通状态的使用方式是一致的 -->
<h3>{{ fullname }}</h3>
<button @click="change">change</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
firstname: 'Klaus',
lastname: 'Wang'
}
},
methods: {
change() {
this.fullname = 'Alex Li'
}
},
computed: {
// 计算属性的完整写法
fullname: {
get() {
return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname
},
set(v) {
this.firstname = v.split(' ')[0]
this.lastname = v.split(' ')[1]
}
}
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>Listener
is defined in the object returned by data The data is bound to the template through interpolation syntax, etc. When the data changes, the template will automatically update to display the latest data
But in some cases, we hope that in the code logic To monitor changes in certain data, you need to use the listener watch at this time
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
info: {
name: 'Klaus'
}
}
},
watch: {
// 可以使用watch监听响应式数据的改变
// 对应有两个参数
// 参数一 --- 新值
// 参数二 --- 旧值
info(newV, oldV) {
// 如果监听的值是对象,获取到的新值和旧值是对应对象的代理对象
console.log(newV, oldV)
// 代理对象 转 原生对象
// 1. 使用浅拷贝获取一个新的对象,获取的新的对象为原生对象
console.log({...newV})
// 2. 使用Vue.toRaw方法获取原生对象
console.log(Vue.toRaw(newV))
}
},
methods: {
change() {
this.info = {
name: 'Steven'
}
}
}
}).mount('#app')Configuration options
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| deep | Whether to turn on deep monitoring The value is boolean When it is not turned on, if the object is monitored, only the reference of the object occurs The watch callback will only be triggered when it changes After starting, if the object is monitored, then as long as any attribute in the object changes, the watch callback will be triggered |
| immediate | Whether to start monitoring immediately By default, the watch monitoring will not be triggered for the first rendering. Only when the value changes, the watch monitoring will be triggered. After setting immediate to true, the watch monitoring will be triggered for the first time. Rendering will also trigger watch monitoring. At this time, the value of oldValue is undefined |
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
info: {
name: 'Klaus'
}
}
},
watch: {
info: {
// 开启了深度监听后,当info的属性发生改变的时候,就会触发对应的watch回调
// 注意: 和直接修改info引用不同的是,如果直接修改的是对象的属性
// 那么此时newV和oldV是同一个对象的引用, 此时也就获取不到对应的旧值
handler(newV, oldV) {
console.log(newV, oldV)
console.log(newV === oldV) // => true
},
deep: true,
immediate: true
}
},
methods: {
change() {
this.info.name = 'Steven'
}
}
}).mount('#app')Other writing methods
Directly monitor the object properties
watch: {
'info.name'(newV, oldV){
console.log(newV, oldV)
}
}String writing method
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
info: {
name: 'Klaus'
}
}
},
watch: {
// watch的值如果是一个字符串的时候
// 会自动以该字符串作为函数名去methods中查找对应的方法
'info.name': 'watchHandler'
},
methods: {
change() {
this.info.name = 'Steven'
},
watchHandler(newV, oldV){
console.log(newV, oldV)
}
}
}).mount('#app')Array writing method
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
info: {
name: 'Klaus'
}
}
},
watch: {
'info.name': [
'watchHandler',
function handle() {
console.log('handler2')
},
{
handler() {
console.log('handler3')
}
}
]
},
methods: {
change() {
this.info.name = 'Steven'
},
watchHandler(){
console.log('handler1')
}
}
}).mount('#app')$watch
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
info: {
name: 'Klaus'
}
}
},
created() {
/*
$watch 参数列表
参数一 --- 侦听源
参数二 --- 侦听回调
参数三 --- 配置对象
*/
this.$watch('info.name', (newV, oldV) => console.log(newV, oldV), {
immediate: true
})
},
methods: {
change() {
this.info.name = 'Steven'
}
}
}).mount('#app')The above is the detailed content of How to use computed properties and listeners in Vue3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
tinymce is a fully functional rich text editor plug-in, but introducing tinymce into vue is not as smooth as other Vue rich text plug-ins. tinymce itself is not suitable for Vue, and @tinymce/tinymce-vue needs to be introduced, and It is a foreign rich text plug-in and has not passed the Chinese version. You need to download the translation package from its official website (you may need to bypass the firewall). 1. Install related dependencies npminstalltinymce-Snpminstall@tinymce/tinymce-vue-S2. Download the Chinese package 3. Introduce the skin and Chinese package. Create a new tinymce folder in the project public folder and download the
 vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite:src uses require to dynamically import images and error reports and solutions. vue3+vite dynamically imports multiple images. If vue3 is using typescript development, require will introduce image errors. requireisnotdefined cannot be used like vue2 such as imgUrl:require(' .../assets/test.png') is imported because typescript does not support require, so import is used. Here is how to solve it: use awaitimport
 How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
To achieve partial refresh of the page, we only need to implement the re-rendering of the local component (dom). In Vue, the easiest way to achieve this effect is to use the v-if directive. In Vue2, in addition to using the v-if instruction to re-render the local dom, we can also create a new blank component. When we need to refresh the local page, jump to this blank component page, and then jump back in the beforeRouteEnter guard in the blank component. original page. As shown in the figure below, how to click the refresh button in Vue3.X to reload the DOM within the red box and display the corresponding loading status. Since the guard in the component in the scriptsetup syntax in Vue3.X only has o
 How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
Vue implements the blog front-end and needs to implement markdown parsing. If there is code, it needs to implement code highlighting. There are many markdown parsing libraries for Vue, such as markdown-it, vue-markdown-loader, marked, vue-markdown, etc. These libraries are all very similar. Marked is used here, and highlight.js is used as the code highlighting library. The specific implementation steps are as follows: 1. Install dependent libraries. Open the command window under the vue project and enter the following command npminstallmarked-save//marked to convert markdown into htmlnpmins
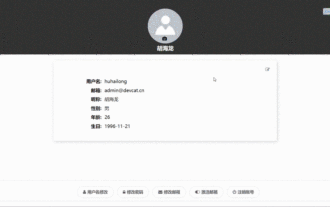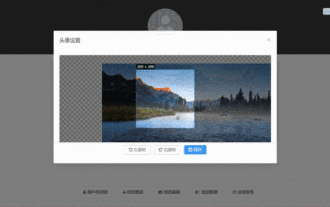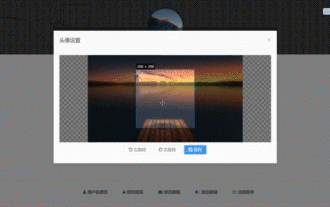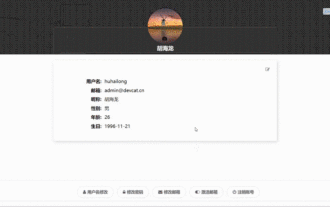 How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
The final effect is to install the VueCropper component yarnaddvue-cropper@next. The above installation value is for Vue3. If it is Vue2 or you want to use other methods to reference, please visit its official npm address: official tutorial. It is also very simple to reference and use it in a component. You only need to introduce the corresponding component and its style file. I do not reference it globally here, but only introduce import{userInfoByRequest}from'../js/api' in my component file. import{VueCropper}from'vue-cropper&
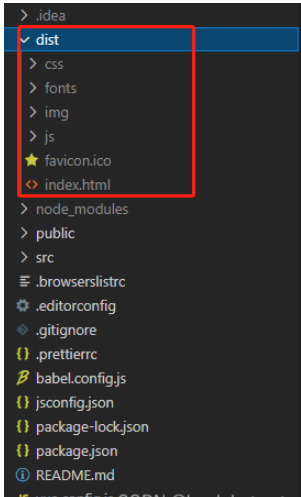 How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
After the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank 1. The publicPath in the vue.config.js file is processed as follows: const{defineConfig}=require('@vue/cli-service') module.exports=defineConfig({publicPath :process.env.NODE_ENV==='production'?'./':'/&
 How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
Preface Whether it is vue or react, when we encounter multiple repeated codes, we will think about how to reuse these codes instead of filling a file with a bunch of redundant codes. In fact, both vue and react can achieve reuse by extracting components, but if you encounter some small code fragments and you don’t want to extract another file, in comparison, react can be used in the same Declare the corresponding widget in the file, or implement it through renderfunction, such as: constDemo:FC=({msg})=>{returndemomsgis{msg}}constApp:FC=()=>{return(
 How to use vue3+ts+axios+pinia to achieve senseless refresh
May 25, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
How to use vue3+ts+axios+pinia to achieve senseless refresh
May 25, 2023 pm 03:37 PM
vue3+ts+axios+pinia realizes senseless refresh 1. First download aiXos and pinianpmipinia in the project--savenpminstallaxios--save2. Encapsulate axios request-----Download js-cookienpmiJS-cookie-s//Introduce aixosimporttype{AxiosRequestConfig ,AxiosResponse}from"axios";importaxiosfrom'axios';import{ElMess




