 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Safety
Safety
 How to analyze network layer related packets and data of TCP and IP
How to analyze network layer related packets and data of TCP and IP
How to analyze network layer related packets and data of TCP and IP
TCP/IP network layer related packets and data
1) IP packet encapsulation: IPv4 has 32 bits and IPv6 has 128 bits. The maximum size of an IP packet can be 65535 bytes. Its structure is as follows:
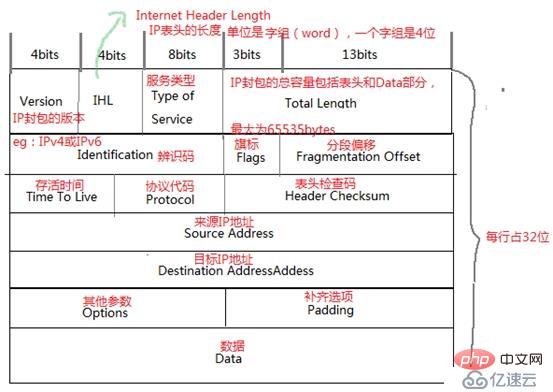
Additional explanations are required:
Service type: Mainly divided into PPP, indicating the priority of this IP packet. Currently Rarely used; D, if it is 0, it means normal delay (delay), if it is 1, it means low delay; T, if it is 0, it means normal transmission volume, if it is 1, it means high transmission volume; R, if it is 0, it means high transmission volume Expressed as general reliability, if it is 1, it indicates high reliability; UU: reserved and not yet used; the total format is PPPDTRUU.
Flag: The format is DM, where D, if it is 0, it means it can be fragmented, if it is 1, it means it cannot be fragmented; M, if it is 0, it means that this IP is the last fragment, if it is 1, it means Not the final segment.
# Small IP segments can be combined at the receiving end through TotalLength, Identification, Flags and Fragment Offset.
Survival time: range 0-255. When the IP packet passes through a router, the TTL will be reduced by one. When the TTL is 0, the packet will be discarded.
Protocol code: The meaning of each code is, 1. ICMP (Internet Message Control); 2. IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol); 3. GGP (Gateway-to-GatewayProtocol); 4. IP (IP in IP encapsulation); 6, TCP (Transmission Control Protocol); 8, EGP (ExteriorGateway Protocol); 17, UDP (Use Data Program).
Header check code: used to check the error check code of this IP header.
Destination address: Destination IP address
Other parameters: Additional options, including security processing mechanisms, routing records, timestamps, strict and loose source routing, etc.
Supplementary project: Since the content of Options is not necessarily too large, each data of the IP must be 32bits. Therefore, if the data of Options is less than 32bits, there will be padding supplement.
2) The composition and classification of IP addresses:
IP composition: network number and host number.
The same network domain (network segment): In the same physical network segment, the IP of the host has the same network number and an independent host number. IPs whose host numbers are all 0 and all 1 (broadcast address) are unavailable. If hosts in the same network segment are set to the same domain IP range (non-duplicate), they can use the CSMA/CD function to directly broadcast network connections in the local network (that is, they can directly transmit data from network card to network card). Within the same physical network segment, if two hosts are set to different IP network segments, the connection cannot be made through broadcast due to different broadcast addresses. At this time, communication must be carried out through a router to connect the two domains together.
ip grading: The entire IP is divided into five levels, as shown in the figure below:

Netmask: an IP address whose network number is all 1 and the host number is all 0. Network: The first IP address of the network segment, that is, the network number is the network number, and the host number is all 0 Network domain representation method: Network and Netmask are commonly used to represent a network area. 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0 or 192.168.0.0/24 (24 means the network number occupies 24 bits) number, so that multiple network domains can be written as one. This way of breaking the original IP hierarchy is called non-hierarchical inter-domain routing (which can reduce routing information and thus improve performance). 5) The concept of routing: When a host sends data to another host, the host will check its own routing information and compare it with the target address of the data. If the target IP is found, it will be sent to The specified machine, otherwise it is transmitted to the default gateway and then transmitted. Repeat this process until the data reaches its destination. 6) route [-n]: Instruction to observe the routing table, parameters a) -n: Display the host name as IP. b) Interpretation of data display, Destination: The meaning of Network Gateway: Default gateway, if it is 0.0.0.0, it means no additional IP is required Genmask: Netmask Flags: Flags, U, represents that the route is available; G, represents that the network needs to be delivered through Gateway; H: represents that the route is a host, not an entire network Iface: The interface is the network card code. 7) ARP (Address Resolution Protocol, Network Address Resolution Protocol), RARP (Revers ARP, Reverse Address Resolution Protocol. 8) arp [-nd];arp –s hostname( IP) Hardware_address: Get the data corresponding to the IP/MAC in the ARP table of the local machine. Parameters: a) -n: Display in the form of host IP b) -d: Will The hardware_address of hostname is deleted from the ARP table. c) -s: Set the MAC of a certain IP or hostname into the ARP table (used to create static ARP). 9) ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): It is an error detection and reporting mechanism. Its biggest function is to ensure the connection status and correctness of our network. ICMP is also one of the important packets in the network layer. However, this packet does not exist independently, but is included in the IP packet. In other words, ICMP also transmits data through IP packets. ICMP The more common ICMP categories: 0: Echo Reply, representing a response message 3: Destination Unreachable, indicating that the destination is unreachable 4: Source Quench ( When the load of the router is too high, this category code can be used to stop the sending end from sending messages) 5: Redirect, (used to redirect routing path information) 8: Echo Request, Request response message 11: Time Exceeded for a Datagram. When the data packet causes a timeout state in certain route transmissions, this category code can inform the source that the packet has been ignored. 12: Parameter Problem on a Datagram, when an ICMP packet repeats the previous error, it will reply to the source host with a message about the parameter error. 13: Timestamp Request, requiring the other party to send time information to calculate the routing time difference to meet the requirements of the synchronization protocol 14: Timestamp Replay, this message is purely used in response to TImestamp Request 15: Information Request. Before the RARP protocol is applied, this message is used to obtain network information when booting. 16: Information Replay, used to respond to the Information Request message 17: Address Mask Request, this message is used to query the subnet mask setting information 18: Address Mask Reply, responds to the subnet mask query message.
The two commands ping and trcaceroute can confirm and report the status of network hosts through ICMP packets,
The above is the detailed content of How to analyze network layer related packets and data of TCP and IP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How do websites set black/whitelist IP restrictions and country and city IP access restrictions through nginx?
Jun 01, 2023 pm 05:27 PM
How do websites set black/whitelist IP restrictions and country and city IP access restrictions through nginx?
Jun 01, 2023 pm 05:27 PM
1. Black/white list IP restricted access configuration nginx There are several ways to configure black and white lists. Here are only two commonly used methods. 1. The first method: allow, denydeny and allow instructions belong to ngx_http_access_module. nginx loads this module by default, so it can be used directly. This method is the simplest and most direct. The setting is similar to the firewall iptable. How to use: Add directly to the configuration file: #Whitelist settings, followed by allow is accessible IPlocation/{allow123.13.123.12;allow23.53.32.1/100;denyall;}#Blacklist settings,
 What does binding ip and mac mean?
Mar 09, 2023 pm 04:44 PM
What does binding ip and mac mean?
Mar 09, 2023 pm 04:44 PM
IP and mac binding refers to associating a specific IP address with a specific MAC address, so that only the device using the MAC address can use the IP address for network communication. Binding ip and mac can prevent the IP address of the bound host from being spoofed. Prerequisites: 1. The MAC address is unique and cannot be spoofed; it can only be bound to hosts on the network directly connected to the router (that is, The host's gateway is on the router).
 How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? In fact, the method is very simple. Users can directly enter the command prompt, and then press the ctrl shift enter key combination to perform the operation, or directly execute the reset command to set it up. Let this site do the following. Let us carefully introduce to users how to reset the TCP/IP protocol stack in Windows 10. Method 1 to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in Windows 10. Administrator permissions 1. We use the shortcut key win R to directly open the run window, then enter cmd and hold down the ctrl shift enter key combination. 2. Or we can directly search for command prompt in the start menu and right-click
 How to check IP address on WeChat
May 31, 2023 am 09:16 AM
How to check IP address on WeChat
May 31, 2023 am 09:16 AM
How to check the IP address on WeChat: 1. Log in to the computer version of WeChat, right-click the taskbar at the bottom of the screen, and click "Task Manager"; 2. When the task manager pops up, click "Details" in the lower left corner; 3. Task management Enter the "Performance" option of the browser and click "Open Resource Monitor"; 4. Select "Network" and check the WeChat process "Wechat.exe"; 5. Click "TCP Connection" below to monitor the WeChat network IP related situation. Sending a message and getting a reply will reveal the other person's IP address.
 How to set directory whitelist and ip whitelist in nginx
May 18, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
How to set directory whitelist and ip whitelist in nginx
May 18, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
1. Set the directory whitelist: There is no restriction on the specified request path. If there is no restriction on the request path to the api directory, it can be written as server{location/app{proxy_passhttp://192.168.1.111:8095/app ;limit_connconn20;limit_rate500k;limit_reqzone=fooburst=5nodelay;}location/app/api{proxy_passhttp://192.168.1.111:8095/app/api}}#Because nginx will give priority to accurate matching
 How does NGINX count the PV, UV, and independent IP of the website?
May 19, 2023 am 09:13 AM
How does NGINX count the PV, UV, and independent IP of the website?
May 19, 2023 am 09:13 AM
Concept: uv (uniquevisitor): unique visitor, each independent Internet computer (based on cookies) is regarded as a visitor, and the number of visitors who visit your website within a day (00:00-24:00). Visits to the same cookie within a day are only counted once PV (pageview): visits, that is, page views or clicks, each visit to the website by the user is recorded once. When a user visits the same page multiple times, the total number of visits is counted. Independent IP: The same IP address is only counted once within 00:00-24:00. Friends who do website optimization are most concerned about this. Let me first state the environment. This run nginx version 1.7, the backend tomcat runs dynamic
 What should I do if my wifi shows no IP allocation?
Aug 30, 2023 am 11:58 AM
What should I do if my wifi shows no IP allocation?
Aug 30, 2023 am 11:58 AM
Solution to wifi showing no IP allocation: 1. Restart the device and router, turn off the Wi-Fi connection on the device, turn off the device, turn off the router, wait a few minutes, then reopen the router to connect to wifi; 2. Check the router settings and restart DHCP, make sure the DHCP function is enabled; 3. Reset network settings, which will delete all saved WiFi networks and passwords. Please make sure they are backed up before performing this operation; 4. Update the router firmware, log in to the router management interface, and find the firmware Update options and follow the prompts.
 How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
TCP client A client sample code that uses the TCP protocol to achieve continuous dialogue: importsocket#Client configuration HOST='localhost'PORT=12345#Create a TCP socket and connect to the server client_socket=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket .SOCK_STREAM)client_socket.connect((HOST,PORT))whileTrue:#Get user input message=input("Please enter the message to be sent:&



