How to start, stop and restart the springboot jar package in Linux
前言
springboot的配置文件中,配置文件的名字都有各自的意义跟用途
dev 开发环境
prod 生产环境(默认)
test 测试环境
加载指定配置文件 --spring.profiles.active=prod
springboot加载jar包的方式有
// 直接在控制台进行启动,缺点就是控制台关闭项目也就关闭了。 java -jar bootdo.jar // 这种方式可以运行在后台,但是如果推出了shell的话,那也会挂 java -jar /bootdo-2.0.0.jar > bootdolog.file 2>&1 & // 加上nohup的话,即使推出shell,也不影响。 nohup java -jar /bootdo-2.0.0.jar > bootdolog.file 2>&1 &
解释
nohup表示永久运行。&表示后台运行
> 代表重定向到哪里
1 表示stdout标准输出,系统默认值是1,所以">/dev/null"等同于"1>/dev/null"
2 表示stderr标准错误
nohup ./mqnamesrv >/home/cxb/mqnamesrv.out 2>&1 & 即标准输出到mqnamesrv.out中,接着,标准错误输出重定向等同于标准输出,输出到同一文件中。
在服务器上通过如下方式启动成功之后,如果涉及到重新启动,那么你需要通过ps -ef | grep bootdo 查询到进程号,再通过kill -s 9 ${pid} 进行杀死再重新启动,很是麻烦。
nohup java -jar /bootdo-2.0.0.jar > bootdolog.file 2>&1 &
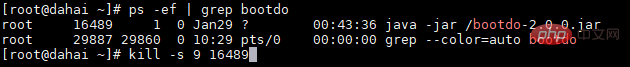
一两次还好说,如果涉及到多次,那就有些崩溃了。
这样,可以通过编写一个shell脚本来进行启动(start)停止(stop)重启(restart)操作,一步到位,方便高效
在自定义目录创建 wss.sh 脚本,编辑内容如下。
#!/bin/bash
#这里可替换为你自己的执行程序,其他代码无需更改
app_name=websocketserver-0.0.1-snapshot.jar
#使用说明,用来提示输入参数
usage() {
echo "usage: sh 脚本名.sh [start|stop|restart|status]"
exit 1
}
#检查程序是否在运行
is_exist(){
pid=`ps -ef|grep $app_name|grep -v grep|awk '{print $2}' `
#如果不存在返回1,存在返回0
if [ -z "${pid}" ]; then
return 1
else
return 0
fi
}
#启动方法
start(){
is_exist
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
echo "${app_name} is already running. pid=${pid} ."
else
nohup java -jar /mnt/ssd1/project/websocket/$app_name > /mnt/ssd1/project/websocket/websocketserverlog.file 2>&1 &
echo "${app_name} start success"
fi
}
#停止方法
stop(){
is_exist
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
kill -9 $pid
else
echo "${app_name} is not running"
fi
}
#输出运行状态
status(){
is_exist
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
echo "${app_name} is running. pid is ${pid}"
else
echo "${app_name} is not running."
fi
}
#重启
restart(){
stop
start
}
#根据输入参数,选择执行对应方法,不输入则执行使用说明
case "$1" in
"start")
start
;;
"stop")
stop
;;
"status")
status
;;
"restart")
restart
;;
*)
usage
;;
esac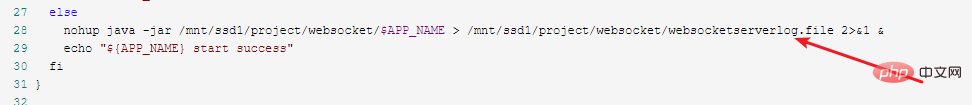
在标红接头行配置启动命令。
之后就可以通过 wss.sh start | stop | restart 实现启动,停止,重启操作了。
补充下
sh xxx.sh与./xxx.sh区别
sh xxx.sh 是不需要有执行权限
./xxx.sh 是需要有执行权限的,可以通过 chmod +x xxx.sh 赋予权限
The above is the detailed content of How to start, stop and restart the springboot jar package in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden error? Check file or directory permissions; 2. Check .htaccess file; 3. Check Nginx configuration file; 4. Restart Nginx. Other possible causes include firewall rules, SELinux settings, or application issues.
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to clean nginx error log
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
The error log is located in /var/log/nginx (Linux) or /usr/local/var/log/nginx (macOS). Use the command line to clean up the steps: 1. Back up the original log; 2. Create an empty file as a new log; 3. Restart the Nginx service. Automatic cleaning can also be used with third-party tools such as logrotate or configured.




