How to implement Java state machine
Suppose we have two states
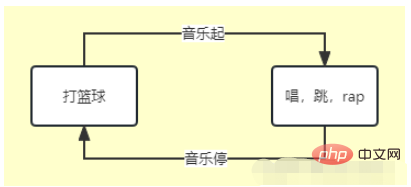
This state transition is very simple, let’s try to implement it in java
The program structure is as shown below
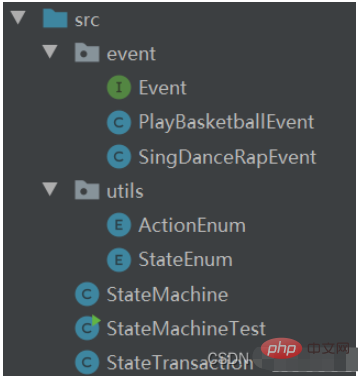
Let’s first introduce the representation of status
public class StateTransaction {
// 当前状态
private StateEnum currentState;
// 相对应动作
private ActionEnum action;
// 下一个状态
private StateEnum nextState;
// 相应事件
private Event event;
public StateTransaction() {
}
public StateEnum getCurrentState() {
return currentState;
}
public ActionEnum getAction() {
return action;
}
public StateEnum getNextState() {
return nextState;
}
public Event getEvent() {
return event;
}
// 链式初始化对象
public StateTransaction source(StateEnum state) {
currentState = state;
return this;
}
public StateTransaction when(ActionEnum action) {
this.action = action;
return this;
}
public StateTransaction target(StateEnum state) {
nextState = state;
return this;
}
public StateTransaction how(Event event) {
this.event = event;
return this;
}
}As you can see, there are four quantities representing status, which are:
currentState: indicates the current state
action: indicates the corresponding action
nextState: indicates the next state
event: Indicates the corresponding event
The meaning of this four-tuple is that when in the currentState state, if an action occurs, it will be transferred to nextState status, and will trigger a response to the event event.
Pay attention to the four methods of chain initialization. The definition of these four methods makes the initialization of state very elegant.
Let’s take a look at events. Event is an interface. Other specific events implement this interface to perform certain operations. Our program will print some information directly without doing complicated operations
public interface Event {
public String handle();
}public class PlayBasketballEvent implements Event{
@Override
public String handle() {
System.out.println("开始打篮球");
return "开始打篮球";
}
}public class SingDanceRapEvent implements Event{
@Override
public String handle() {
System.out.println("开始唱,跳,rap");
return "开始唱,跳,rap";
}
}In addition, we also need to define two enumeration classes to represent states and actions respectively
public enum StateEnum {
// 打篮球
PLAY_BASKETBALL,
// 唱跳rap
SING_DANCE_RAP
}
public enum ActionEnum {
// 音乐起
MUSIC_ON,
// 音乐结束
MUSIC_OFF
}After the above preparations are completed, we need a state machine class to perform state transfer
public class StateMachine {
// 存储状态信息
private List<StateTransaction> stateTransactionList;
// 记录当前状态
private StateEnum currentState;
public StateMachine(StateEnum state) {
currentState = state;
stateTransactionList = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 添加一条状态信息
public StateTransaction addone() {
StateTransaction stateTransaction = new StateTransaction();
stateTransactionList.add(stateTransaction);
return stateTransaction;
}
// 进行状态转移
public StateTransaction execute(ActionEnum action) {
for(int i=0; i<stateTransactionList.size(); i++) {
if(currentState==stateTransactionList.get(i).getCurrentState() &&
action==stateTransactionList.get(i).getAction()) {
stateTransactionList.get(i).getEvent().handle();
currentState = stateTransactionList.get(i).getNextState();
return stateTransactionList.get(i);
}
}
return null;
}
}There are two key methods in the above code, namely addone() and execute()
Let’s talk about addone() first. The method first initializes a StateTransaction object, then puts it in the List, and finally adds this The object is returned. Once we get this object, we can fill in the content.
Let’s talk about execute(). This method receives ActionEnum as a parameter, and then traverses the list to look for such a piece of status information of the next object obtained by changing the current status through the corresponding action. If found, execute the event. The handle() method, and transfer the current state, and finally return StateTransaction, if not found, return null.
Finally let’s look at the initialization method
public class StateMachineTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StateMachine machine = new StateMachine(StateEnum.PLAY_BASKETBALL);
// 打篮球的时候,一旦音乐起,就会开始唱跳rap
machine.addone().source(StateEnum.PLAY_BASKETBALL).when(ActionEnum.MUSIC_ON)
.target(StateEnum.SING_DANCE_RAP).how(new SingDanceRapEvent());
// 唱跳rap的时候,一旦音乐停止,就会开始打篮球
machine.addone().source(StateEnum.SING_DANCE_RAP).when(ActionEnum.MUSIC_OFF)
.target(StateEnum.PLAY_BASKETBALL).how(new PlayBasketballEvent());
machine.execute(ActionEnum.MUSIC_ON);
machine.execute(ActionEnum.MUSIC_OFF);
}
}As you can see, we can create a state transfer message directly using the chain method, which is very elegant
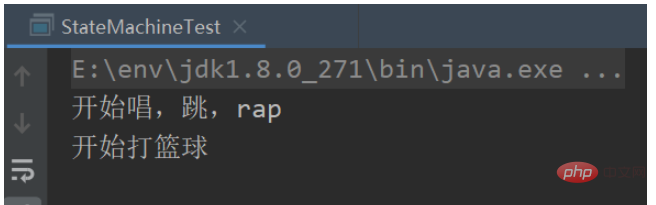
The program output is as follows
The above is the detailed content of How to implement Java state machine. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




