 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 How to configure and test virtual domain names in Nginx environment
How to configure and test virtual domain names in Nginx environment
How to configure and test virtual domain names in Nginx environment
Using nginx virtual domain name configuration, you can access the local server through a specific domain name without purchasing a domain name. Reduce unnecessary expenses before launch.
Configuration steps
1. Edit the nginx.conf configuration file
sudo vim /usr/local/nginx/nginx/conf/ nginx.xonf
(1) Add the domain name to the file name (to facilitate future management)
The code added here is in the http end of nginx.conf Click to add.
But you need to pay attention to the path of the vhost folder. The path of the vhost folder created here is: /usr/local/nginx/nginx/conf/vhost, but nginx.conf is in /usr/local/ nginx/conf/nginx.conf. Need to pay attention to the path settings.
include vhost/*.conf
(2) Save and exit
Save and exit through vim's ":wq" command. If you are still in editing mode, you need to press the esc key first and then enter the command.
2. Configure domain name forwarding
(1) Create the vhost folder in the installation directory
mkdir /usr/local/nginx/nginx/conf/vhost
(2) Create and edit the domain name forwarding configuration file
# www.huaiangg.com 为你想要自定义的域名,加上后缀 .vonf 便可 vim /usr/local/nginx/nginx/conf/vhost/www.huaiangg.com.conf
In the vim editor, copy the following code into it
server {
listen 80;
autoindex on;
# 这是你想要设置域名
server_name www.huaiangg.com;
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log combined;
index index.html index.htm index.jsp index.php;
#error_page 404 /404.html;
if ( $query_string ~* ".*[\;'\<\>].*" ){
return 404;
}
location / {
# 这里把反向代理设置成 tomcat 的访问路径
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/;
add_header access-control-aloow-origin *;
}
}Save and exit, pass vim's ":wq" command saves and exits. If you are still in editing mode, you need to press the esc key and then enter the command.
3. Set hosts. Set hosts under
linux in /etc/hosts. Use vim to open the corresponding path.
vim /etc/ hosts
Configure related domain names
#centos # 反向代理 --> tomcat 地址 192.168.197.130 www.huaiangg.com # 图床 192.168.197.130 iamge.huaiangg.com # 前后端分离服务器 192.168.197.130 s.huaiangg.com
Save and exit, use vim's ":wq" command to save and exit. If you are still in editing mode, you need to press the esc key and then enter the command.
4. Startup (restart) verification
Note: ${nginx} represents the default installation path installed in the system, for example: /usr/local/nginx/
( 1) Start
${nginx}/sbin/nginx
(2) Restart
${nginx}/sbin/nginx -s reload
5. Access verification
Use the default port verification. If the port is occupied, modify the default access port in nginx.conf.
or
5. To test
, you only need to enter and set the reverse proxy address in the browser in the Linux environment, for example: , see details below:
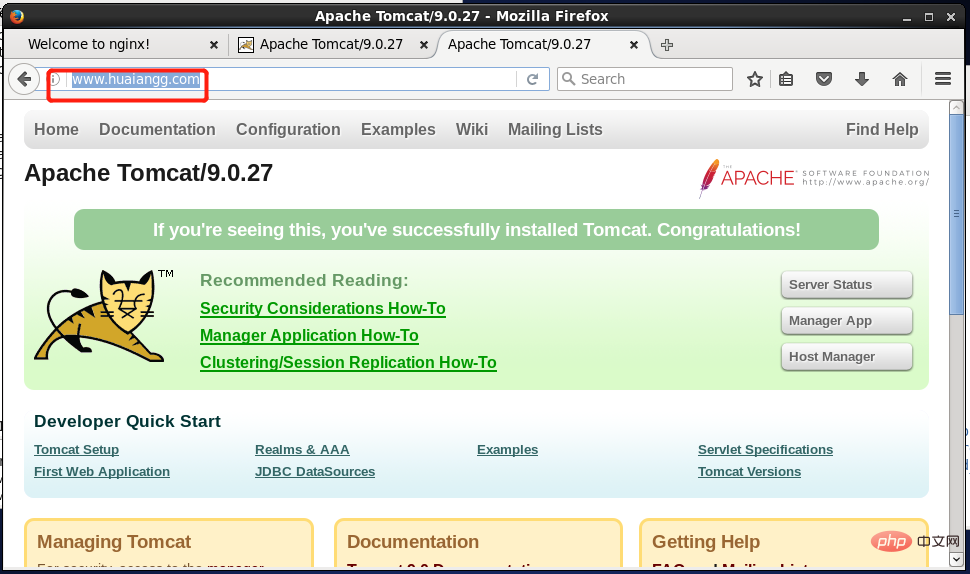
The above is the detailed content of How to configure and test virtual domain names in Nginx environment. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
How to allow external network access to tomcat server
Apr 21, 2024 am 07:22 AM
To allow the Tomcat server to access the external network, you need to: modify the Tomcat configuration file to allow external connections. Add a firewall rule to allow access to the Tomcat server port. Create a DNS record pointing the domain name to the Tomcat server public IP. Optional: Use a reverse proxy to improve security and performance. Optional: Set up HTTPS for increased security.
 How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Steps to run ThinkPHP Framework locally: Download and unzip ThinkPHP Framework to a local directory. Create a virtual host (optional) pointing to the ThinkPHP root directory. Configure database connection parameters. Start the web server. Initialize the ThinkPHP application. Access the ThinkPHP application URL and run it.
 Welcome to nginx!How to solve it?
Apr 17, 2024 am 05:12 AM
Welcome to nginx!How to solve it?
Apr 17, 2024 am 05:12 AM
To solve the "Welcome to nginx!" error, you need to check the virtual host configuration, enable the virtual host, reload Nginx, if the virtual host configuration file cannot be found, create a default page and reload Nginx, then the error message will disappear and the website will be normal show.
 How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
How to generate URL from html file
Apr 21, 2024 pm 12:57 PM
Converting an HTML file to a URL requires a web server, which involves the following steps: Obtain a web server. Set up a web server. Upload HTML file. Create a domain name. Route the request.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application
 What are the most common instructions in a dockerfile
Apr 07, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
What are the most common instructions in a dockerfile
Apr 07, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
The most commonly used instructions in Dockerfile are: FROM: Create a new image or derive a new image RUN: Execute commands (install software, configure the system) COPY: Copy local files to the image ADD: Similar to COPY, it can automatically decompress tar archives or obtain URL files CMD: Specify the command when the container starts EXPOSE: Declare the container listening port (but not public) ENV: Set the environment variable VOLUME: Mount the host directory or anonymous volume WORKDIR: Set the working directory in the container ENTRYPOINT: Specify what to execute when the container starts Executable file (similar to CMD, but cannot be overwritten)
 Can nodejs be accessed from the outside?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:43 AM
Can nodejs be accessed from the outside?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:43 AM
Yes, Node.js can be accessed from the outside. You can use the following methods: Use Cloud Functions to deploy the function and make it publicly accessible. Use the Express framework to create routes and define endpoints. Use Nginx to reverse proxy requests to Node.js applications. Use Docker containers to run Node.js applications and expose them through port mapping.
 How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
How to deploy and maintain a website using PHP
May 03, 2024 am 08:54 AM
To successfully deploy and maintain a PHP website, you need to perform the following steps: Select a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) Install PHP Create a database and connect PHP Upload code to the server Set up domain name and DNS Monitoring website maintenance steps include updating PHP and web servers, and backing up the website , monitor error logs and update content.



