This reference and object construction initialization methods in java
1. this reference
1.1 Why is there a this reference
Let’s write one first Example of date class:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
|
The above code defines a date class, and then creates three objects in the main method and passes them through the member methods in the classCode class To set and print objects, the overall logic of the code is very simple and there are no problems.
There are two things to note:
1. The formal parameter name is accidentally the same as the member variable name:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
Who assigns value to whom in the function body? Member variable to member variable? Parameter to parameter? Parameters to member variables? Member variable parameters?
2. All three objects are calling the setDate and printDate functions, but there is no description of the objects in these two functions. How do the setDate and printDate functions know which object's data is being printed?
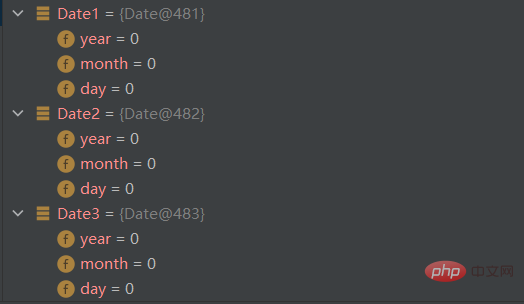
You can see that if the formal parameter name and member variable name are different, the value of the variable after assignment is 0, indicating that the assignment was not successful.
What should we do? Look down.
1.2 What is this reference
This reference points to the current object (the object that calls the member method when the member method is running). All member variable operations in the member method are through this reference. Go visit . It’s just that all operations are transparent to the user, that is, the user does not need to pass it, the compiler automatically completes it.
Improved code:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
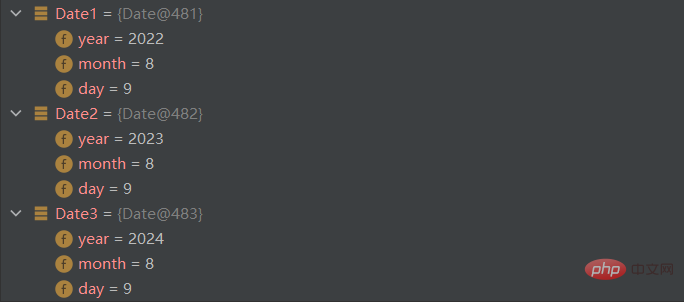
You can see that after adding the this reference, the assignment is successful.
this is added by default. Even if this is not added, there will be a this added by default. But if you don't add it, it will cause problems if the formal parameter name and the member variable name are the same.
In the following code, you can see that the three objects are calling the setDate and printDate functions, and there is no explanation, so how do you know which one is being printed? Object data?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
You can judge which object to print by the following two points:
Which object is the previous object and which object’s data is printed?
Hidden parameters.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
Three ways to use this:
this. Member variable
this.Access member method
this();Access constructor method
1.3 Characteristics of this reference
Type of this: Corresponding class type reference, that is, which object is called is the reference class of that object.
This can only be used in "member methods".
In "member methods", this can only refer to the current object and cannot refer to other objects.
This is the first hidden parameter of the "member method", which will be automatically passed by the compiler. When the member method is executed, the compiler will be responsible for calling the member method.
The reference of the object is passed to the member method, and this is responsible for receiving it.
Even if the member variable name is different from the formal parameter name, it is recommended to write this. This is equivalent to a protective measure, and it is also a good programming practice.
1.4 This reference exercise question
Write an academic class with attributes such as name, age, etc., and then set the values of these attributes through a method, and then write two methods, in one method Use this to call another method.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
2. Construction and initialization of objects
2.1 How to initialize objects
Through the study of the previous knowledge points, we know that in Java methods When a local variable is defined internally, it must be initialized, otherwise the compilation will fail.
1 2 3 4 |
|
If it is an object, no error will be reported even if it is not assigned a value, because it is a reference variable.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
Through the above examples, two problems were discovered:
It is troublesome to call the setDate method to set the specific date after each object is created. How should the object be initialized?
Local variables must be initialized before they can be used. Why can they still be used without giving a value after the field is declared?
This introduces the construction method. Then look down.
2.2 Constructor method
2.2.1 Concept
The constructor method (also called constructor) is a special member method. The name must be the same as the class name. When creating It is automatically called by the compiler when an object is created, and is only called once during the entire object's life cycle.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
Student student = new Student();
new在实例化对象,而实例化对象一定会调用构造方法。
注意:当我们没有提供构造方法时,编译器会自动提供一个不带参数的构造方法。
2.2.2 特性
名字必须与类名相同。
没有返回值类型,设置为void也不行。
创建对象时由编译器自动调用,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次。
构造方法可以重载(用户根据自己的需求提供不同参数的构造方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
上述两个构造方法:名字相同,参数列表不同,因此构成了方法重载。
如果用户没有显式定义,编译器会生成一份默认的构造方法,生成的默认构造方法一定是无参的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
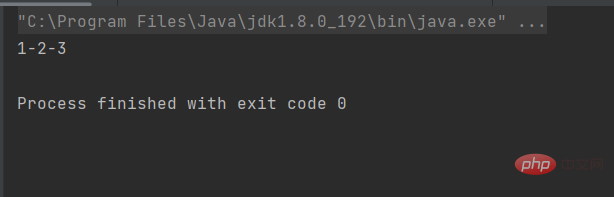
上述Work类中,没有定义任何构造方法,编译器会默认生成一个不带参数的构造方法。
那如何调用带参数的构造方法呢?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
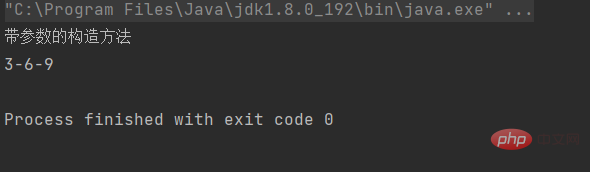
注意:一旦用户定义,编译器则不再生成。
构造方法中,可以通过this调用其他构造方法来简化代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
注意:
this调用必须在构造方法里面,
要在在第一行,
不能写成循环调用。
绝大多数情况下使用public来修饰,特殊场景下会被private修饰(后序讲单例模式时会遇到)
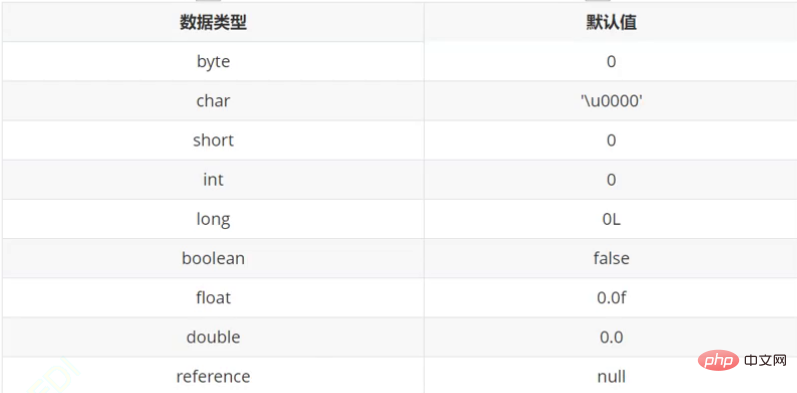
2.3 默认初始化
为什么使用成员变量不需要初始化呢?

在程序层面只是简单的一条语句,在JVM(以后讲)层面需要做好多事情,下面简单介绍下:
检测对象对应的类是否加载了,如果没有加载则加载
为对象分配内存空间
处理并发安全问题
比如:多个线程同时申请对象,JVM要保证给对象分配的空间不冲突初始化所分配的空间
即:对象空间被申请好之后,对象中包含的成员已经设置好了初始值
比如:
设置对象头信息(关于对象内存模型后面会介绍)调用构造方法,给对象中各个成员赋值
2.4 就地初始化
定义成员变量的时候就已经赋值好了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
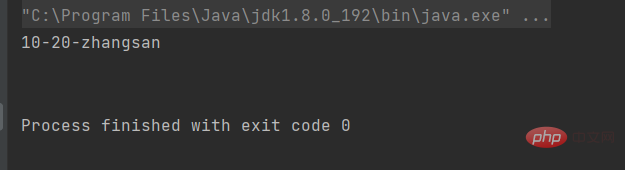
注意:代码编译完成后,编译器会将所有给成员初始化的这些语句添加到各个构造函数中。
The above is the detailed content of This reference and object construction initialization methods in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1205
1205
 24
24
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




