How to use dockerfile to build nginx image
Introduction to dockerfile
Docker can automatically build the image by reading the contents of the dockerfile. The dockerfile is a text file that contains all the commands that need to be executed during the build process. It can also be understood that dockfile is a script interpreted by the docker program. It consists of instructions one by one. Each instruction corresponds to a command under the Linux system. The docker program translates these dockerfile instructions into real Linux commands. Dockerfile has its own writing format and supported commands. The docker program resolves the dependencies between these commands, similar to makefile.
The docker program will read the dockerfile and generate a customized image according to the instructions. Compared with a black box like image, an obvious script like dockerfile is easier for users to accept. It clearly shows how the image is generated. With dockerfile, when we need to customize our own additional requirements, we only need to add or modify instructions on the dockerfile and regenerate the image, eliminating the trouble of typing commands.
Docker method of building an image: commit, dockerfile
1. Use commit to build an image:
Commit is built based on the original image The purpose of using this method to build an image is to save some configuration information and modified information in the image. Equivalent to a snapshot of an image.
2. Use dockerfile to build the image:
Dockerfile is the (custom) image required to quickly build.
Dockerfile instructions:
From: Specify the base image (from is a required instruction and must be the first instruction).
run: used to execute command line commands. Its basic format:
Shell format: run
exec format: run , this method is like the format in function calls;
copy: Copy the file. Its basic format:
Format 1: copy
Format 2: copy ["
add: A more advanced copy file, adding some functions on the basis of copy. If the compressed package is copied, it will be decompressed directly, and No need to use run to decompress;
cmd: container startup command. Its basic format:
Shell format: cmd
Exec format: cmd ["executable file", "Parameter 1", "Parameter 2"...]
Parameter list format: cmd ["Parameter 1", "Parameter 2"...], after specifying the entrypoint command, use cmd to specify the specific parameters
Entrypoint: Entry point. Its basic format is divided into exec and shell.
The purpose of entrypoint is the same as cmd, which is to specify the container startup program and parameters. Entrypoint can be replaced during operation, but it is more cumbersome than cmd and needs to be specified through the parameter --entrypoint of docker run. When entrypoint is specified, the meaning of cmd changes. Instead of running its command directly, the content of cmd is passed to the entrypoint command as a parameter. When executed, it becomes:
env: Set environment variables. (You can use the variables used here) Its basic format:
Format 1: env
Format 2: env
arg: Build parameters. The effect of build parameters is the same as that of env, which is to set environment variables. The difference is that the environment variables built by arg will not exist when the container is run in the future. Its basic format:
Format 1: arg
Format 2: This default value can be used in the build command docker build - -build-arg
volume: Define an anonymous volume. Its basic format:
Format 1: volume ["
Format 2: volume
Expose: Expose port. The expose directive declares the port provided by the runtime container. When starting the container, the port will not be opened because of this declaration. Its basic format:
Format 1: expose
Workdir: Specify the working directory. Its basic format:
Format 1: workdir
User: Specify the current user. user helps you switch to the specified user. Its basic format:
Format 1: user
healthcheck: Health check to determine whether the status of the container is normal. Its basic format:
Format 1: healthcheck [option] cmd
Format 2: healthcheck none: If the base image has a health check command , use this format to block its health check instructions
Build nginx image:
Create a directory and write dockerfile in the directory:
[root@docker ~]# mkdir mynginx [root@docker ~]# cd mynginx/ [root@docker mynginx]# pwd /root/mynginx [root@docker mynginx]#
Download the nginx source code package to the created directory (mynginx directory):
[root@docker ~]# wget -p /root/mynginx/ http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.15.2.tar.gz
Write the dockerfile:
[root@docker mynginx]# vi dockerfile
The content is as follows:
from centos run ping -c 1 www.baidu.com run yum -y install gcc make pcre-devel zlib-devel tar zlib add nginx-1.15.2.tar.gz /usr/src/ run cd /usr/src/nginx-1.15.2 \ && mkdir /usr/local/nginx \ && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx && make && make install \ && ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/ \ && nginx run rm -rf /usr/src/nginx-1.15.2 expose 80
Run the docker command to build the image:
[root@docker mynginx]# docker build -t nginx:v3 . sending build context to docker daemon 1.029mb step 1/7 : from centos ---> 5182e96772bf step 2/7 : run ping -c 1 www.baidu.com ---> using cache ---> 2f70f8abaf2a step 3/7 : run yum -y install gcc make pcre-devel zlib-devel tar zlib ---> using cache ---> dbdda4b7ae6f step 4/7 : add nginx-1.15.2.tar.gz /usr/src/ ---> using cache ---> 18ace6285668 step 5/7 : run cd /usr/src/nginx-1.15.2 && mkdir /usr/local/nginx && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx && make && make install && ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/ && nginx ---> using cache ---> 99629488ede9 step 6/7 : run rm -rf /usr/src/nginx-1.15.2 ---> using cache ---> 869fbad71879 step 7/7 : expose 80 ---> using cache ---> 384bed72ea6f successfully built 384bed72ea6f successfully tagged nginx:v3
Outputting two successfully means the build is successful!
Start the custom image:
Use docker images to view the built image:
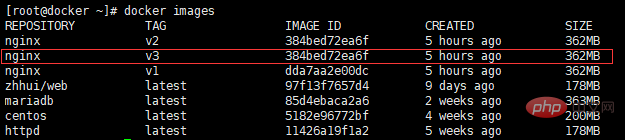
Start the custom image:
[root@docker ~]# docker run -dit -p 80:80 --name nginx nginx:v3 ecaafe1190447878b98dfb0198e92439db60ff7dab57a1674e0e9e7282a9c858 [root@docker ~]# docker ps -a container id image command created status ports names ecaafe119044 nginx:v3 "/bin/bash" 3 seconds ago up 2 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp nginx
Note: At this time, no matter how you start the container, it is still in the exited state.
After various solutions, I finally figured out where the problem was. It turns out that when the container starts, it is started in the background corresponding to a thread. It is already started at startup, but after it executes the command, it exits and is not running in the background, so use the -dit parameter to let it Just run it in the background.
[root@docker ~]# docker run -dit -p 80:80 --name nginx nginx:v3 ecaafe1190447878b98dfb0198e92439db60ff7dab57a1674e0e9e7282a9c858 [root@docker ~]# docker ps -a container id image command created status ports names ecaafe119044 nginx:v3 "/bin/bash" 3 seconds ago up 2 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp nginx
However...
At this time, another problem occurred. Although it was up, the nginx web page interface could not be accessed, and the connection was refused! ! ! !
[root@docker ~]# curl 192.168.100.22 curl: (7) failed connect to 192.168.100.22:80; 拒绝连接 [root@docker ~]# elinks --dump 192.168.100.22 elinks: 拒绝连接
Then, after asking Baidu, fq and Google, I finally found the problem. It turns out that you only need to use exec to enter the container and start nginx.
[root@docker ~]# docker exec -it nginx bash [root@ecaafe119044 /]# nginx [root@ecaafe119044 /]# exit exit
The above is the detailed content of How to use dockerfile to build nginx image. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
To get Nginx to run Apache, you need to: 1. Install Nginx and Apache; 2. Configure the Nginx agent; 3. Start Nginx and Apache; 4. Test the configuration to ensure that you can see Apache content after accessing the domain name. In addition, you need to pay attention to other matters such as port number matching, virtual host configuration, and SSL/TLS settings.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.




