How to use the threading module in python
May 15, 2023 pm 06:16 PMDetailed explanation of the threading module in python. Threading provides a higher-level API than the thread module to provide thread concurrency. These threads run concurrently and share memory.
Let’s look at the specific usage of the threading module:
1. Use of Thread
The target function can instantiate a Thread object, and each Thread object represents a thread. You can start running through the start() method.
Here is a comparison between using multi-threaded concurrency and not using multi-threaded concurrency:
The first is the operation without using multi-threading:
The code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/python
#compare for multi threads
import time
def worker():
print"worker"
time.sleep(1)
return
if__name__ =="__main__":
for i in xrange(5):
worker()The execution results are as follows:
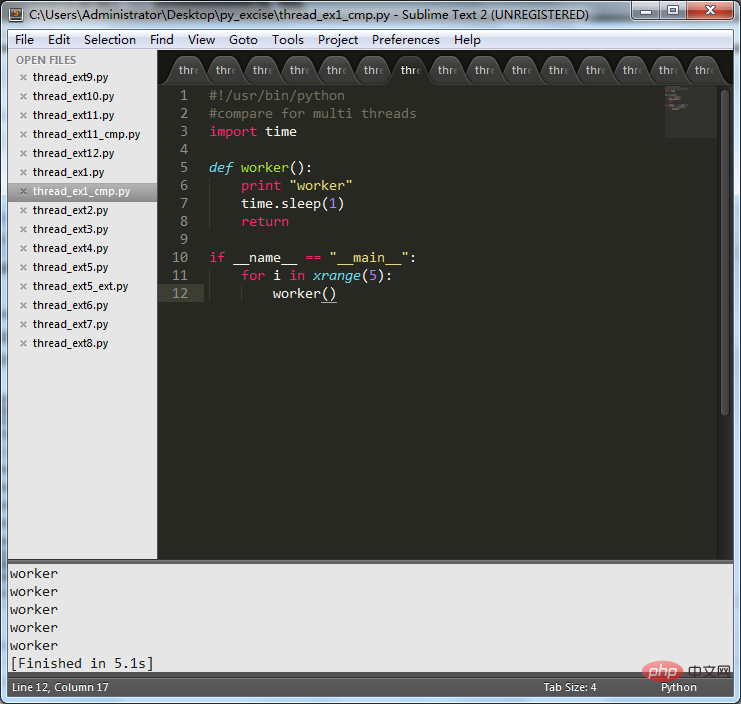
The following is the operation using multi-thread concurrency:
The code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/python
import threading
import time
defworker():
print"worker"
time.sleep(1)
return
fori in xrange(5):
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
t.start()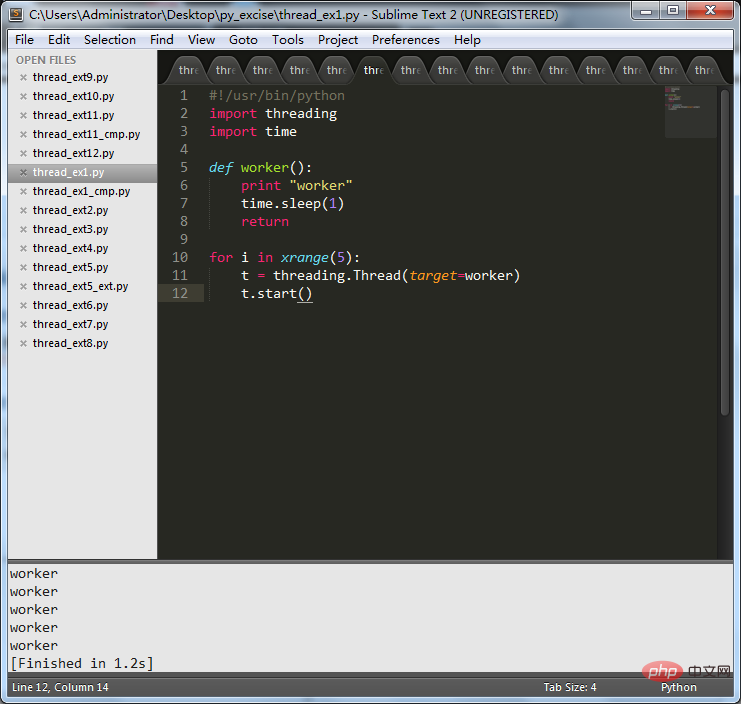
It can be clearly seen that the multi-threaded concurrent operation takes much less time.
2. Use of threading.activeCount()
This method returns the number of threads in the current process. The number returned includes the main thread.
The code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/python
#current's number of threads
import threading
import time
defworker():
print"test"
time.sleep(1)
for i in xrange(5):
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
t.start()
print"current has %d threads" % (threading.activeCount() -1)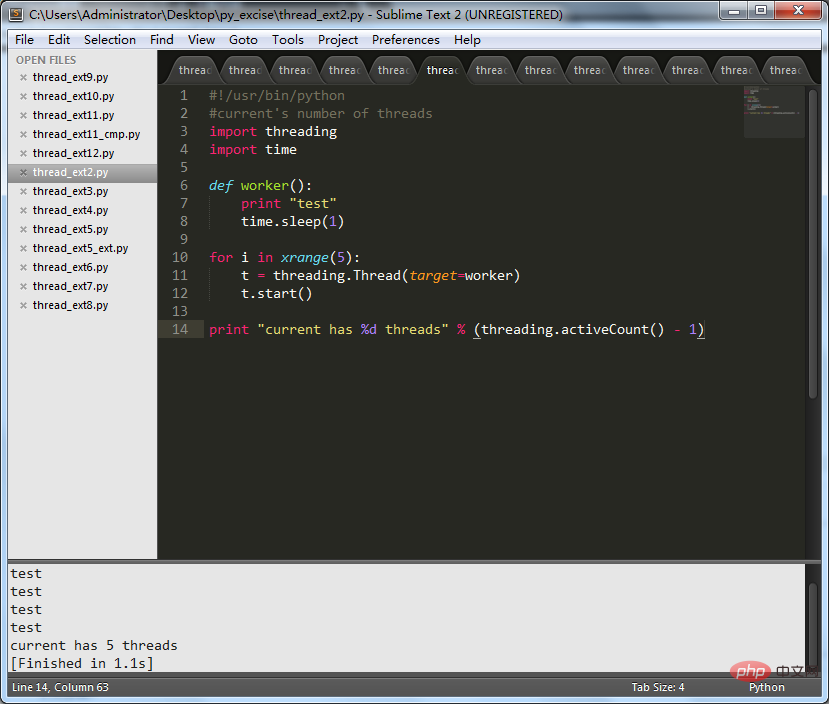
3. Use of threading.enumerate().
This method returns the list of Thread objects currently running.
The code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/python
#test the variable threading.enumerate()
import threading
import time
defworker():
print"test"
time.sleep(2)
threads=[]
for i in xrange(5):
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
threads.append(t)
t.start()
for item in threading.enumerate():
print item
print for item in threads:
print item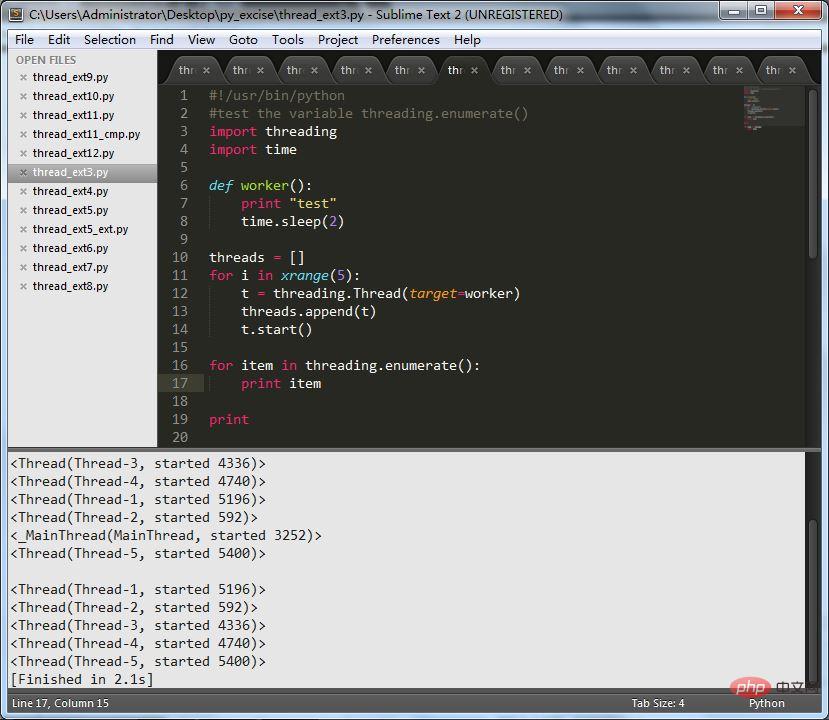
4. Use of threading.setDaemon().
Set the background process.
The code is as follows:
#!/usr/bin/python
#create a daemon
import threading
import time
def worker():
time.sleep(3)
print"worker"
t=threading.Thread(target=worker)
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
print"haha"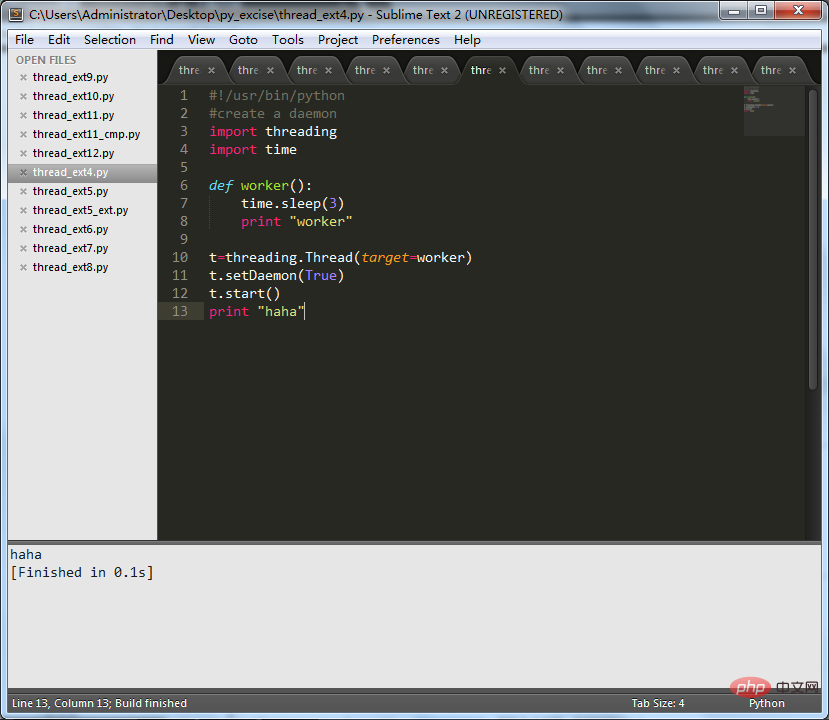
It can be seen that the printing operation in the worker() method is not displayed, indicating that it has become a background process.
The above is the detailed content of How to use the threading module in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
May 08, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
May 08, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of templating?
 Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
Jul 01, 2024 am 07:22 AM
Google AI announces Gemini 1.5 Pro and Gemma 2 for developers
 For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
May 06, 2024 pm 03:52 PM
For only $250, Hugging Face's technical director teaches you how to fine-tune Llama 3 step by step
 Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
May 06, 2024 pm 04:43 PM
Share several .NET open source AI and LLM related project frameworks
 A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis
May 06, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis
May 06, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
A complete guide to golang function debugging and analysis










