
Vue.property.xxx
import Vue from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
Vue.prototype.$http= axios;
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount("#app");this.$http.xxx();
app.config.globalProperties.xxx
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import ElementPlus, { ElMessage, ElMessageBox } from 'element-plus'
import 'element-plus/dist/index.css'
const app = createApp(App);
app.config.globalProperties.$messageBox = ElMessageBox;
app.config.globalProperties.$message1 = ElMessage;// 引入vue的 getCurrentInstance 方法
import { defineComponent, getCurrentInstance } from "vue";
// 获取当前组件实例
const { appContext } = getCurrentInstance();
// 打印看一下结构
console.log(appContext)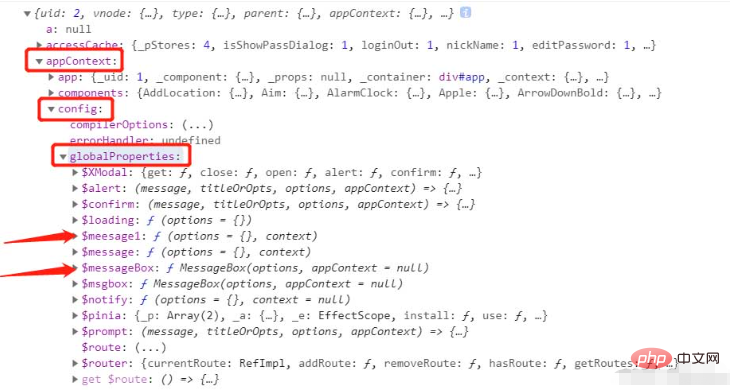
You can already see the mounted $messageBox and $message1 in appContext.config.globalProperties. As for why there is another $message
, we can see a screenshot of the element plus official website

You can see that this is mounted by default for element plus, and we can use it directly. Adding $message1 here is just for demonstration. In fact, you can use the default mount directly.
Complete usage example
// 引入vue的 getCurrentInstance 方法
import { defineComponent, getCurrentInstance } from "vue";
// 获取当前组件实例
const { appContext } = getCurrentInstance();
const globalProxy = appContext.config.globalProperties;
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
// 退出登录按钮
const loginOut = () => {
globalProxy.$messageBox.confirm("确定退出登录吗?", "提示", {
confirmButtonText: "确定",
cancelButtonText: "取消",
type: "warning",
})
.then(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
globalProxy.$message1({message: "已退出登录", type: "success"});
localStorage.removeItem("userInfo");
router.push("/login");
}, 200);
})
.catch((e) => {
console.log(e);
});
};
return {
loginOut
}
}
})The above is the detailed content of vue3 configures global parameters and how to use components. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




