How does Python's import work?
Hello, I am somenzz, you can call me Brother Zheng.
Python’s import is very intuitive, but even so, sometimes you will find that even though the package is there, we will still encounter ModuleNotFoundError. Even though the relative path is very correct, an error is reported
1 |
|
Importing modules in the same directory and modules in different directories are completely different. This article analyzes some problems often encountered when using import to help you easily handle import. Based on this, you can easily create your own package.
1. What is a module (module) and what is a package (package)
Module (module)
The relationship between modules and packages can be compared to files and directories. Modules Just files.
As described in the Python documentation, a Python file is a module, and the Python file name (without the suffix .py) is the module name.
A module can contain variables, functions and classes, which are part of the namespace defined by the module, so the naming of variables is not a problem because two different modules can have variables, functions and classes with the same name. .
Package
The relationship between modules and packages can be compared to files and directories. A package is a directory.
Package can have modules or sub-packages. A module defines a namespace so that variables, functions and classes can have the same name in two different modules. Similarly, a package does the same for its component packages and modules. The main package can be accessed through the dot. modules and packages in .
A basic package can include sub-package, modules, __init__.py (not required after Python 3.3), setup.py. A possible package structure looks like this:
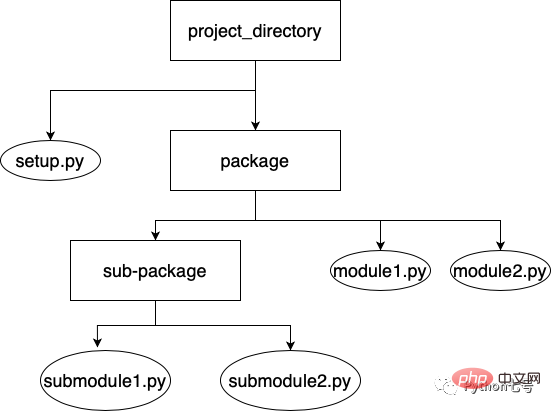
And setup.py exists in the home directory where your package is located, containing configuration information such as required dependencies, Scripts and subpackages. You can also specify metadata about the package, such as the package's name, author, description, etc.
setup.py is the file pip uses to install your package.
2.What happened during import
Let’s take a simple example first. For example, there are two files in the same directory, file1.py and file2.py. The content is very simple, just print The difference between their respective file names is that file1 is imported in file2.py:
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
When you run file2.py, you can get the following results:
1 2 3 |
|
You can see:
- import is very intuitive, whoever uses it can import it.
- The import statement is an ordinary statement and can be placed anywhere.
- When a file is imported, it will be executed, and its internal classes or objects will be added to its namespace.
We also need to know the search order of import. We only need to remember one thing, that is, import will search in sys.path.
For example, if I add a line of code at the end of file2.py: import sys; print(sys.path), I can print the import search path:
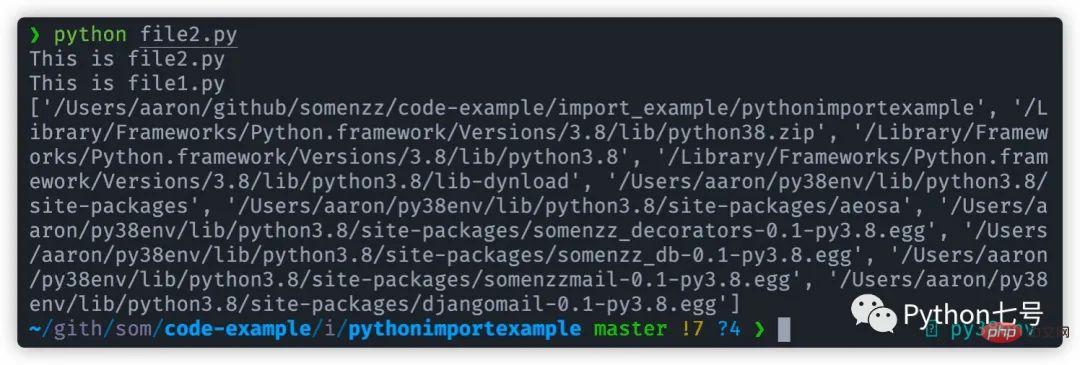
You can see the order of sys.path:
- The path where the execution script is located will be searched first
- Standard library
- Third-party library site-packages
What you need to pay attention to about sys.path is:
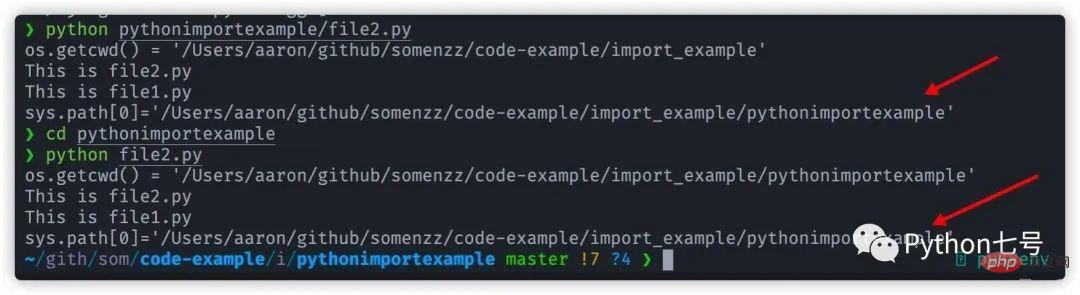
- In the interpreter environment, sys.path[0] is the path where the interpreter is started''
- sys.path does not depend on the working path of the current program - os.getcwd(), but only depends on the path of the first script:
- If one module imports another module, which in turn imports another module, the sys.path of the first module is where the interpreter searches for the second import statement.
Once a module or package is found, it will be executed. If there is an initialization file __init__.py in the package, __init__.py will be executed first when importing.
Then the project to be imported is added to its namespace, and we can use it through xx.yy.
3. When to use relative import and when to use absolute import
Let’s first look at what absolute import is. The so-called absolute import is in the form:
1 2 3 |
|
like this The method is very intuitive. Import will search in sys.path. If you encounter a ModuleNotFoundError, think about why sys.path does not have the package we want to import, or manually insert the path of the package into sys.path.
Let’s take a look at what relative import is. The so-called relative import is in the form:
1 2 3 |
|
That is to say, there is a . sign in the relative path to indicate the module to be imported or the current module. The relative position of the package.
For example, we create a new directory subpackage1 under the pythonimportexample directory, and create two new files file3.py and file4.py in subpackage1.
The content is as follows:
file3.py :
1 |
|
file4.py:
1 2 |
|
只要我们直接运行 file4.py,那是一定会报错的: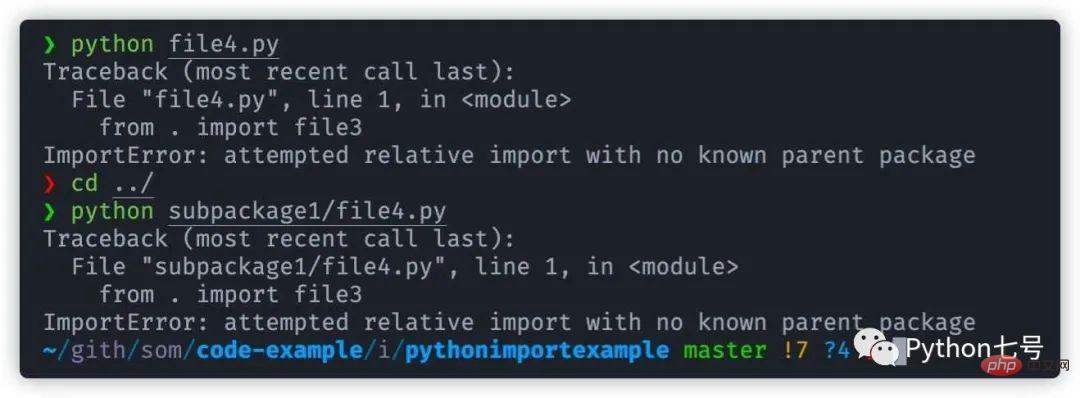
Python 提示我们:
1 |
|
也就是说相对导入不知道父包是谁,换句话说,这是一个子包,必须让父包来调用它,直接运行这个文件是不行的,即使你在 file4.py 的目录 subpackage1 同级的目录执行该文件也是不行的,见上图。
但是在 file4.py 的目录 subpackage1 同级的目录作为一个 module 来执行是可以的,如下图:
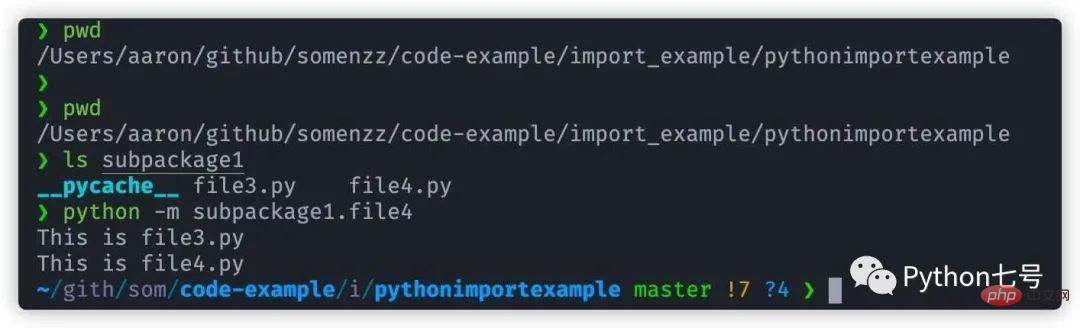
换句话说,我们把 subpackage1 作为一个包来让别人用,相对导入是可以的,比如说我们在目录 subpackage1 同级的目录新建一个 file5.py 的文件,内容如下:
file5.py:
from subpackage1 import file4。
然后,执行 python file5.py 可以看出,相对导入已经正常工作:
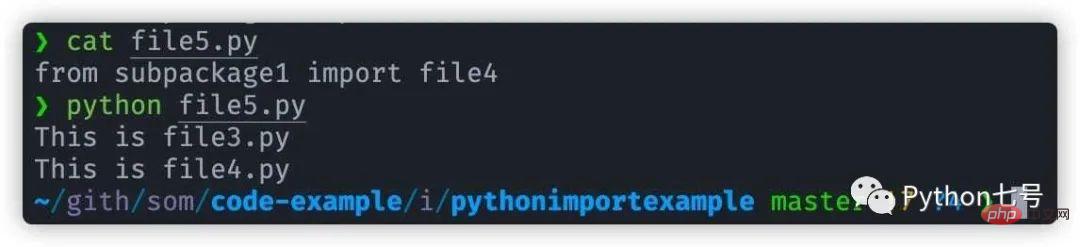
结论
- 如果是当做脚本文件直接运行的,使用绝对导入。
- 如果是当做模块供其他文件导入,使用相对导入。
4.一个自定义包的例子
先上一个图来看下目录及引用结构,方块的是目录,椭圆的是文件,曲线是引用:
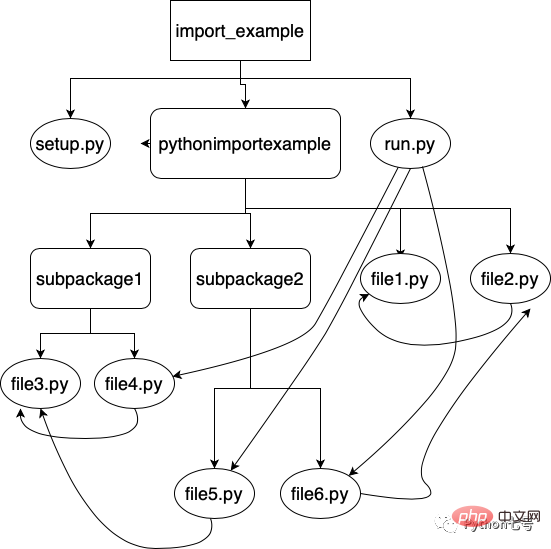
其中 import_example 目录下有 setup.py 和 run.py
run.py 导入了 file4、file5、file6。
file4 导入了 file3,file5 导入了 file3。
file6 导入了 file2,file2 导入了 file1。
现在我们来执行一下 run.py 看下效果:
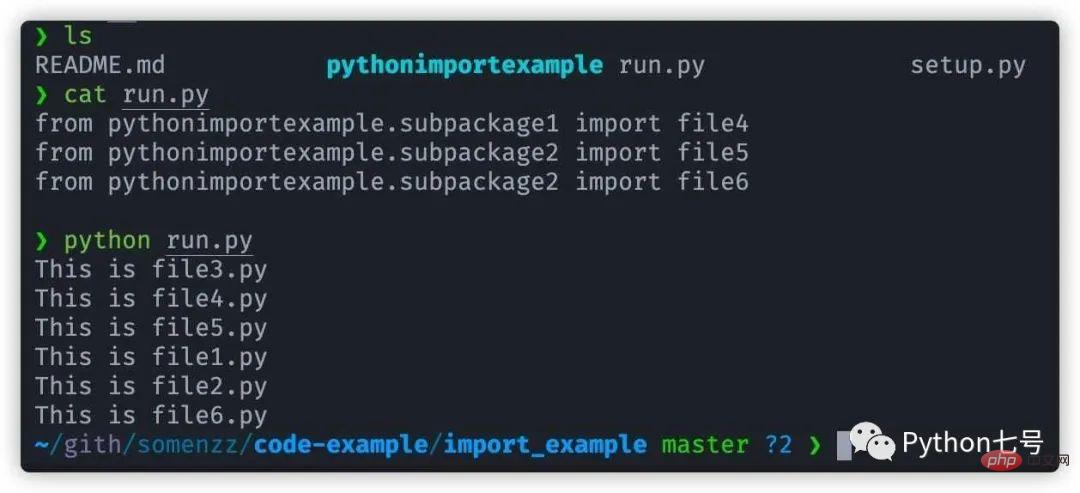
可以看出所有相对导入都已正常工作,虽然 file3 被导入了两次,但只执行了一次,说明 Python 内部已经考虑了同一个包的多重导入问题。
自定义包就是让其他文件导入使用的,因此 pythonimportexample目录下都使用相对导入,源代码见:
https://gitee.com/somenzz/code-example/tree/master/import_example
点阅读原文也可以直接访问。
这里还有一些自定义包的例子:
- dbinterface[1]
- transferfile[2]
最后的话
本文分享了什么是模块(module),什么是包(package),import 的搜索路径,也分享了相对导入和绝对导入的区别,最后举了一个非常实用的 import 例子,方便你构建自己的包。
The above is the detailed content of How does Python's import work?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
VS Code not only can run Python, but also provides powerful functions, including: automatically identifying Python files after installing Python extensions, providing functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Relying on the installed Python environment, extensions act as bridge connection editing and Python environment. The debugging functions include setting breakpoints, step-by-step debugging, viewing variable values, and improving debugging efficiency. The integrated terminal supports running complex commands such as unit testing and package management. Supports extended configuration and enhances features such as code formatting, analysis and version control.
 Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Yes, VS Code can run Python code. To run Python efficiently in VS Code, complete the following steps: Install the Python interpreter and configure environment variables. Install the Python extension in VS Code. Run Python code in VS Code's terminal via the command line. Use VS Code's debugging capabilities and code formatting to improve development efficiency. Adopt good programming habits and use performance analysis tools to optimize code performance.




