
1. Concept
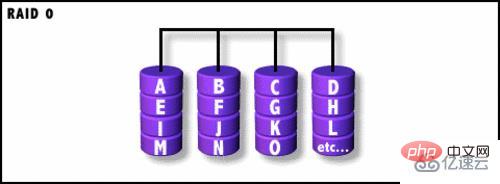
1. RAID 0:
RAUD 0 means simultaneous writing and reading of data groups on multiple disks.
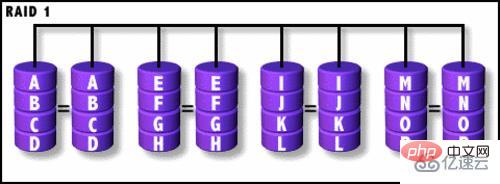
2. RAID 1:
RAID 1 means that multiple disks write and read the same data simultaneously.
2. Security
1. RAID 0:
No data backup function and poor security.
2. RAID 1:
The disks back up each other and are highly secure.
3. Performance
1. RAID 0
The theoretical read and write speed is X times the read and write speed of a single disk, where X refers to the number of disks added to the same array. At the same time, the capacity is also X times that of a single disk.
2. RAID 1
The read and write speed is the same as that of a single disk, and the capacity is that of a single disk.
RAID 0 continuously splits data in units of bits or bytes, and reads/writes on multiple disks in parallel. It has a high data transfer rate, but it has no data redundancy and cannot be regarded as a true RAID structure.
It represents the storage performance in all RAID levels, and the disk usage is 100%; because the data is stored separately on each hard disk that makes up the array, once one of the hard disks has a problem, all data will be damaged.
RAID 0 simply improves performance and does not provide guarantees for data reliability, and the failure of one of the disks will affect all data, which is why RAID 0The reason why it cannot be used in situations with high data security requirements.
Advantages and disadvantages:
RAID The disadvantage of 0 is that it does not provide data redundancy, so once user data is damaged, the damaged data cannot be recovered. When RAID0 is running, as long as any one of the hard disks has a problem, the entire data will fail. It is generally not recommended for enterprise users to use it alone.
RAID 0 has unique characteristics that make it particularly suitable for areas that have high performance requirements but don't care much about data security, such as graphics workstations. For individual users, RAID 0 is also an excellent choice for improving hard drive storage performance.
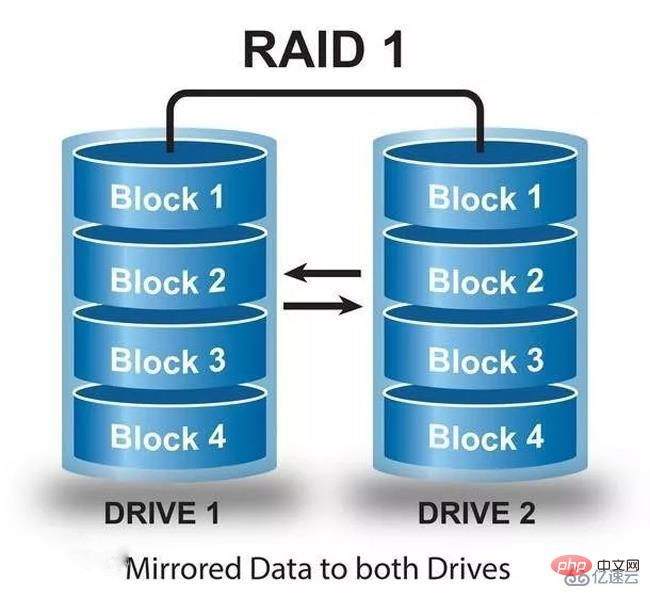
RAID 1, also known as a mirror disk, mirrors the data of one disk to another disk. It uses mirror fault tolerance to improve reliability and has the highest data redundancy capability in RAID.
When saving data, the data will be written to the mirror disk at the same time, and when reading data, it will only be read from the working disk. When a failure occurs, the system will read data from the mirror disk and then restore the correct data from the working disk.
This array method is extremely reliable, but its capacity will be reduced by half. It is widely used in applications with extremely strict data requirements, such as commercial finance, file management and other fields. Only one hard drive is allowed to fail. And two hard drives can only use the capacity of one hard drive.
Advantages and disadvantages:
RAID1 realizes data redundancy through hard disk data mirroring to protect data security. It generates mutual backup data on the two disks. When the original data is busy, the data can be read directly from the mirror backup, so RAID1 can provide read performance. .
RAID1 has the highest unit cost among hard drives, but it provides high data security and availability. When a hard drive fails, the system can automatically switch to the mirrored hard drive for reading/writing, and there is no need to reorganize the failed data.
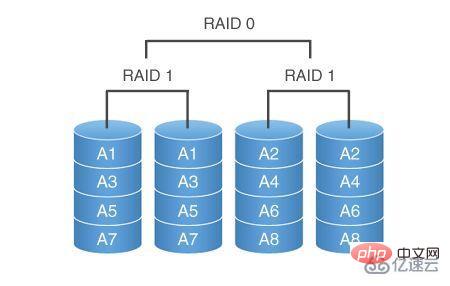
Raid0 1 combines Raid0 and Raid1 technologies, taking into account the advantages of both. While data is protected, it can also provide strong storage performance. However, it requires at least 4 or more hard disks, which is a three-high array technology with high cost, high reliability and high storage performance.
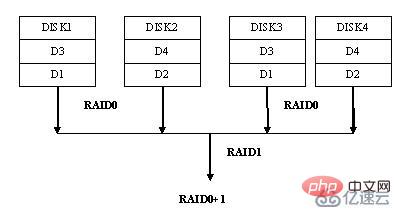
Raid0 1 hard disk magnetic array group
The corresponding parity information is distributed and stored on each disk that makes up RAID5. When the data on one of the disks is damaged, the remaining disks and corresponding parity information are used Recover/generate lost data without affecting data availability. At least 3 or more hard drives are required. Suitable for operations with large amounts of data. An array method with slightly higher cost, new storage capabilities and high reliability.
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between raid0 and raid1 in windows. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




