How does SpringBoot read JSON files in the resource directory?
Idea
Use Spring's ResourceUtils to read the json file in the resource directory.
Use common-io to convert the read file into a json string.
Use fastjson to deserialize json strings into objects.
Example
1.Maven depends on
pom.xml, mainly the introduction of common-io and fastjson.
<!-- 资源目录资源文件读取 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 反序列化json字符串 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson2</artifactId>
<version>2.0.14</version>
</dependency>2.json resource file
notice.json, simply list the json content to be used.
[
{
"title": "新功能xxx上线",
"content": "支持xxx"
},
{
"title": "旧功能xxx下线",
"content": "不支持xxx"
}
]3. Read json Service
3.1. Define the interface
package com.example.springbootjson.service;
import com.example.springbootjson.domain.NoticeInfo;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author hongcunlin
*/
public interface NoticeService {
/**
* 获取公告
*
* @return 公告
* @throws IOException 文件
*/
List<NoticeInfo> getNoticeInfoList() throws IOException;
}3.2. Implement the interface
This can be said to be the core part of this article , you can see the implementation in the code for details, read the notice.json json file through ResourceUtils, convert the file into a json string through common-io's FileUtils, and deserialize the json object through fastjson's JSON.
package com.example.springbootjson.service.impl;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import com.example.springbootjson.domain.NoticeInfo;
import com.example.springbootjson.service.NoticeService;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.ResourceUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author hongcunlin
*/
@Service
public class NoticeServiceImpl implements NoticeService {
@Override
public List<NoticeInfo> getNoticeInfoList() throws IOException {
File file = ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:notice.json");
String json = FileUtils.readFileToString(file, "UTF-8");
List<NoticeInfo> noticeInfoList = JSON.parseArray(json, NoticeInfo.class);
return noticeInfoList;
}
}4. Test interface
Write a simple integration test, inject the Service written above, execute the method, and print the execution results.
package com.example.springbootjson;
import com.example.springbootjson.service.NoticeService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootJsonApplicationTests {
@Resource
private NoticeService noticeService;
@Test
void contextLoads() throws IOException {
System.out.println(noticeService.getNoticeInfoList());
}
}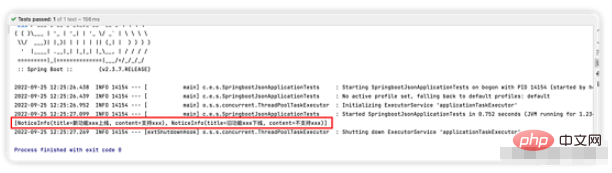
You can see that the content in the json file can be output normally, indicating that our program is correct.
The above is the detailed content of How does SpringBoot read JSON files in the resource directory?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Combination of golang WebSocket and JSON: realizing data transmission and parsing
Dec 17, 2023 pm 03:06 PM
Combination of golang WebSocket and JSON: realizing data transmission and parsing
Dec 17, 2023 pm 03:06 PM
The combination of golangWebSocket and JSON: realizing data transmission and parsing In modern Web development, real-time data transmission is becoming more and more important. WebSocket is a protocol used to achieve two-way communication. Unlike the traditional HTTP request-response model, WebSocket allows the server to actively push data to the client. JSON (JavaScriptObjectNotation) is a lightweight format for data exchange that is concise and easy to read.
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 What is the difference between MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
What is the difference between MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0?
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:21 AM
MySQL5.7 and MySQL8.0 are two different MySQL database versions. There are some main differences between them: Performance improvements: MySQL8.0 has some performance improvements compared to MySQL5.7. These include better query optimizers, more efficient query execution plan generation, better indexing algorithms and parallel queries, etc. These improvements can improve query performance and overall system performance. JSON support: MySQL 8.0 introduces native support for JSON data type, including storage, query and indexing of JSON data. This makes processing and manipulating JSON data in MySQL more convenient and efficient. Transaction features: MySQL8.0 introduces some new transaction features, such as atomic
 Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization tips for converting PHP arrays to JSON
May 04, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Performance optimization methods for converting PHP arrays to JSON include: using JSON extensions and the json_encode() function; adding the JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE option to avoid character escaping; using buffers to improve loop encoding performance; caching JSON encoding results; and considering using a third-party JSON encoding library.
 Use the json.MarshalIndent function in golang to convert the structure into a formatted JSON string
Nov 18, 2023 pm 01:59 PM
Use the json.MarshalIndent function in golang to convert the structure into a formatted JSON string
Nov 18, 2023 pm 01:59 PM
Use the json.MarshalIndent function in golang to convert the structure into a formatted JSON string. When writing programs in Golang, we often need to convert the structure into a JSON string. In this process, the json.MarshalIndent function can help us. Implement formatted output. Below we will explain in detail how to use this function and provide specific code examples. First, let's create a structure containing some data. The following is an indication
 Pandas usage tutorial: Quick start for reading JSON files
Jan 13, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Pandas usage tutorial: Quick start for reading JSON files
Jan 13, 2024 am 10:15 AM
Quick Start: Pandas method of reading JSON files, specific code examples are required Introduction: In the field of data analysis and data science, Pandas is one of the important Python libraries. It provides rich functions and flexible data structures, and can easily process and analyze various data. In practical applications, we often encounter situations where we need to read JSON files. This article will introduce how to use Pandas to read JSON files, and attach specific code examples. 1. Installation of Pandas
 How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
How do annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization?
May 06, 2024 pm 10:09 PM
Annotations in the Jackson library control JSON serialization and deserialization: Serialization: @JsonIgnore: Ignore the property @JsonProperty: Specify the name @JsonGetter: Use the get method @JsonSetter: Use the set method Deserialization: @JsonIgnoreProperties: Ignore the property @ JsonProperty: Specify name @JsonCreator: Use constructor @JsonDeserialize: Custom logic
 Use PHP's json_encode() function to convert an array or object into a JSON string and format the output
Nov 03, 2023 pm 03:44 PM
Use PHP's json_encode() function to convert an array or object into a JSON string and format the output
Nov 03, 2023 pm 03:44 PM
Using PHP's json_encode() function to convert an array or object into a JSON string and format the output can make it easier to transfer and exchange data between different platforms and languages. This article will introduce the basic usage of the json_encode() function and how to format and output a JSON string. 1. Basic usage of json_encode() function The basic syntax of json_encode() function is as follows: stringjson_encod




