How to realize MySQL read and write separation in SpringBoot project
1. MySQL master-slave replication
But if we look carefully, we will find that when our projects all use a single database, then There may be the following problems:
All reading and writing pressure is borne by one database, High pressure
If the database server disk is damaged, data will be lost, a single point of failure
In order to solve the two problems mentioned above, we can prepare two (more) MySQL, one The master (Master) server, a slave (Slave) server, and the data change (write, update, delete operations) of the main database require Synchronization to the slave database (master-slave replication). When users access our project, if it is a write operation (insert, update, delete), they will directly operate main library; if it is a read operation (select ), then directly operate the slave library. This structure is read-write separation.

In this read-write separation structure, there can be multiple slave libraries
1.1. Introduction
MySQL master Slave replication is an asynchronous replication process, and the underlying layer is based on the binary log function that comes with the Mysql database. It means that one or more MySQL databases (slave, that is, slave library) copies the log from another MySQL database (master, that is, main library), and then parses the log and Apply it to itself, and finally realize that the data of slave library is consistent with the data of main library. MySQL master-slave replication is a built-in function of the MySQL database and does not require the use of third-party tools.
Binary log:
The binary log (BINLOG) records all DDL (data definition language) statements and DML (data manipulation language) statements, but does not include data query statements. This log plays an extremely important role in data recovery during disasters. MySQL's master-slave replication is implemented through this binlog. By default, MySQL does not enable this log.
MySQL replication process is divided into three steps:
MySQL master writes data changes to the binary log ( binary log )
slave copies the master’s binary log to its relay log (relay log)
slave redoes events in the relay log , reflect the data changes to its own data

1.2. Master-slave library construction
Before setting up the environment, we need to prepare There are two servers. If you live a wealthy life and use two cloud servers, remember to open the security group, that is, the firewall; if you live a better life than me but still use a virtual machine, remember not to start with so much memory. It's a blue screen (don't ask how you know it)
I won't show you the installation of the database and the operation of the firewall here. I feel that there are many resources on the Internet that can meet the problems encountered. When building the master-slave library Sometimes I saw on the Internet that MySQL versions should be consistent. I didn’t pay much attention and just operated on the previous MySQL. You can verify it yourself.
1.2.1. Main library configuration
Server: 192.168.150.100 (Don’t try to hack it, this is the IP of the virtual machine)
1. Modify the configuration file of the Mysql database vim /etc/my.cnf
1 2 3 |
|
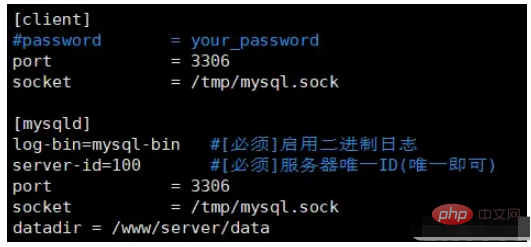
2. Restart the Mysql service
here There are three ways to restart MySQL. The simplest is undoubtedly to turn it off and on:
1 2 3 |
|
3. Create a user for data synchronization and authorize
After logging in to MySQL To be able to execute the following command, because this is a SQL command, Linux does not know what this thing is.
1 2 3 4 |
|
4. Check the master synchronization status
There is no need to exit MySQL at this time, because the following command is still a SQL command, execute the following SQL , we can get the two important parameters we need later.
1 |
|
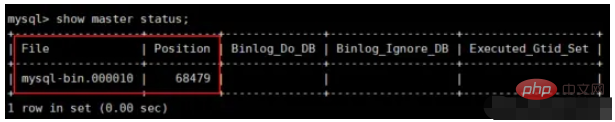
two attribute values in the red box to change. If an error occurs later, it may be the same as the two cents here. It’s related.
1.2.2、从库配置
服务器:192.168.150.101(别试了黑不了的,这也是虚拟机的ip)
1、 修改Mysql数据库的配置文件 vim /etc/my.cnf

这里要注意server-id和主库以及其他从库都不能相同,否则后面将会配置不成功。
2、重启Mysql服务
这里有三个方法都能重启MySQL,最简单的无疑就是一关一开:
1 2 3 |
|
3、设置主库地址及同步位置
登录进去MySQL之后才能够执行下面的命令,因为这是SQL命令
1 2 3 4 |
|
参数说明:
master_host: 主库的 IP地址
master_user: 访问主库进行主从复制的 用户名 ( 上面在主库创建的 )
master_password: 访问主库进行主从复制的用户名对应的 密码
master_log_file: 从哪个 日志文件 开始同步 ( 即1.2.1中第4步获取的 File )
master_log_pos: 从指定日志文件的哪个 位置 开始同步 ( 即1.2.1中第4步获取的 Position )
4、查看从数据库的状态
这个时候还 不用退出MySQL ,因为下面的命令还是SQL命令,执行下面的SQL,可以看到从库的状态信息。通过状态信息中的 Slave_IO_running 和 Slave_SQL_running 可以看出主从同步是否就绪,如果这两个参数全为 Yes ,表示主从同步已经配置完成。
1 |
|

1.3、坑位介绍
1.3.1、UUID报错
这可能是由于linux 是复制出来的,MySQL中还有一个 server_uuid 是一样的,我们也需要修改。 vim /var/lib/mysql/auto.cnf

1.3.2、server_id报错
这应该就是各位大牛设置server_id的时候不小心设置相同的id了,修改过来就行,步骤在上面的配置中。
1.3.3、同步异常解决
这是狗子在操作过程中搞出来的一个错误……
出错的原因是在主库中删除了用户信息,但是在从库中同步的时候失败导致同步停止,下面记录自己的操作(是在进入MySQL的操作且是从库)。
1 |
|
1 2 3 4 |
|
在数据库中操作时,一定要注意当前所在的数据库是哪个,作为一个良好的实践:在SQL语句前加 USE dbname 。
操作不规范,亲人两行泪……
2、项目中实现
2.1、ShardingJDBC
Sharding-JDBC定位为 轻量级Java框架 ,在Java的JDBC层提供的额外服务。 它使用客户端直连数据库,以 jar包 形式提供服务,无需额外部署和依赖,可理解为增强版的JDBC驱动, 完全兼容JDBC和各种ORM框架 。
使用Sharding-JDBC可以在程序中轻松的实现数据库 读写分离 。
Sharding-JDBC具有以下几个特点:
适用于任何基于JDBC的ORM框架,如:JPA, Hibernate, Mybatis, Spring JDBC Template或直接使用JDBC。
支持任何第三方的数据库连接池,如:DBCP, C3P0, BoneCP, Druid, HikariCP等。
支持任意实现JDBC规范的数据库。目前支持MySQL,Oracle,SQLServer,PostgreSQL以及任何遵循SQL92标准的数据库。
下面我们将用ShardingJDBC在项目中实现MySQL的读写分离。
2.2、依赖导入
在pom.xml文件中导入ShardingJDBC的依赖坐标
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
2.3、配置文件
在application.yml中增加数据源的配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
|
2.4、测试跑路
这时我们就可以对我们项目中的配置进行一个测试,下面分别调用一个更新接口和一个查询接口,通过查看日志中记录的数据源来判断是否能够按照我们预料中的跑。
更新操作(写操作)

查询操作(读操作)

Done! ! ! The program ran normally and successfully as we expected. With the help of ShardingJDBC, we successfully realized the separation of reading and writing of the database in our project.
The above is the detailed content of How to realize MySQL read and write separation in SpringBoot project. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to recover data after SQL deletes rows
Apr 09, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
Recovering deleted rows directly from the database is usually impossible unless there is a backup or transaction rollback mechanism. Key point: Transaction rollback: Execute ROLLBACK before the transaction is committed to recover data. Backup: Regular backup of the database can be used to quickly restore data. Database snapshot: You can create a read-only copy of the database and restore the data after the data is deleted accidentally. Use DELETE statement with caution: Check the conditions carefully to avoid accidentally deleting data. Use the WHERE clause: explicitly specify the data to be deleted. Use the test environment: Test before performing a DELETE operation.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.




