What are the two types of transactions in Java Spring?
1. Transaction control method in Spring
Spring’s transaction control can be divided into programmatic transaction control and Declarative transaction control.
Programmatic
Developers directly couple transaction code and business code together, which is not used in actual development.
Declarative
Developers use configuration to achieve transaction control, decoupling business code and transaction code, and using AOP ideas.
2. Programmatic transaction control related objects
2.1PlatformTransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager interface is spring's transaction manager interface, which provides our commonly used methods for operating transactions.
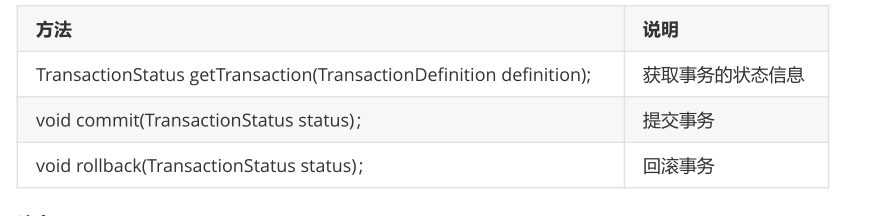
(1) Transaction isolation level
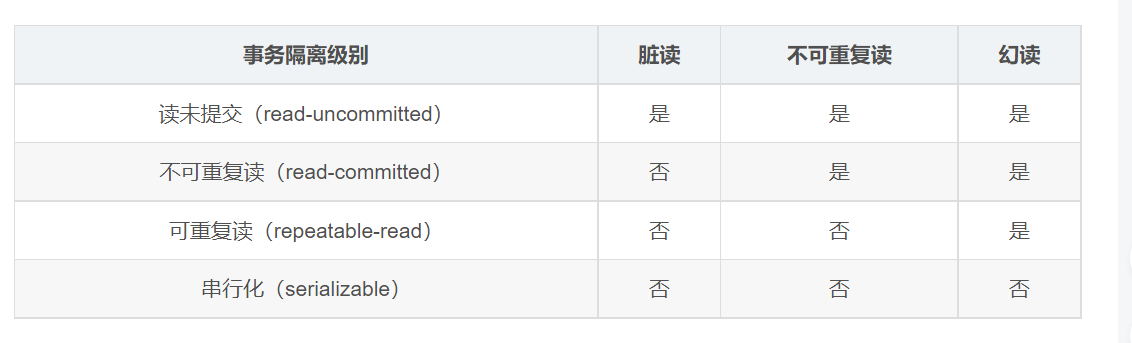
Setting the isolation level can solve problems caused by transaction concurrency, such as dirty reads, unavailable Repeated reading and virtual reading (phantom reading).Note: Use the database default level. If the database is mysql, the default is repeatable read, oracle is read committed.
ISOLATION_DEFAULT Use database default level
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED Read uncommitted
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED Read committed ( Can solve dirty read problem)
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ Repeatable read (can solve dirty read and non-repeatable read problem)
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE Serialization
Can be solved:
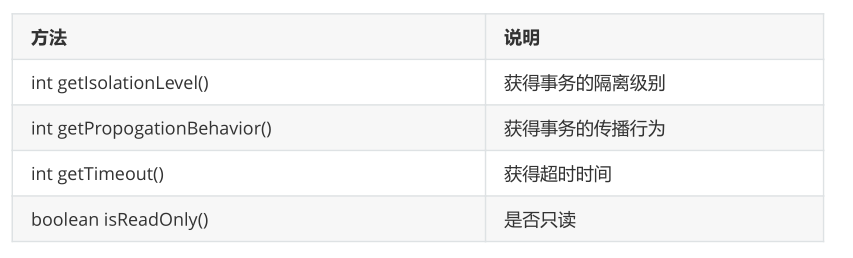
(2) Transaction propagation behavior
Transaction propagation behavior refers to What is involved is how transaction control should be performed when a business method is called by another business method.
Key points:

- ##read-only
(Whether it is read-only): It is recommended to set it to read-only when querying
- timeout
(timeout time): The default value is -1, there is no timeout limit. If so, set it in seconds
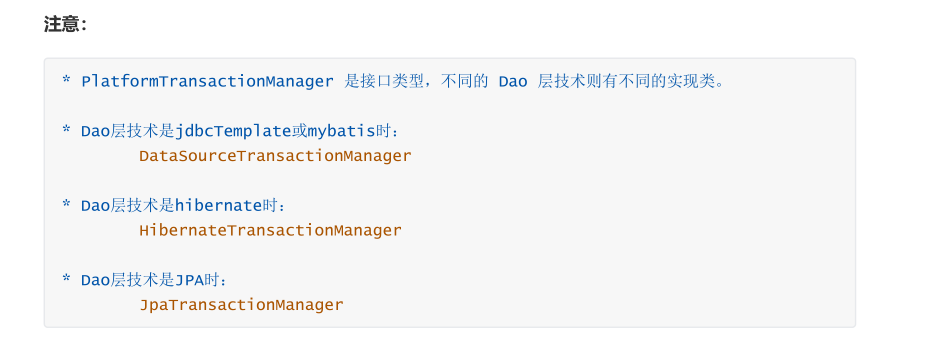
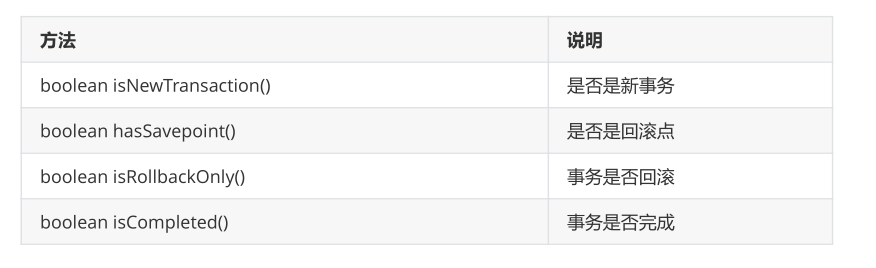
2.3 TransactionStatus
The TransactionStatus interface provides the specific running status of the transaction.
 You can simply understand the relationship between the three: the transaction manager performs transaction management by reading the transaction definition parameters, and then generates a series of transaction states.
You can simply understand the relationship between the three: the transaction manager performs transaction management by reading the transaction definition parameters, and then generates a series of transaction states.
Transaction control in Spring is mainly implemented through these three APIs
PlatformTransactionManageris responsible for the management of transactions. It is an interface and its subclasses are responsible for specific work
Defines some relevant parameters of the transaction
Represents a real-time status of the transaction runningUnderstand the relationship between the three:
performs transaction management by reading transaction definition parameters, and then generates a series of transaction status. 3. XML-based declarative transaction control [Key points]
Declarative processing of transactions in the Spring configuration file instead of code processing. The bottom layer is implemented using AOP ideas.
Declarative transaction control clear matters:Core business code (target object) (Who is the entry point?)
Transaction enhancement code (Spring Transaction manager has been provided)) (Who is notified?)
Aspect configuration (How to configure the aspect?) (Aspect = pointcut notification)
3.1 Quick Start
Use Spring declarative transaction control transfer business.
Steps:1.Introduce the tx namespace
2.Transaction manager notification configuration
3.Transaction manager AOP configuration
4. Test transaction control transfer business code
(1)Introduce tx namespace
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
">(2)Transaction manager notification configuration
<!--事务管理器对象-->
<!--<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>-->
// 通知增强
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
//定义事务的一些属性 * 表示当前任意名称的方法都走默认配置
<!--
name: 切点方法名称
isolation:事务的隔离级别
propagation:事务的传播行为
read-only:是否只读
timeout:超时时间
-->
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" timeout="-1"/>
//CRUD常用配置
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>(3) Transaction manager AOP configuration
When using spring to manage transactions declaratively, use aop:advisor to configure aop!
//aop配置:配置切面
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.lagou.servlet.impl.AccountServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
</aop:config>-->##
name:切点方法名称isolation:事务的隔离级别propogation:事务的传播行为timeout:超时时间read-only:是否只读
4.基于注解的声明式事务控制(重点)
步骤:
修改service层,增加事务注解
修改spring核心配置文件,开启事务注解支持
4.1 修改service层,增加事务注解
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation =
Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ, timeout = -1, readOnly = false)
@Override
public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) {
accountDao.out(outUser, money);
int i = 1 / 0;
accountDao.in(inUser, money);
}
}4.2修改spring核心配置文件,开启事务注解支持
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w2.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--省略之前datsSource、jdbcTemplate、组件扫描配置-->
<!--事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--事务的注解支持-->
<tx:annotation-driven/>
</beans4.3纯注解方式
核心配置类:
@Configuration // 声明该类为核心配置类
@ComponentScan("com.lagou") // 包扫描
@Import(DataSourceConfig.class) //导入其他配置类
@EnableTransactionManagement //事务的注解驱动
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager getPlatformTransactionManager(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}数据源配置类:
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") //引入properties文件
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean //会把当前方法的返回值对象放进IOC容器中
public DataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
druidDataSource.setUrl(url);
druidDataSource.setUsername(username);
druidDataSource.setPassword(password);
return druidDataSource;
}
}The above is the detailed content of What are the two types of transactions in Java Spring?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






