
1. Declarative transactions
Use AOP (aspect-oriented) method to open the transaction using the programmatic transaction method before the method, and submit or submit after the method rollback. Use configuration file methods or annotation methods (such as @Transactional) to control transactions.
The annotation on the method is that the method automatically starts the transaction, and on the class it is that all methods in the entire class use transactions
2. Method
1. Declarative transaction management based on TransactionProxyFactoryBean
Configure in applicationContext.xml
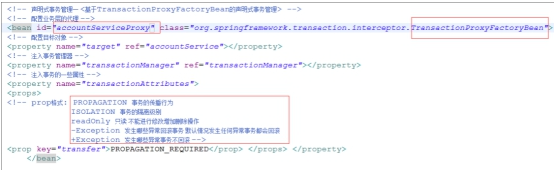
Then when needed The service layer for transaction management injects the proxy class accountrviceProxy
@Resource(name="accountrviceProxy")
This method has a disadvantage, that is, we need to match each service class that needs transaction management with its proxy class, which is relatively easy to configure. Cumbersome.
2. Declarative transaction management based on AspectJ XML
There is an expression when configuring the entry point:
expression="execution(* com.cn.study.spring.service.IAccountService+.*(..))"
execution in brackets The parameters in turn represent the method return type, package name, class name, method name and method parameters
where * represents any
IAccountService represents the methods of all implementation classes of the IAccountService interface
This method is one of the more commonly used.
3. Declarative transaction management based on annotations
The third way is the simplest. We only need to configure the driver that enables annotation transactions in applicationContext.xml, and then Add annotations before the classes that require transaction management:
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
The above is the detailed content of What are the methods of declarative transactions in java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




