How to use python code to remove moiré from images
1. Introduction
When the spatial frequency of the pixels of the photosensitive element is close to the spatial frequency of the stripes in the image, a new wavy interference pattern, the so-called moiré pattern, may be produced. The sensor's grid-like texture creates one such pattern. If the thin strips in the pattern intersect the structure of the sensor at a small angle, this will produce a noticeable interference effect in the image. This phenomenon is very common in fashion photography with fine textures such as cloth. This moiré pattern may appear through brightness or color. But here, only the image moiré produced during the remake is processed.
Recapture is to capture pictures from the computer screen, or take pictures against the screen; this method will produce moiré patterns on the pictures
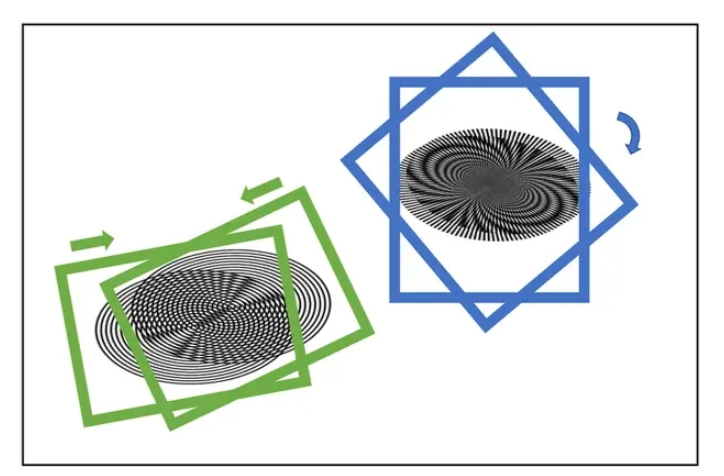
The main processing ideas of the paper
Perform Haar transformation on the original image to obtain four down-sampled feature maps (two-sampled cA, Horizontal horizontal high frequency cH, Vertical vertical high frequency under the original image cV, Diagonal oblique high-frequency cD)
Then use four independent CNNs to convolute and pool the four downsampled feature maps to extract feature information
The original text then compares each channel and each pixel of the three high-frequency information convolution and pooling results, and takes max
to complete the previous step The obtained result and the result after cA convolution and pooling are made into a Cartesian product
Paper address
2. Reproduction of network structure
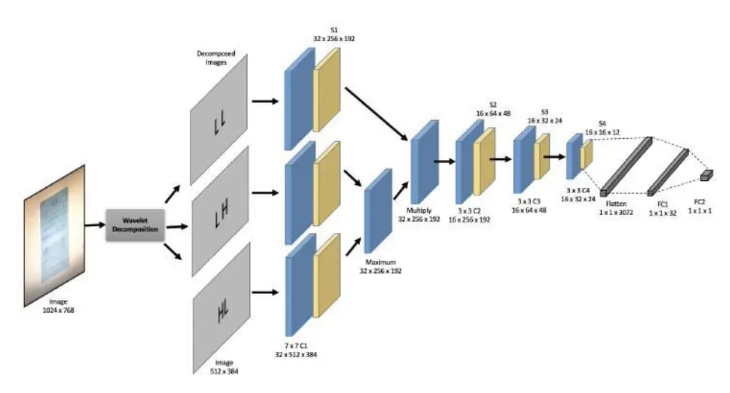
As shown in the figure below, this project reproduces the image demoire method of the paper, and modifies the data processing part. The network structure also refers to the structure in the source code to generate four downsampled feature maps for the image. , instead of the three in the paper, you can refer to the network structure for specific processing methods.
import math
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
# import pywt
from paddle.nn import Linear, Dropout, ReLU
from paddle.nn import Conv2D, MaxPool2D
class mcnn(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(mcnn, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
self._conv1_LL = Conv2D(3,32,7,stride=2,padding=1,)
# self.bn1_LL = nn.BatchNorm2D(128)
self._conv1_LH = Conv2D(3,32,7,stride=2,padding=1,)
# self.bn1_LH = nn.BatchNorm2D(256)
self._conv1_HL = Conv2D(3,32,7,stride=2,padding=1,)
# self.bn1_HL = nn.BatchNorm2D(512)
self._conv1_HH = Conv2D(3,32,7,stride=2,padding=1,)
# self.bn1_HH = nn.BatchNorm2D(256)
self.pool_1_LL = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2,stride=2, padding=0)
self.pool_1_LH = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2,stride=2, padding=0)
self.pool_1_HL = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2,stride=2, padding=0)
self.pool_1_HH = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2,stride=2, padding=0)
self._conv2 = Conv2D(32,16,3,stride=2,padding=1,)
self.pool_2 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2,stride=2, padding=0)
self.dropout2 = Dropout(p=0.5)
self._conv3 = Conv2D(16,32,3,stride=2,padding=1,)
self.pool_3 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2,stride=2, padding=0)
self._conv4 = Conv2D(32,32,3,stride=2,padding=1,)
self.pool_4 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=2,stride=2, padding=0)
self.dropout4 = Dropout(p=0.5)
# self.bn1_HH = nn.BatchNorm1D(256)
self._fc1 = Linear(in_features=64,out_features=num_classes)
self.dropout5 = Dropout(p=0.5)
self._fc2 = Linear(in_features=2,out_features=num_classes)
def forward(self, inputs1, inputs2, inputs3, inputs4):
x1_LL = self._conv1_LL(inputs1)
x1_LL = F.relu(x1_LL)
x1_LH = self._conv1_LH(inputs2)
x1_LH = F.relu(x1_LH)
x1_HL = self._conv1_HL(inputs3)
x1_HL = F.relu(x1_HL)
x1_HH = self._conv1_HH(inputs4)
x1_HH = F.relu(x1_HH)
pool_x1_LL = self.pool_1_LL(x1_LL)
pool_x1_LH = self.pool_1_LH(x1_LH)
pool_x1_HL = self.pool_1_HL(x1_HL)
pool_x1_HH = self.pool_1_HH(x1_HH)
temp = paddle.maximum(pool_x1_LH, pool_x1_HL)
avg_LH_HL_HH = paddle.maximum(temp, pool_x1_HH)
inp_merged = paddle.multiply(pool_x1_LL, avg_LH_HL_HH)
x2 = self._conv2(inp_merged)
x2 = F.relu(x2)
x2 = self.pool_2(x2)
x2 = self.dropout2(x2)
x3 = self._conv3(x2)
x3 = F.relu(x3)
x3 = self.pool_3(x3)
x4 = self._conv4(x3)
x4 = F.relu(x4)
x4 = self.pool_4(x4)
x4 = self.dropout4(x4)
x4 = paddle.flatten(x4, start_axis=1, stop_axis=-1)
x5 = self._fc1(x4)
x5 = self.dropout5(x5)
out = self._fc2(x5)
return out
model_res = mcnn(num_classes=2)
paddle.summary(model_res,[(1,3,512,384),(1,3,512,384),(1,3,512,384),(1,3,512,384)])---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Input Shape Output Shape Param #
===========================================================================
Conv2D-1 [[1, 3, 512, 384]] [1, 32, 254, 190] 4,736
Conv2D-2 [[1, 3, 512, 384]] [1, 32, 254, 190] 4,736
Conv2D-3 [[1, 3, 512, 384]] [1, 32, 254, 190] 4,736
Conv2D-4 [[1, 3, 512, 384]] [1, 32, 254, 190] 4,736
MaxPool2D-1 [[1, 32, 254, 190]] [1, 32, 127, 95] 0
MaxPool2D-2 [[1, 32, 254, 190]] [1, 32, 127, 95] 0
MaxPool2D-3 [[1, 32, 254, 190]] [1, 32, 127, 95] 0
MaxPool2D-4 [[1, 32, 254, 190]] [1, 32, 127, 95] 0
Conv2D-5 [[1, 32, 127, 95]] [1, 16, 64, 48] 4,624
MaxPool2D-5 [[1, 16, 64, 48]] [1, 16, 32, 24] 0
Dropout-1 [[1, 16, 32, 24]] [1, 16, 32, 24] 0
Conv2D-6 [[1, 16, 32, 24]] [1, 32, 16, 12] 4,640
MaxPool2D-6 [[1, 32, 16, 12]] [1, 32, 8, 6] 0
Conv2D-7 [[1, 32, 8, 6]] [1, 32, 4, 3] 9,248
MaxPool2D-7 [[1, 32, 4, 3]] [1, 32, 2, 1] 0
Dropout-2 [[1, 32, 2, 1]] [1, 32, 2, 1] 0
Linear-1 [[1, 64]] [1, 2] 130
Dropout-3 [[1, 2]] [1, 2] 0
Linear-2 [[1, 2]] [1, 2] 6
===========================================================================
Total params: 37,592
Trainable params: 37,592
Non-trainable params: 0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 9.00
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 59.54
Params size (MB): 0.14
Estimated Total Size (MB): 68.68
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
{'total_params': 37592, 'trainable_params': 37592}3. Data preprocessing
Different from the source code, this project integrates the wavelet decomposition part of the image into the data The reading part is changed to perform wavelet decomposition online instead of performing wavelet decomposition offline in the source code and saving the image. First, define the function of wavelet decomposition
!pip install PyWavelets
import numpy as np
import pywt
def splitFreqBands(img, levRows, levCols):
halfRow = int(levRows/2)
halfCol = int(levCols/2)
LL = img[0:halfRow, 0:halfCol]
LH = img[0:halfRow, halfCol:levCols]
HL = img[halfRow:levRows, 0:halfCol]
HH = img[halfRow:levRows, halfCol:levCols]
return LL, LH, HL, HH
def haarDWT1D(data, length):
avg0 = 0.5;
avg1 = 0.5;
dif0 = 0.5;
dif1 = -0.5;
temp = np.empty_like(data)
# temp = temp.astype(float)
temp = temp.astype(np.uint8)
h = int(length/2)
for i in range(h):
k = i*2
temp[i] = data[k] * avg0 + data[k + 1] * avg1;
temp[i + h] = data[k] * dif0 + data[k + 1] * dif1;
data[:] = temp
# computes the homography coefficients for PIL.Image.transform using point correspondences
def fwdHaarDWT2D(img):
img = np.array(img)
levRows = img.shape[0];
levCols = img.shape[1];
# img = img.astype(float)
img = img.astype(np.uint8)
for i in range(levRows):
row = img[i,:]
haarDWT1D(row, levCols)
img[i,:] = row
for j in range(levCols):
col = img[:,j]
haarDWT1D(col, levRows)
img[:,j] = col
return splitFreqBands(img, levRows, levCols)!cd "data/data188843/" && unzip -q 'total_images.zip'
import os
recapture_keys = [ 'ValidationMoire']
original_keys = ['ValidationClear']
def get_image_label_from_folder_name(folder_name):
"""
:param folder_name:
:return:
"""
for key in original_keys:
if key in folder_name:
return 'original'
for key in recapture_keys:
if key in folder_name:
return 'recapture'
return 'unclear'
label_name2label_id = {
'original': 0,
'recapture': 1,}
src_image_dir = "data/data188843/total_images"
dst_file = "data/data188843/total_images/train.txt"
image_folder = [file for file in os.listdir(src_image_dir)]
print(image_folder)
image_anno_list = []
for folder in image_folder:
label_name = get_image_label_from_folder_name(folder)
# label_id = label_name2label_id.get(label_name, 0)
label_id = label_name2label_id[label_name]
folder_path = os.path.join(src_image_dir, folder)
image_file_list = [file for file in os.listdir(folder_path) if
file.endswith('.jpg') or file.endswith('.jpeg') or
file.endswith('.JPG') or file.endswith('.JPEG') or file.endswith('.png')]
for image_file in image_file_list:
# if need_root_dir:
# image_path = os.path.join(folder_path, image_file)
# else:
image_path = image_file
image_anno_list.append(folder +"/"+image_path +"\t"+ str(label_id) + '\n')
dst_path = os.path.dirname(src_image_dir)
if not os.path.exists(dst_path):
os.makedirs(dst_path)
with open(dst_file, 'w') as fd:
fd.writelines(image_anno_list)import paddle
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import PIL.Image as Image
from paddle.vision import transforms
# from haar2D import fwdHaarDWT2D
paddle.disable_static()
# 定义数据预处理
data_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(size=(448,448)),
transforms.ToTensor(), # transpose操作 + (img / 255)
# transforms.Normalize( # 减均值 除标准差
# mean=[0.31169346, 0.25506335, 0.12432463],
# std=[0.34042713, 0.29819837, 0.1375536])
#计算过程:output[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]
])
# 构建Dataset
class MyDataset(paddle.io.Dataset):
"""
步骤一:继承paddle.io.Dataset类
"""
def __init__(self, train_img_list, val_img_list, train_label_list, val_label_list, mode='train', ):
"""
步骤二:实现构造函数,定义数据读取方式,划分训练和测试数据集
"""
super(MyDataset, self).__init__()
self.img = []
self.label = []
# 借助pandas读csv的库
self.train_images = train_img_list
self.test_images = val_img_list
self.train_label = train_label_list
self.test_label = val_label_list
if mode == 'train':
# 读train_images的数据
for img,la in zip(self.train_images, self.train_label):
self.img.append('/home/aistudio/data/data188843/total_images/'+img)
self.label.append(paddle.to_tensor(int(la), dtype='int64'))
else:
# 读test_images的数据
for img,la in zip(self.test_images, self.test_label):
self.img.append('/home/aistudio/data/data188843/total_images/'+img)
self.label.append(paddle.to_tensor(int(la), dtype='int64'))
def load_img(self, image_path):
# 实际使用时使用Pillow相关库进行图片读取即可,这里我们对数据先做个模拟
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
# image = data_transforms(image)
return image
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""
步骤三:实现__getitem__方法,定义指定index时如何获取数据,并返回单条数据(训练数据,对应的标签)
"""
image = self.load_img(self.img[index])
LL, LH, HL, HH = fwdHaarDWT2D(image)
label = self.label[index]
# print(LL.shape)
# print(LH.shape)
# print(HL.shape)
# print(HH.shape)
LL = data_transforms(LL)
LH = data_transforms(LH)
HL = data_transforms(HL)
HH = data_transforms(HH)
print(type(LL))
print(LL.dtype)
return LL, LH, HL, HH, np.array(label, dtype='int64')
def __len__(self):
"""
步骤四:实现__len__方法,返回数据集总数目
"""
return len(self.img)
image_file_txt = '/home/aistudio/data/data188843/total_images/train.txt'
with open(image_file_txt) as fd:
lines = fd.readlines()
train_img_list = list()
train_label_list = list()
for line in lines:
split_list = line.strip().split()
image_name, label_id = split_list
train_img_list.append(image_name)
train_label_list.append(label_id)
# print(train_img_list)
# print(train_label_list)
# 测试定义的数据集
train_dataset = MyDataset(mode='train',train_label_list=train_label_list, train_img_list=train_img_list, val_img_list=train_img_list, val_label_list=train_label_list)
# test_dataset = MyDataset(mode='test')
# 构建训练集数据加载器
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
# 构建测试集数据加载器
valid_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
print('=============train dataset=============')
for LL, LH, HL, HH, label in train_dataset:
print('label: {}'.format(label))
break4. Model training
model2 = paddle.Model(model_res)
model2.prepare(optimizer=paddle.optimizer.Adam(parameters=model2.parameters()),
loss=nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),
metrics=paddle.metric.Accuracy())
model2.fit(train_loader,
valid_loader,
epochs=5,
verbose=1,
)The above is the detailed content of How to use python code to remove moiré from images. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Do mysql need to pay
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Do mysql need to pay
Apr 08, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
MySQL has a free community version and a paid enterprise version. The community version can be used and modified for free, but the support is limited and is suitable for applications with low stability requirements and strong technical capabilities. The Enterprise Edition provides comprehensive commercial support for applications that require a stable, reliable, high-performance database and willing to pay for support. Factors considered when choosing a version include application criticality, budgeting, and technical skills. There is no perfect option, only the most suitable option, and you need to choose carefully according to the specific situation.
 How to use mysql after installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to use mysql after installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
The article introduces the operation of MySQL database. First, you need to install a MySQL client, such as MySQLWorkbench or command line client. 1. Use the mysql-uroot-p command to connect to the server and log in with the root account password; 2. Use CREATEDATABASE to create a database, and USE select a database; 3. Use CREATETABLE to create a table, define fields and data types; 4. Use INSERTINTO to insert data, query data, update data by UPDATE, and delete data by DELETE. Only by mastering these steps, learning to deal with common problems and optimizing database performance can you use MySQL efficiently.
 MySQL download file is damaged and cannot be installed. Repair solution
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:21 AM
MySQL download file is damaged and cannot be installed. Repair solution
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:21 AM
MySQL download file is corrupt, what should I do? Alas, if you download MySQL, you can encounter file corruption. It’s really not easy these days! This article will talk about how to solve this problem so that everyone can avoid detours. After reading it, you can not only repair the damaged MySQL installation package, but also have a deeper understanding of the download and installation process to avoid getting stuck in the future. Let’s first talk about why downloading files is damaged. There are many reasons for this. Network problems are the culprit. Interruption in the download process and instability in the network may lead to file corruption. There is also the problem with the download source itself. The server file itself is broken, and of course it is also broken when you download it. In addition, excessive "passionate" scanning of some antivirus software may also cause file corruption. Diagnostic problem: Determine if the file is really corrupt
 MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
MySQL can't be installed after downloading
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The main reasons for MySQL installation failure are: 1. Permission issues, you need to run as an administrator or use the sudo command; 2. Dependencies are missing, and you need to install relevant development packages; 3. Port conflicts, you need to close the program that occupies port 3306 or modify the configuration file; 4. The installation package is corrupt, you need to download and verify the integrity; 5. The environment variable is incorrectly configured, and the environment variables must be correctly configured according to the operating system. Solve these problems and carefully check each step to successfully install MySQL.
 How to optimize MySQL performance for high-load applications?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
How to optimize MySQL performance for high-load applications?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:03 PM
MySQL database performance optimization guide In resource-intensive applications, MySQL database plays a crucial role and is responsible for managing massive transactions. However, as the scale of application expands, database performance bottlenecks often become a constraint. This article will explore a series of effective MySQL performance optimization strategies to ensure that your application remains efficient and responsive under high loads. We will combine actual cases to explain in-depth key technologies such as indexing, query optimization, database design and caching. 1. Database architecture design and optimized database architecture is the cornerstone of MySQL performance optimization. Here are some core principles: Selecting the right data type and selecting the smallest data type that meets the needs can not only save storage space, but also improve data processing speed.
 How to optimize database performance after mysql installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
How to optimize database performance after mysql installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL performance optimization needs to start from three aspects: installation configuration, indexing and query optimization, monitoring and tuning. 1. After installation, you need to adjust the my.cnf file according to the server configuration, such as the innodb_buffer_pool_size parameter, and close query_cache_size; 2. Create a suitable index to avoid excessive indexes, and optimize query statements, such as using the EXPLAIN command to analyze the execution plan; 3. Use MySQL's own monitoring tool (SHOWPROCESSLIST, SHOWSTATUS) to monitor the database health, and regularly back up and organize the database. Only by continuously optimizing these steps can the performance of MySQL database be improved.
 Does mysql need the internet
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
Does mysql need the internet
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:18 PM
MySQL can run without network connections for basic data storage and management. However, network connection is required for interaction with other systems, remote access, or using advanced features such as replication and clustering. Additionally, security measures (such as firewalls), performance optimization (choose the right network connection), and data backup are critical to connecting to the Internet.
 Solutions to the service that cannot be started after MySQL installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:18 AM
Solutions to the service that cannot be started after MySQL installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:18 AM
MySQL refused to start? Don’t panic, let’s check it out! Many friends found that the service could not be started after installing MySQL, and they were so anxious! Don’t worry, this article will take you to deal with it calmly and find out the mastermind behind it! After reading it, you can not only solve this problem, but also improve your understanding of MySQL services and your ideas for troubleshooting problems, and become a more powerful database administrator! The MySQL service failed to start, and there are many reasons, ranging from simple configuration errors to complex system problems. Let’s start with the most common aspects. Basic knowledge: A brief description of the service startup process MySQL service startup. Simply put, the operating system loads MySQL-related files and then starts the MySQL daemon. This involves configuration




