What is the reason why SpringBoot starts slowly?
The reason why SpringBoot starts slowly
The architecture of Spring Boot is so common that if you don’t master it, sometimes you are embarrassed to say that you are engaged in Java Work. But fire returns to fire, and there are some small problems that we need to pay attention to.
If it is a single project and there are no requirements on startup speed, please ignore it.
Let’s enter the topic below. Under what circumstances will the spring boot project start slower?
Prerequisites
The machine hardware configuration for starting the project cannot be delayed, otherwise you will say that the project The startup is slow, and the project still feels that the machine is not good... For example, the network, memory size, number of CPU cores, etc. The requirements are not too high, at least it must be enough.
Put aside all kinds of artificial Factors such as long connection times and slow startup of other components lead to waiting...
Cause 1
There are too many useless configurations used in the project. For example, in the simplest web, you have also added various other maven configurations and configured them into the project (this is just an exaggerated example, these configurations are not needed), and then the project itself does not understand it. Since you configured , then load it.
One takes 0.1 seconds, 10 takes 1 second, 100 takes 10 seconds...and so on. This is the easiest thing to understand.
Reason 2
Automatic configuration of spring boot. Although automatic configuration is a highlight of Spring Boot, it is also a drawback that leads to slow startup times.
No way, usually something that is easy to use and has full functions will always have defects in some places.
As mentioned above, there are many useless configurations. What I want to say here is that spring boot has too many things assembled by itself.
You can see that the spring.factories files are stored in the relevant jar packages of spring boot. When you look inside, you will see that most of them have written a lot of classes, which implement the automatic assembly of spring boot. One of the core.
But if you look carefully, you will find that there are actually many categories that you may not use at all.
But what can you do? Whether you use it or not, at least it will check it for you. Isn’t this a place to spend time?
Reason 3
The project is not streamlined enough. The concept of microservices is quite popular now. I think its core meaning is simplicity and simplicity, and most of the places that need to emphasize startup speed are mostly in microservice projects.
In a microservice project, it is best to start it within 10 seconds. But most of them can't do it because the projects are not divided into details enough.
Whether it is faster to start one interface, or 10, or more, the answer is obvious. Many projects are large and comprehensive. The so-called large and comprehensive means that there are many functions, complete configurations, various expandable configurations, etc. It may not be comprehensive, but what does this mean? You have many configurations. It doesn’t matter whether they are useful or not. At least there will be a lot more class files that need to be compiled and loaded. You said you want such a project to start quickly, how can it start quickly?
Solution
- Check whether there are too many useless dependencies in maven
- It’s more complicated, use spring-boot-maven Start the plug-in debug, check which configurations are used in the project and which configurations are useless, then directly indicate in the startup class that only the used classes will be started, delete the @SpringBootApplication annotation, and manually fill in the @Configuration and @Import annotations , and add those configured classes in the @Import annotation.
- Replace some dependencies with faster configuration. For example, you use A database connection pool, which has full functions and many configurations, but is slower. However, in fact, B connection pool can also meet the project needs, but has relatively few functions, so there are less configurations and faster startup. Do you need You should choose one between A and B.
- Split out more streamlined projects to run independently. Big and comprehensive means more but not refined, lean and simple means less but proficient. Their speed is self-evident.
- How to improve the startup speed of SpringBoot application
Narrow the scope of @ComponentScan and @SpringBootApplication scanning classes
2. Turn off Spring Boot’s JMX monitoring. Set spring.jmx.enabled=false
3. Set the JVM parameter -noverify, and do not verify the class
4. Delay loading of beans that are not necessarily loaded at startup
5. Use Spring Boot’s global lazy loading
6. Try not to use annotations for AOP aspects, which will cause all methods to be scanned at startup
7. Turn off some endpoint monitoring functions
8. Exclude unnecessary jar dependencies of the project
9. When swagger scans the interface, specify to scan only the classes under a certain path
10. Scan the shrink package of the Feign client interface Scan range
The above is the detailed content of What is the reason why SpringBoot starts slowly?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How Springboot integrates Jasypt to implement configuration file encryption
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
How Springboot integrates Jasypt to implement configuration file encryption
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
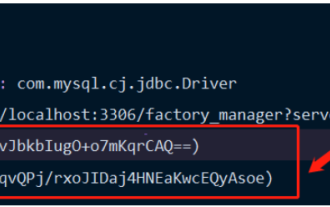
Introduction to Jasypt Jasypt is a java library that allows a developer to add basic encryption functionality to his/her project with minimal effort and does not require a deep understanding of how encryption works. High security for one-way and two-way encryption. , standards-based encryption technology. Encrypt passwords, text, numbers, binaries... Suitable for integration into Spring-based applications, open API, for use with any JCE provider... Add the following dependency: com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2. 1.1Jasypt benefits protect our system security. Even if the code is leaked, the data source can be guaranteed.
 How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
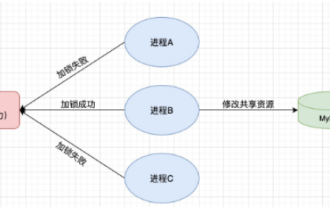
1. Redis implements distributed lock principle and why distributed locks are needed. Before talking about distributed locks, it is necessary to explain why distributed locks are needed. The opposite of distributed locks is stand-alone locks. When we write multi-threaded programs, we avoid data problems caused by operating a shared variable at the same time. We usually use a lock to mutually exclude the shared variables to ensure the correctness of the shared variables. Its scope of use is in the same process. If there are multiple processes that need to operate a shared resource at the same time, how can they be mutually exclusive? Today's business applications are usually microservice architecture, which also means that one application will deploy multiple processes. If multiple processes need to modify the same row of records in MySQL, in order to avoid dirty data caused by out-of-order operations, distribution needs to be introduced at this time. The style is locked. Want to achieve points
 How SpringBoot integrates Redisson to implement delay queue
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
How SpringBoot integrates Redisson to implement delay queue
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Usage scenario 1. The order was placed successfully but the payment was not made within 30 minutes. The payment timed out and the order was automatically canceled. 2. The order was signed and no evaluation was conducted for 7 days after signing. If the order times out and is not evaluated, the system defaults to a positive rating. 3. The order is placed successfully. If the merchant does not receive the order for 5 minutes, the order is cancelled. 4. The delivery times out, and push SMS reminder... For scenarios with long delays and low real-time performance, we can Use task scheduling to perform regular polling processing. For example: xxl-job Today we will pick
 How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot reads the file, but cannot access the latest development after packaging it into a jar package. There is a situation where springboot cannot read the file after packaging it into a jar package. The reason is that after packaging, the virtual path of the file is invalid and can only be accessed through the stream. Read. The file is under resources publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
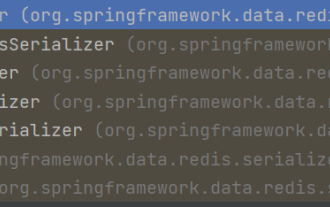
1. Customize RedisTemplate1.1, RedisAPI default serialization mechanism. The API-based Redis cache implementation uses the RedisTemplate template for data caching operations. Here, open the RedisTemplate class and view the source code information of the class. publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations, BeanClassLoaderAware{//Declare key, Various serialization methods of value, the initial value is empty @NullableprivateRedisSe
 How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
When Springboot+Mybatis-plus does not use SQL statements to perform multi-table adding operations, the problems I encountered are decomposed by simulating thinking in the test environment: Create a BrandDTO object with parameters to simulate passing parameters to the background. We all know that it is extremely difficult to perform multi-table operations in Mybatis-plus. If you do not use tools such as Mybatis-plus-join, you can only configure the corresponding Mapper.xml file and configure The smelly and long ResultMap, and then write the corresponding sql statement. Although this method seems cumbersome, it is highly flexible and allows us to
 How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
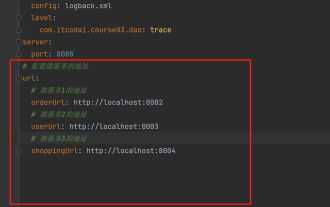
In projects, some configuration information is often needed. This information may have different configurations in the test environment and the production environment, and may need to be modified later based on actual business conditions. We cannot hard-code these configurations in the code. It is best to write them in the configuration file. For example, you can write this information in the application.yml file. So, how to get or use this address in the code? There are 2 methods. Method 1: We can get the value corresponding to the key in the configuration file (application.yml) through the ${key} annotated with @Value. This method is suitable for situations where there are relatively few microservices. Method 2: In actual projects, When business is complicated, logic






