GPT4ALL: The ultimate open source large language model solution
There is a growing ecosystem of open source language models that provides individuals with comprehensive resources to create language applications for research and commercial purposes.
This article takes a deep dive into GPT4ALL, which goes beyond specific use cases by providing comprehensive building blocks that enable anyone to develop chatbots like ChatGPT.
What is the GPT4ALL project?
GPT4ALL can provide all the support needed when using state-of-the-art open-source large language models.. It can access open source models and datasets, train and run them using the provided code, interact with them using a web interface or desktop application, connect to the Langchain backend for distributed computing, and use the Python API for easy integration.
The developers recently launched the Apache-2 licensed GPT4All-J chatbot, which is trained on a large and curated corpus of assistant interactions, including word questions, multi-turn conversations, code, poetry, songs and stories. To make it more accessible, they also released Python bindings and a chat UI, allowing almost anyone to run the model on a CPU.
You can try it yourself by installing a local chat client on your desktop.
- Mac/OSX(https://gpt4all.io/installers/gpt4all-installer-darwin.dmg)
- Windows(https://gpt4all.io/installers/gpt4all -installer-win64.exe)
- Ubuntu(https://gpt4all.io/installers/gpt4all-installer-linux.run)
After that, run the GPT4ALL program and download itself Selected model. You can also manually download the model here (https://github.com/nomic-ai/gpt4all-chat#manual-download-of-models) and install it in the location indicated by the model download dialog in the GUI.
Using GPT4ALL has a better experience on a laptop, getting fast and accurate responses. Even non-technical people can easily use GPT4ALL as it is very user-friendly.
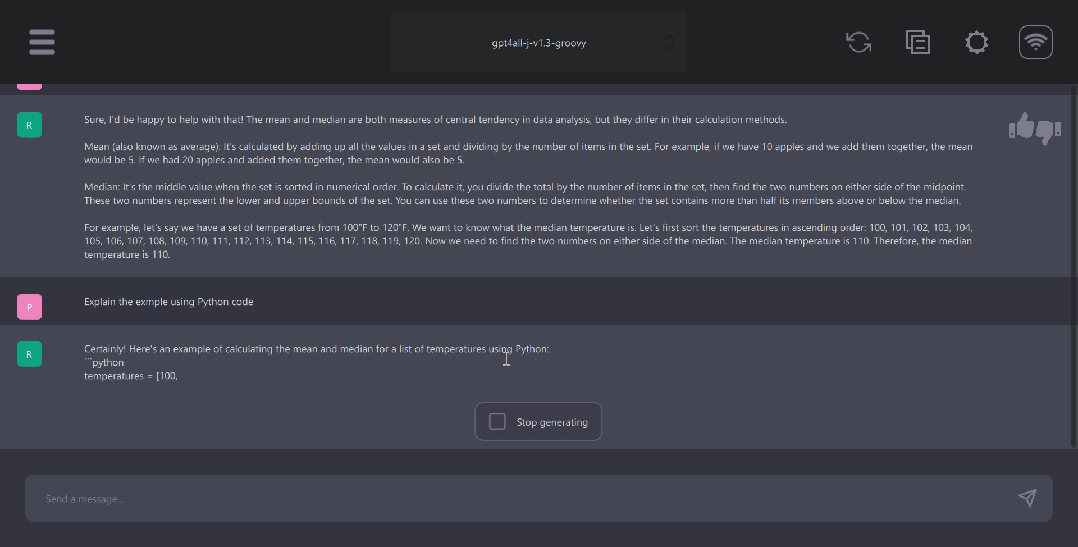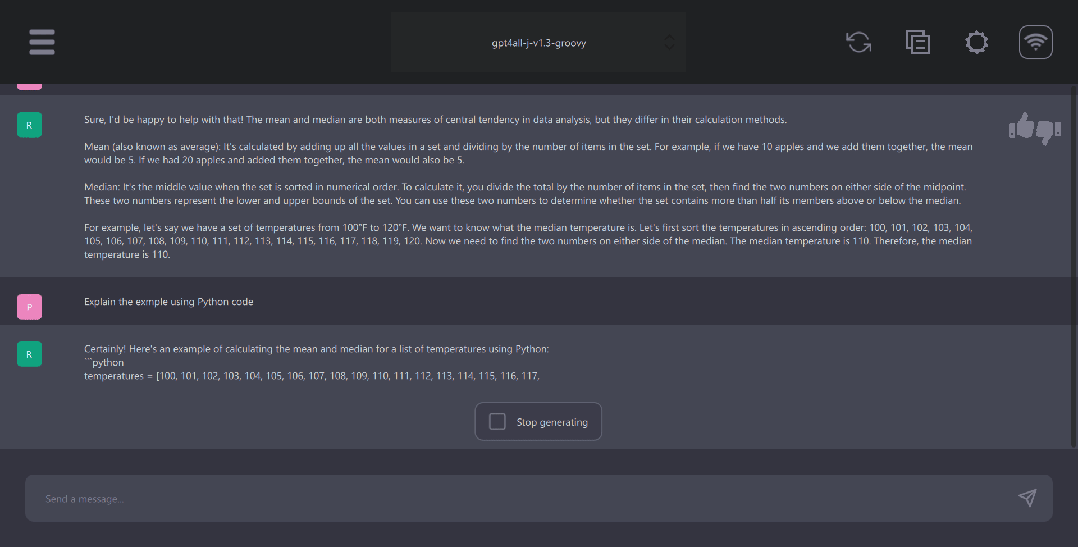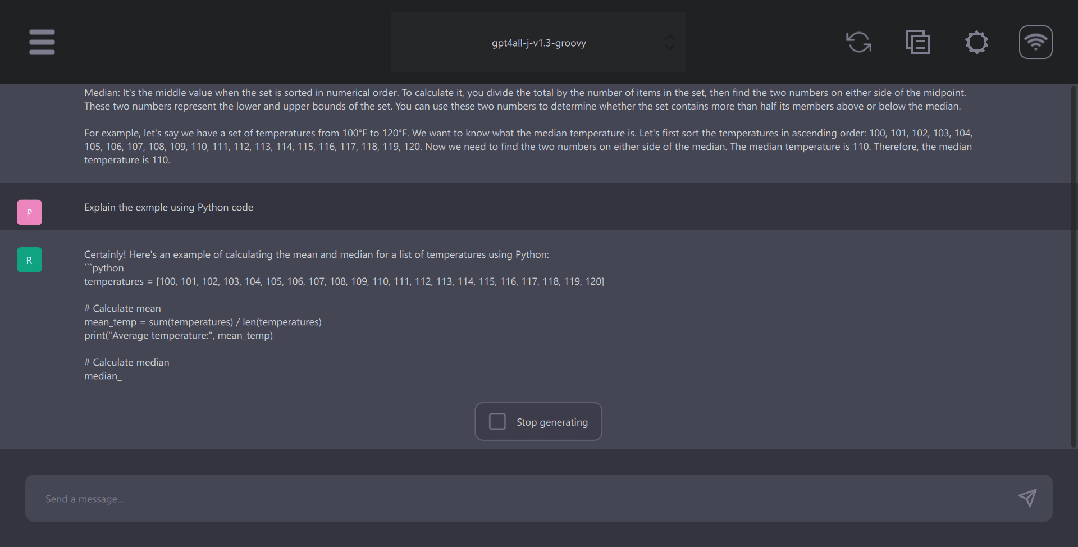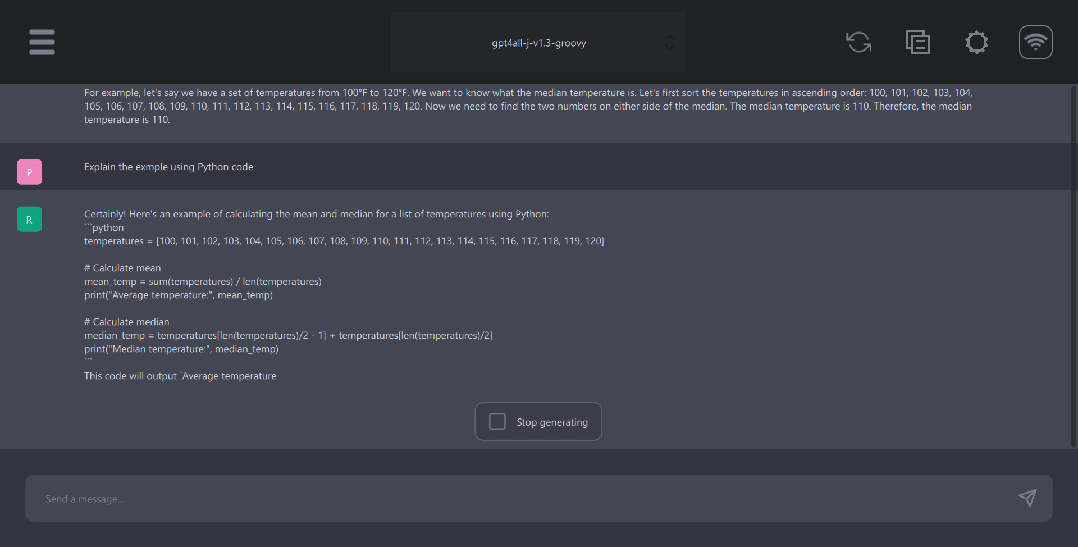
GPT4ALL Python client
GPT4ALL has Python, TypeScript, Web Chat interface, and Langchain backends.
In this section, we will look at the Python API for accessing models using nomic-ai/pygpt4all.
- Use PIP to install the Python GPT4ALL library.
<code>pip install pygpt4all</code>
- Download the GPT4All model from http://gpt4all.io/models/ggml-gpt4all-l13b-snoozy.bin, also available here (https://github.com/ nomic-ai/gpt4all-chat#manual-download-of-models) to browse other models.
- Create a text callback function, load the model, and provide a hint to the mode.generate() function to generate text. Check out the library's documentation (https://nomic-ai.github.io/pygpt4all/) to learn more.
<code>from pygpt4all.models.gpt4all import GPT4Alldef new_text_callback(text):print(text, end="")model = GPT4All("./models/ggml-gpt4all-l13b-snoozy.bin")model.generate("Once upon a time, ", n_predict=55, new_text_callback=new_text_callback)</code>Additionally, converters can be used to download and run inference. Just provide the model name and version. The examples in this article are accessing the latest and improved v1.3-groovy model.
<code>from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLMmodel = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("nomic-ai/gpt4all-j", revisinotallow="v1.3-groovy")</code>Getting Started
In the nomic-ai/gpt4all repository, you can obtain source code, model weights, datasets, and documentation for training and inference. You can try out some models first and then integrate them using the Python client or LangChain.
GPT4ALL provides us with a CPU-quantified GPT4All model checkpoint. To access it we must:
- Download the gpt4all-lora-quantized.bin file from Direct Link or [Torrent-Magnet].
- Clone this resource library and move the downloaded bin file to the chat folder.
- Run the appropriate command to access the model:
- M1 Mac/OSX: cd chat;./gpt4all-lora-quantized-OSX-m1
Linux :cd chat;./gpt4all-lora-quantized-linux-x86
- Windows (PowerShell): cd chat;./gpt4all-lora-quantized-win64.exe
- Intel Mac/OSX: cd chat;./gpt4all-lora-quantized-OSX-intel
资源:
- 技术报告:GPT4All-J: An Apache-2 Licensed Assistant-Style Chatbot(https://static.nomic.ai/gpt4all/2023_GPT4All-J_Technical_Report_2.pdf)
- GitHub:nomic-ai/gpt4all(https://github.com/nomic-ai/gpt4all)
- Python API:nomic-ai/pygpt4all(https://github.com/nomic-ai/pygpt4all)
- 模型:nomic-ai/gpt4all-j(https://huggingface.co/nomic-ai/gpt4all-j)
- 数据集:nomic-ai/gpt4all-j-prompt-generations(https://huggingface.co/datasets/nomic-ai/gpt4all-j-prompt-generations)
- Hugging Face演示:Gpt4all(https://huggingface.co/spaces/Monster/GPT4ALL)
- ChatUI:nomic-ai/gpt4all-chat: gpt4all-j chat(https://github.com/nomic-ai/gpt4all-chat)
- GPT4ALL后端:GPT4ALL - ????LangChain 0.0.154(https://python.langchain.com/en/latest/modules/models/llms/integrations/gpt4all.html)
The above is the detailed content of GPT4ALL: The ultimate open source large language model solution. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
 AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI is indeed changing mathematics. Recently, Tao Zhexuan, who has been paying close attention to this issue, forwarded the latest issue of "Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society" (Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society). Focusing on the topic "Will machines change mathematics?", many mathematicians expressed their opinions. The whole process was full of sparks, hardcore and exciting. The author has a strong lineup, including Fields Medal winner Akshay Venkatesh, Chinese mathematician Zheng Lejun, NYU computer scientist Ernest Davis and many other well-known scholars in the industry. The world of AI has changed dramatically. You know, many of these articles were submitted a year ago.
 Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
The performance of JAX, promoted by Google, has surpassed that of Pytorch and TensorFlow in recent benchmark tests, ranking first in 7 indicators. And the test was not done on the TPU with the best JAX performance. Although among developers, Pytorch is still more popular than Tensorflow. But in the future, perhaps more large models will be trained and run based on the JAX platform. Models Recently, the Keras team benchmarked three backends (TensorFlow, JAX, PyTorch) with the native PyTorch implementation and Keras2 with TensorFlow. First, they select a set of mainstream
 Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Boston Dynamics Atlas officially enters the era of electric robots! Yesterday, the hydraulic Atlas just "tearfully" withdrew from the stage of history. Today, Boston Dynamics announced that the electric Atlas is on the job. It seems that in the field of commercial humanoid robots, Boston Dynamics is determined to compete with Tesla. After the new video was released, it had already been viewed by more than one million people in just ten hours. The old people leave and new roles appear. This is a historical necessity. There is no doubt that this year is the explosive year of humanoid robots. Netizens commented: The advancement of robots has made this year's opening ceremony look like a human, and the degree of freedom is far greater than that of humans. But is this really not a horror movie? At the beginning of the video, Atlas is lying calmly on the ground, seemingly on his back. What follows is jaw-dropping
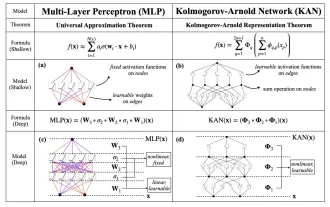 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
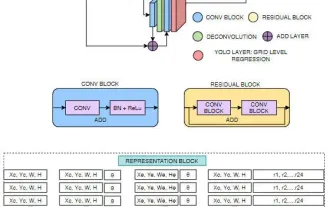 FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
Target detection is a relatively mature problem in autonomous driving systems, among which pedestrian detection is one of the earliest algorithms to be deployed. Very comprehensive research has been carried out in most papers. However, distance perception using fisheye cameras for surround view is relatively less studied. Due to large radial distortion, standard bounding box representation is difficult to implement in fisheye cameras. To alleviate the above description, we explore extended bounding box, ellipse, and general polygon designs into polar/angular representations and define an instance segmentation mIOU metric to analyze these representations. The proposed model fisheyeDetNet with polygonal shape outperforms other models and simultaneously achieves 49.5% mAP on the Valeo fisheye camera dataset for autonomous driving
 The latest from Oxford University! Mickey: 2D image matching in 3D SOTA! (CVPR\'24)
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:20 PM
The latest from Oxford University! Mickey: 2D image matching in 3D SOTA! (CVPR\'24)
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:20 PM
Project link written in front: https://nianticlabs.github.io/mickey/ Given two pictures, the camera pose between them can be estimated by establishing the correspondence between the pictures. Typically, these correspondences are 2D to 2D, and our estimated poses are scale-indeterminate. Some applications, such as instant augmented reality anytime, anywhere, require pose estimation of scale metrics, so they rely on external depth estimators to recover scale. This paper proposes MicKey, a keypoint matching process capable of predicting metric correspondences in 3D camera space. By learning 3D coordinate matching across images, we are able to infer metric relative




