How to use the np.random.permutation function in python
1: Function introduction
np.random.permutation() Generally speaking, it is a random permutation function, which is to The input data is randomly arranged. The official document states that this function can only randomly arrange one-dimensional data, and for multi-dimensional data, it can only randomly arrange the data in the first dimension.
In short: the function of np.random.permutation function is to generate a scrambled random list according to the given list
When processing the data When setting up a data set, you can usually use this function to shuffle the internal order of the data set and shuffle the label sequence in the same order.
2: Example
2.1 Directly process array or list numbers
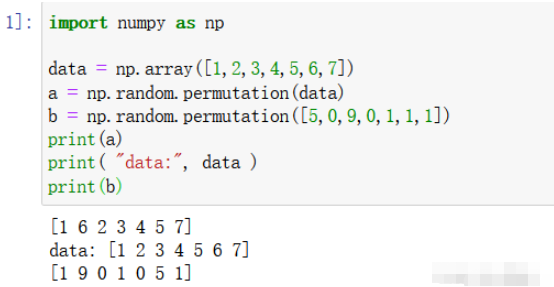
import numpy as np data = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7]) a = np.random.permutation(data) b = np.random.permutation([5,0,9,0,1,1,1]) print(a) print( "data:", data ) print(b)
2.2 Indirect processing: do not change the original data (for arrays Index processing)
label = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
a = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(label)))
print("Label[a] :" ,label[a] )
##Supplement: Generally it can only be used for N-dimensional arrays and can only convert integer scalar arrays to scalar indexes
why?label1[a1] label1 is a list, a1 is a random arrangement of list subscripts but! The list structure does not have a scalar index label1[a1] error
label1=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
print(len(label1))
a1 = np.random.permutation(np.arange(len(label1)))#有结果
print(a1)
print("Label1[a1] :" ,label1[a1] )#这列表结构没有标量索引 所以会报错
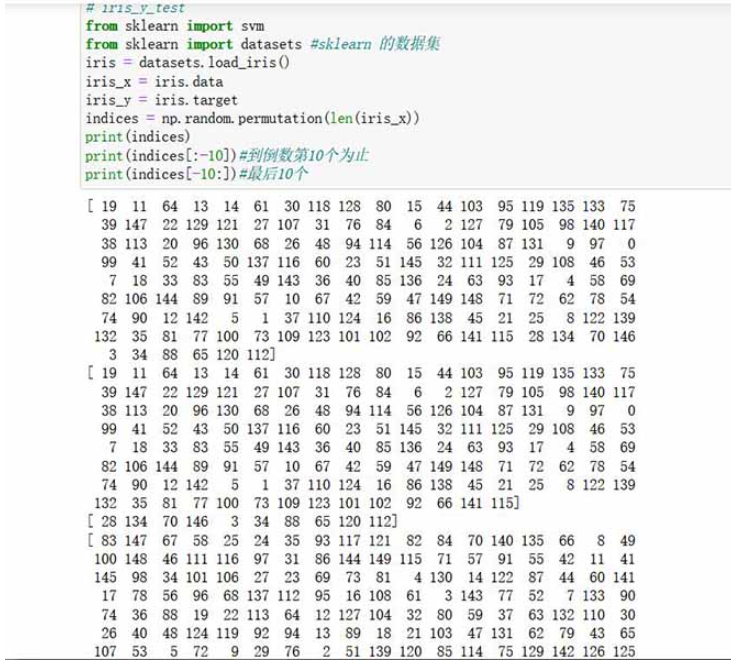
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets #sklearn 的数据集
iris = datasets.load_iris()
iris_x = iris.data
iris_y = iris.target
indices = np.random.permutation(len(iris_x))
#此时 打乱的是数组的下标的排序
print(indices)
print(indices[:-10])#到倒数第10个为止
print(indices[-10:])#最后10个
# print(type(iris_x)) <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
#9:1分类
#iris_x_train = iris_x[indices[:-10]]#使用的数组打乱后的下标
#iris_y_train = iris_y[indices[:-10]]
#iris_x_test= iris_x[indices[-10:]]
#iris_y_test= iris_y[indices[-10:]]
Copy after loginThe array subscript is the redistribution of scalar index: The subscript starts from 0
from sklearn import svm from sklearn import datasets #sklearn 的数据集 iris = datasets.load_iris() iris_x = iris.data iris_y = iris.target indices = np.random.permutation(len(iris_x)) #此时 打乱的是数组的下标的排序 print(indices) print(indices[:-10])#到倒数第10个为止 print(indices[-10:])#最后10个 # print(type(iris_x)) <class 'numpy.ndarray'> #9:1分类 #iris_x_train = iris_x[indices[:-10]]#使用的数组打乱后的下标 #iris_y_train = iris_y[indices[:-10]] #iris_x_test= iris_x[indices[-10:]] #iris_y_test= iris_y[indices[-10:]]
The above is the detailed content of How to use the np.random.permutation function in python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.




