How nginx realizes dynamic and static separation of tomcat
1. Why should dynamic and static separation be achieved
1) nginx has a strong ability to process static resources
Mainly nginx processes static pages The efficiency is much higher than tomcat's processing capacity. If tomcat's request volume is 1000 times, then nginx's request volume is 6000 times. Tomcat's throughput per second is 0.6m, and nginx's throughput per second is 3.6m. It can be said that , nginx's ability to process static resources is 6 times that of tomcat, and the advantages are obvious.
2) Dynamic resources and static resources are separated to make the server structure clearer.
2. Principle of dynamic and static separation
Among the requests received by the server from the client, some are requests for static resources, such as html, css, js and Picture resources, etc., some of which are dynamic data requests. Because tomcat processes static resources relatively slowly, we can consider separating all static resources and handing them over to a server that processes static resources faster, such as nginx, and handing over dynamic requests to tomcat.
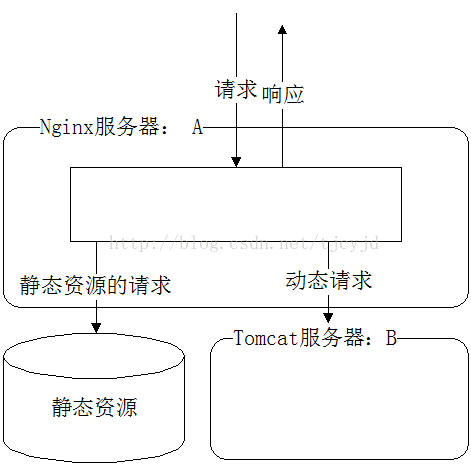
As shown in the figure below, we installed nginx and tomcat at the same time on the machine, placed all static resources under the webroot directory of nginx, and placed all dynamically requested programs in tomcat's webroot Under the directory, when the client accesses the server, if it is a request for static resources, it will go directly to nginx's webroot directory to obtain the resources. If it is a request for dynamic resources, nginx will use the principle of reverse proxy to forward the request to tomcat. Processing, thus realizing the separation of dynamic and static, and improving the performance of the server in processing requests.
3. Detailed configuration of dynamic and static separation
1) First, familiarize yourself with nginx’s important configuration file nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log logs/error.log;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#日志格式定义
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user[$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent"$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip压缩功能设置
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
gzip_http_version 1.0;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_types text/plain application/x-javascripttext/css application/xml;
gzip_vary on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.test.com;
location / {
#jsp网站程序根目录,一般nginx与tomcat在同一个目录
root /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/root;
index index.html index.jsp index.html;
}
location ~ .*.jsp$ {
index index.jsp;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080; #来自jsp请求交给tomcat处理
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header host $host; #后端的web服务器可以通过x-forwarded-for获取用户真实ip
proxy_set_header x-real-ip $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header x-forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
client_max_body_size 10m; #允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数
client_body_buffer_size 128k; #缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数
proxy_connect_timeout 90; #nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
proxy_read_timeout 90; #连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时)
proxy_buffer_size 4k; #设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
proxy_buffers 6 32k; #proxy_buffers缓冲区,网页平均在32k以下的话,这样设置
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;#高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2)
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; #设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream服务器传
}
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|png|bmp|swf)$ #由nginx处理静态页面
{
expires 30d; #使用expires缓存模块,缓存到客户端30天
}
location ~ .*\.( jsp|js|css)?$
{
expires 1d;
}
error_page 404 /404.html; #错误页面
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}2) Configure dynamic and static separation
#配置nginx动静分离,定义的静态页面直接从nginx发布目录读取。
location ~ .*\.(html|htm|gif|jpg|jpeg|bmp|png|ico|txt|js|css)$ {
root /webapps/myproject/code/static-resource;
#expires定义用户浏览器缓存的时间为7天,如果静态页面不常更新,可以设置更长,这样可以节省带宽和缓解服务器的压力
expires 1d;
}
location ~ ^/(web-inf)/ {#这个很重要,不然用户就可以访问了
deny all;
}It should be noted here that the storage path of external static files should be consistent with the path in the request to avoid nginx splicing paths. Finally, the file cannot be found because the path does not exist. If js, css, etc. are not loaded, you can check the errorlog of nginx for debugging and correction. The log is located in the logs directory under the nginx directory. An error log is intercepted as follows:
Copy code The code is as follows:
[error] 7195#0: *1693 open() "/home/cms/include/dedeajax2.js" failed (2: no such file or directory), client: 101.226.35.225, server: localhost, request: "get /cms/include/dedeajax2.js http/1.1"
You can see that the get request is "/cms/include/dedeajax2.js", then nginx will Under /home in the configuration, look for the file with this path. The full path is:
/home/cms/include/dedeajax2.js
If the error is reported as no such file or directory, you can check the file path problem in the corresponding /home directory.
After the configuration is successful, you can find that the static files are processed through nginx, and the requests for static files no longer enter the tomcat server. Therefore, when packaging, the directories of static files such as js, css, etc. are no longer opened. Enter the war package.
The above is the detailed content of How nginx realizes dynamic and static separation of tomcat. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
To get Nginx to run Apache, you need to: 1. Install Nginx and Apache; 2. Configure the Nginx agent; 3. Start Nginx and Apache; 4. Test the configuration to ensure that you can see Apache content after accessing the domain name. In addition, you need to pay attention to other matters such as port number matching, virtual host configuration, and SSL/TLS settings.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".




