
java.lang.NullPointerException is one of the most common exceptions in java programming. Anyone who uses java has seen java.lang.NullPointerException exception in java programs as well as java web applications.
NullPointerException is a runtime exception, so there is no need to catch it in the program.
When trying to perform certain operations on a null object, a NullPointerException exception is thrown in the application. Following are some common reasons why NullPointerException exception occurs in java program-
A method is called on an object instance, but at runtime the object is null.
Access variables of an object instance that are null at runtime.
Throws null in the program.
The array accessing the index or modifying the index is null.
Check the length of an array that is null at runtime.
This article mainly introduces several reasons and solutions for the occurrence of java.lang.NullPointerException. This article introduces you to it in great detail and has certain reference for your study or work. Value, friends in need can refer to it
In Java programming, NullPointerException is a common runtime exception. The reasons for its occurrence may include:
Methods to avoid NullPointerException exceptions in Java programming include:
1. Initialize string variables.
2. Use a specific class to initialize the interface type object.
3. Perform null judgment processing when the object is empty.
4. Avoid using null values for string comparisons.
5. Use the String.valueOf() method instead of the toString() method to avoid throwing a NullPointerException when the reference is null.
6. Instantiate the class type object before calling.
7. The return value can be defined as an array to avoid NullPointerException caused by returning null value.
In order to ensure the robustness and stability of the program, we should try our best to avoid the above situations during programming. In order to ensure the correctness and stability of the code, we should use null operations or follow safe programming habits when dealing with unavoidable situations.
NullPointerException is a runtime exception in Java, which usually occurs when trying to access a null reference (that is, a variable that has not allocated memory space). If you try to operate on a null object, the program will throw a NullPointerException exception.
In order to avoid the occurrence of this exception, we can perform a null value check (i.e., null judgment) before using it, or allocate memory space to the variable and assign it an initial value.
For example, when judging whether a String type instance s is equal to "a", it should be written as "a".equals(s) instead of s.equals("a"), because the former can prevent s from being Null situation, thus avoiding the occurrence of NullPointerException.
In order to avoid returning null values, the return value of the method can be defined as an array type. If you need to return a null value, you can return an empty array.
To sum up, the key to avoid NullPointerException is to fully detect and initialize variables, try to avoid using null values, and adopt safe programming habits to avoid this exception.
The sample code is as follows
public class Temp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Temp t = initT();
t.foo("Hi");
}
private static Temp initT() {
return null;
}
public void foo(String s) {
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());
}
}When the above program is run, it will throw NullPointerExceptionException error information.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at Temp.main(Temp.java:7)
In statementt. A NullPointerException exception is thrown in foo("Hi"); because t is null here.
Sample code-
public class Temp {
public int x = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Temp t = initT();
int i = t.x;
}
private static Temp initT() {
return null;
}
}Execute the above sample code and get the following results-
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at Temp.main(Temp.java:9)
Thrown in statement int i = t.x NullPointerExceptionException; Because t is null here.
Sample code-
public class Temp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
foo(null);
}
public static void foo(String s) {
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());
}
}This is one of the most common cases of java.lang.NullPointerException One, because it passes null parameters to the caller.
Sample code
public class Temp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
throw null;
}
}The following is the exception stack trace of the above program, due to throw nullSo throw NullPointerException exception.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at Temp.main(Temp.java:5)
public class Temp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = null;
int len = data.length;
}
}执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at Temp.main(Temp.java:7)
示例代码 -
public class Temp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = null;
int len = data[2];
}
}执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 -
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at Temp.main(Temp.java:7)
public class Temp {
public static String mutex = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
synchronized(mutex) {
System.out.println("synchronized block");
}
}
}synchronized(mutex)将抛出NullPointerException,因为mutex对象为null。
8. java.lang.NullPointerException引发HTTP状态500
有时会将错误页面作为java Web应用程序响应发送,错误消息为“HTTP状态500 - 内部服务器错误”,根本原因就是java.lang.NullPointerException异常。
下面是一段编辑了Spring MVC Example项目并更改了HomeController方法,如下所示。
@RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String user(@Validated User user, Model model) {
System.out.println("User Page Requested");
System.out.println("User Name: "+user.getUserName().toLowerCase());
System.out.println("User ID: "+user.getUserId().toLowerCase());
model.addAttribute("userName", user.getUserName());
return "user";
}下图显示了Web应用程序响应引发的错误消息。
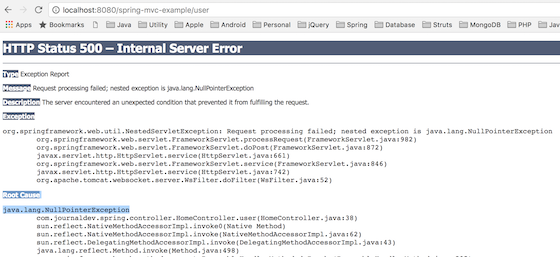
异常堆栈跟踪
HTTP Status 500 – Internal Server Error
Type Exception Report
Message Request processing failed; nested exception is java.lang.NullPointerException
Description The server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request.
Exception
org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletException: Request processing failed; nested exception is java.lang.NullPointerException
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.processRequest(FrameworkServlet.java:982)
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doPost(FrameworkServlet.java:872)
javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:661)
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.service(FrameworkServlet.java:846)
javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:742)
org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter.doFilter(WsFilter.java:52)
Root Cause
java.lang.NullPointerException
com.journaldev.spring.controller.HomeController.user(HomeController.java:38)
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)根本原因是语句user.getUserId().toLowerCase()中引发了NullPointerException,因为user.getUserId()返回null。
检测NullPointerException非常简单,只需查看异常跟踪,它将显示异常的类名和行号。然后查看代码并查看可能为null。只要看一下上面的所有例子,从堆栈跟踪中可以清楚地看出是什么导致了null指针异常。
如何修复java.lang.NullPointerException异常
java.lang.NullPointerException是一个未经检查的异常,因此不必捕获它。通常可以使用空检查和预防性编码技术来防止空指针异常。请看下面的代码示例,演示如何避免java.lang.NullPointerException异常。
示例1
if(mutex ==null) mutex =""; //preventive coding
synchronized(mutex) {
System.out.println("synchronized block");
}示例2
//using null checks
if(user!=null && user.getUserName() !=null) {
System.out.println("User Name: "+user.getUserName().toLowerCase());
}
if(user!=null && user.getUserName() !=null) {
System.out.println("User ID: "+user.getUserId().toLowerCase());
}1 . 考虑下面的代码示例。
public void foo(String s) {
if(s.equals("Test")) {
System.out.println("test");
}
}2 . 现在,如果将null作为s参数的值传递,则会发生NullPointerException异常。可以如下编写相同的方法以避免NullPointerException。
public void foo(String s) {
if ("Test".equals(s)) {
System.out.println("test");
}
}3 . 需要为参数添加null检查,并在需要时抛出IllegalArgumentException异常。
public int getArrayLength(Object[] array) {
if(array == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("array is null");
return array.length;
}4 . 使用三元运算符,如下面的示例代码所示。
String msg = (str == null) ? "" : str.substring(0, str.length()-1);
5 . 使用String.valueOf()而不是toString()方法。例如,检查PrintStream println()方法代码定义如下。
public void println(Object x) {
String s = String.valueOf(x);
synchronized (this) {
print(s);
newLine();
}
}6 . 下面显示了使用valueOf()方法而非toString()的示例。
Object mutex = null;//prints nullSystem.out.println(String.valueOf(mutex));//will throw java.lang.NullPointerExceptionSystem.out.println(mutex.toString());
7 . 写入方法尽可能返回空对象而不是null,例如空列表,空字符串等。
8 . 应该使用在集合类中定义了一些用来避免NullPointerException的方法。例如
contains(),containsKey()和containsValue()。
这是关于java中的NullPointerException异常的所有情况。希望它能帮助您编写更好的代码,以尽可能避免java.lang.NullPointerException异常。
The above is the detailed content of What is the cause and solution of java.lang.NullPointerException exception. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




