
This is similar to the SPI function in Java. When SpringBoot starts, it will read the META-INF/spring.factories files under all jar packages;
And map the implementation classes corresponding to the interfaces/abstract classes in the file, and instantiate the corresponding implementation classes when needed
Let’s analyze the source code and take a lookspring.factoriesUsage scenarios
Start SpringApplication and look at the construction method
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}The method getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class) is used to obtain the specified class instance in Spring; and when obtaining it, the corresponding instance class is instantiated based on the content in the file path META-INF/spring.factories read in the entire project. ;
For example, the ApplicationContextInitializer here is an interface, so which of its implementation classes should be instantiated? Then look for the META-INF/spring.factories file; then we found this file in the spring-boot:2.1.0jar package
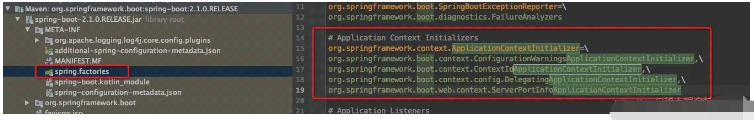
Read that the implementation class that needs to be instantiated is
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
and also found this file in spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.0.RELEASE.jar
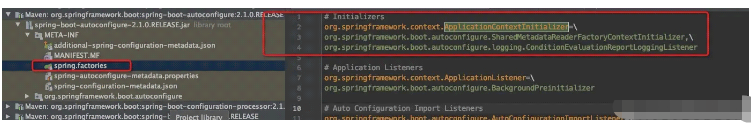
Then the two implementation classes in the file will also be instantiated; plus the above 4, there are 6 in total
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
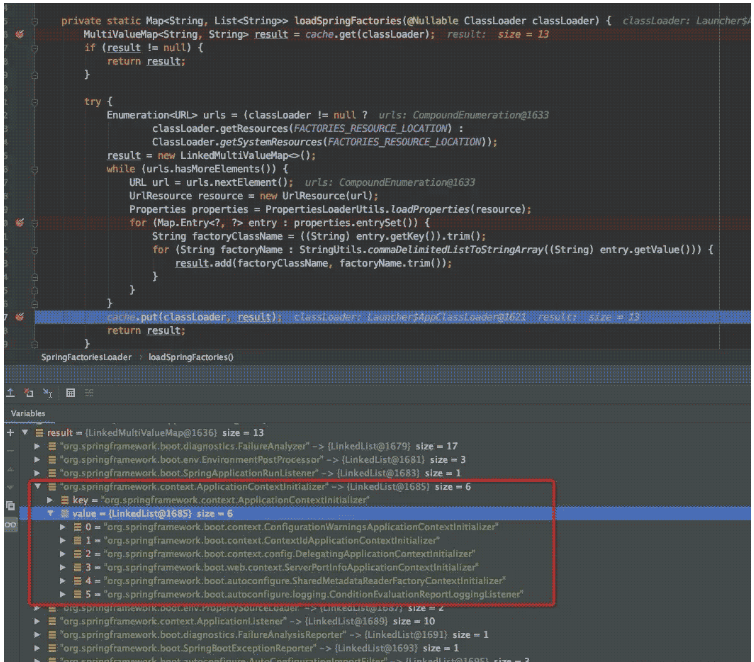
You can see that not only the instance classes of org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer are parsed; but all of them are parsed and saved. Other classes will need it next time When instantiated, it can be taken directly from the memory;
After the above process obtains the instance class, the next step is the instantiation process
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}MethodcreateSpringFactoriesInstancesIt is the process of creating an instance; you can see that the corresponding interface class is passed inorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer ;Then the corresponding implementation class will be instantiated;
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args,
Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass
.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}If there is nothing special to explain about the instantiation process;
There is a method above AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);is used to sort all instances; the implementation class needs to implement Interface Ordered; The smaller the value returned by getOrder, the higher the priority
After knowing the usage of spring.factories, then we You can use this feature to achieve your own purposes;
For example, we can also write an implementation class of the interface classApplicationContextInitializer.
The above is the detailed content of SpringBoot spring.factories loading timing source code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




