How to use recursion to implement a tree structure tool class in Java
Requirement Description
Sometimes, our data is hierarchical. For example, the common three-level linkage between provinces and municipalities is one layer inside another, as shown below:
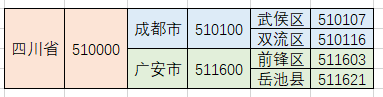
When we store data in the database, it is often in list form, as shown below:
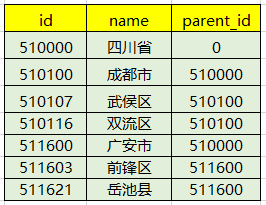
Then when we query it from the database, When returning to the front end, when the front end needs to give a tree level, it may need to be recursively processed into a tree structure, so the following tool may be useful.
Usage example
We define a Place object as above and add tool annotations:
@TreeKey unique identifier
@TreeParentKey identifies the parent node identification
@TreeChildren identifies the collection of descendant nodes
@Data
@Data
public class Place {
@TreeKey
private String id;
@TreeParentKey
private String parentId;
private String name;
@TreeChildren
private List<Place> children;
public Place(String id, String name, String parentId) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.parentId = parentId;
}
}Test:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Place> places = new ArrayList<>();
places.add(new Place("510000", "四川省", "0"));
places.add(new Place("510100", "成都市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("510107", "武侯区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("510116", "双流区", "510100"));
places.add(new Place("511600", "广安市", "510000"));
places.add(new Place("511603", "前锋区", "511600"));
places.add(new Place("511621", "岳池县", "511600"));
List<Place> treeList = TreeUtils.getTree(places, "0");
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(treeList));
}
}Final effect:

Tool code
@TreeKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeKey {
}@TreeParentKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeParentKey {
}@TreeChildren
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TreeChildren {
}@TreeUtils
package com.csd.utils.tree;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 递归求树形工具类
*
* @author Yuanqiang.Zhang
* @since 2023/3/8
*/
public class TreeUtils {
/**
* 集合转化为树形
*
* @param list 集合
* @param highestParentKey 最高层父节点值
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 树形
*/
public static <T> List<T> getTree(List<T> list, Object highestParentKey) {
if (Objects.isNull(list) || list.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Field key = null;
Field parentKey = null;
Field children = null;
Field[] fields = list.get(0).getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (Objects.isNull(key)) {
TreeKey treeKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeKey)) {
key = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(parentKey)) {
TreeParentKey treeParentKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeParentKey.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeParentKey)) {
parentKey = field;
continue;
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(children)) {
TreeChildren treeChildren = field.getAnnotation(TreeChildren.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(treeChildren)) {
children = field;
continue;
}
}
}
if (Objects.isNull(key) || Objects.isNull(parentKey) || Objects.isNull(children)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
key.setAccessible(true);
parentKey.setAccessible(true);
children.setAccessible(true);
// 获取最高层数据
List<T> highs = new ArrayList<>();
try {
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(pk).equals(getString(highestParentKey))) {
highs.add(t);
}
}
// 获取最高层子孙节点
for (T t : highs) {
setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children);
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return highs;
}
/**
* 获取子孙节点
*
* @param list 集合
* @param parent 父节点对象
* @param key 唯一属性
* @param parentKey 父唯一属性
* @param children 节点
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 带有子孙集合的父节点对象
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
private static <T> T setChildren(List<T> list, T parent, Field key, Field parentKey, Field children) throws IllegalAccessException {
Object k = key.get(parent);
List<T> tempList = new ArrayList<>();
for (T t : list) {
Object pk = parentKey.get(t);
if (getString(k).equals(getString(pk))) {
tempList.add(setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children));
}
}
children.set(parent, tempList);
return parent;
}
/**
* 获取字符串
*
* @param o 值
* @return 字符串
*/
private static String getString(Object o) {
return Objects.isNull(o) ? "" : o.toString();
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to use recursion to implement a tree structure tool class in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




