What is the role of string constant pool and buffer pool in JAVA

1 Constant pool
The constant pool is divided into two types, one is the static constant in the .class file Pool, the second is the runtime constant pool formed by the static constant pool in the .class file being loaded into the JVM.
1.1 Static constant pool
The constant pool in the .class file can be regarded as an array. Some constants are stored in the array. When needed in the bytecode instructions When this constant is used, it is accessed through the index of the array.
Look at the following code:
String m = "hellohellohellohellohello"; String n = "hellohellohellohellohello";
It will look like this in the bytecode:
// 常量池: #1 hellohellohellohellohello #2 ... ... ---------------------------- String m = #1; String n = #1;
Of course, this is just a simplified version, in fact More complicated (for the actual version, you can see the answer posted in the reference section at the end of the article. For now, you can only consider the simplified version)
Note that the string constant stored in this is just a simple UTF8 An encoded byte sequence, not a Java string object. It is the same as the string you store in a txt text. We use UTF8 format to open a .class file and you can see hellohellohellohellohello It can be parsed: 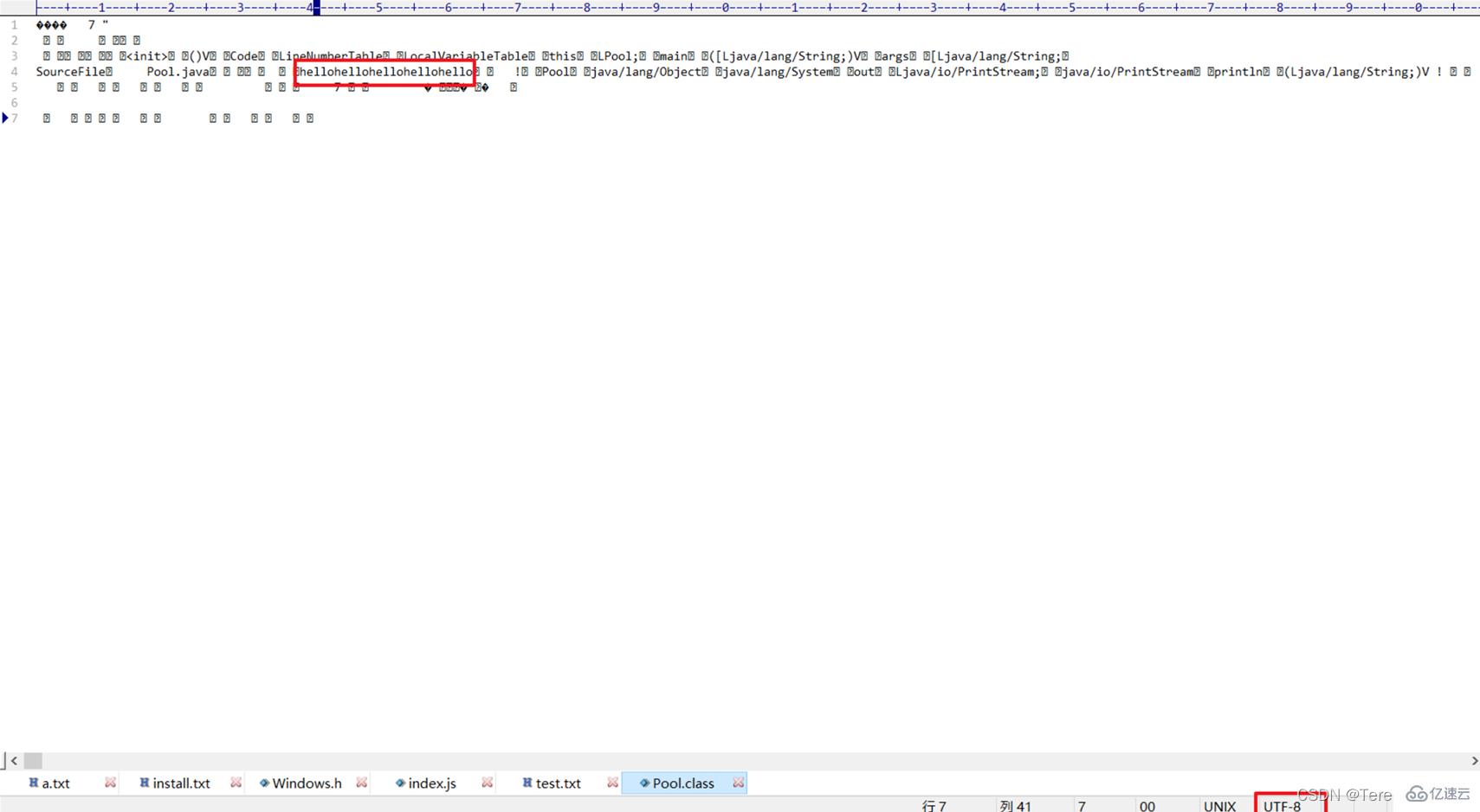
1.2 Runtime constant pool
After understanding the static constant pool, the runtime constant pool is easy to understand. . Simply put, the runtime constant pool is the runtime representation of the static constant pool in the .class file in the JVM. Each static constant pool in the .class file will generate a corresponding runtime constant pool. When the JVM interprets the instruction String m = #1, it can go to the runtime constant pool of this class to find the definition of #1.
2 String pool
The string pool is a cache pool set up by Java to reuse the String object. It was set in the method area before Java 1.7 and saved It is a String object; it is set on the heap after Java 1.7 and saves a reference to the String object. The String object itself exists elsewhere on the heap. The following takes the situation after Java 1.7 as the standard.
Continue with the above example. When the JVM is interpreting String m = #1, it has obtained the corresponding UTF8 sequence from the runtime constant pool. Next, it will look for the String object corresponding to this UTF8 sequence in the string pool, and add the object's The reference is assigned to m. You may be curious about the timing when this String is created. According to this R article, when the class where this statement is located is loaded, if the corresponding object already exists in the string pool, then nothing will be done. If If it does not exist, a corresponding String object will be created and its reference will be placed in the pool.
In addition to the string pool, Wrapper types such as Integer and Long also have their own cache pools. For example, Integer will cache from -128~127 The Integer object, when using literal assignment or Integer.valueOf(), if the corresponding object exists in the pool, the object in the pool will be returned. Only when there is no such object in the pool Only then will new objects be created on the heap.
However, unlike the string pool, these Wrapper pools will not grow like the string pool, that is, the number of objects in the pool is fixed, and there will only be -128~127 in the Integer pool. .
The buffer pool corresponding to the basic type is as follows:
boolean values true and false all byte values short values between -128 and 127 int values between -128 and 127 char in the range \u0000 to \u007F
Among all the numerical buffer pools in jdk 1.8, the Integer buffer pool IntegerCache is very special. The lower bound of this buffer pool is - 128, upper The default limit is 127, but this upper limit is adjustable. When starting the jvm, specify the size of this buffer pool through -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=. This option will set a file named java.lang when the JVM is initialized. .IntegerCache.high system property, and then when IntegerCache is initialized, it will read the system property to determine the upper bound.
The above is the detailed content of What is the role of string constant pool and buffer pool in JAVA. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo




