
1. Spring's transaction mechanism
All data access technologies have transaction processing mechanisms. These technologies provide APIs to start transactions and submit transactions to complete data operations, or Roll back data when an error occurs.
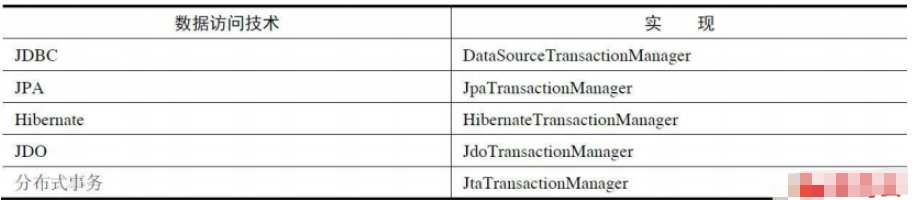
Spring’s transaction mechanism uses a unified mechanism to handle transactions with different data access technologies. Spring's transaction mechanism provides a PlatformTransactionManager interface. Transactions with different data access technologies are implemented using different interfaces:
The code to define the transaction manager in the program is as follows:
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource());
return transactionManager;
}2. Declarative transactions
Spring supports declarative transactions, that is, using annotations to select the methods that need to use transactions, it uses the @Transactional annotation to indicate the method on the method Method requires transaction support.
@Transactional
public void saveSomething(Long id, String name) {
//数据库操作
}What needs special attention here is that this @Transactional annotation comes from the org.springframework.transaction.annotation package, not javax.transaction.
Spring provides an @EnableTransactionManagement annotation on the configuration class to enable declarative transaction support. After using @EnableTransactionManagement, the Spring container will automatically scan methods and classes annotated with @Transactional. The usage of @EnableTransactionManagement is as follows:
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class AppConfig {
}3. Use @Transactional at class level
@Transactional can be annotated not only on methods, but also on classes. When annotated on a class, it means that all public methods of this class are transaction enabled. If the @Transactional annotation is used at both the class level and the method level, the annotation used at the class level will override the method level annotation.
4. Transaction support of Spring Data JPA
Spring Data JPA enables transaction support for all default methods, and query-type transactions enable readOnly by default =true attribute.
As can be seen from the source code SimpleJpaRepository, SimpleJpaRepository defines @Transactional (readOnly=true) at the class level, and the @Transactional attribute is rewritten in operations related to save and delete. At this time, the readOnly attribute is false, readOnly remains false for the rest of the query operations.
5. Spring Boot’s transaction support
1. Automatically configured transaction manager
When using JDBC as the data access technology At that time, SpringBoot defined for us the Bean of PlatformTransactionManager that implements DataSourceTransactionManager; for configuration, see the definition in the org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration class:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(this.dataSource);
}When using JPA as the data access technology, Spring Boot defines a Bean for us that implements PlatformTransactionManager and JpaTransactionManager; for configuration, see the definition in the org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaBaseConfiguration.class class:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
return new JpaTransactionManager();
}2. Automatically enable annotation transaction support
Spring Boot's class specifically used to configure transactions is: org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration. This configuration class depends on JpaBaseConfiguration and DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.
In the DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration configuration, support for declarative transactions is also enabled. The code is as follows:
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class)
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
protected static class TransactionManagementConfiguration {
}So in Spring Boot, there is no need to explicitly enable the @EnableTransactionManagement annotation. .
6. Example (Springboot)
1.pom.xml:
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>mysql</groupid> <artifactid>mysql-connector-java</artifactid> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
2.application.yml:
server: port: 5000 spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&characterSetResults=utf8 username: root password: password jpa: hibernate: ddl-auto: update # 第一次简表create 后面用update show-sql: true
3. Entity class Staff:
@Entity
public class Staff {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
public Staff() {
super();
}
public Staff(Long id, String name, Integer age, String address) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
//省略get、set方法
}4. Staff’s Repository:
public interface StaffRepository extends JpaRepository<staff> {
}</staff>5. Service interface:
public interface StaffService {
public Staff saveStaffWithRollBack(Staff staff);//回滚
public Staff saveStaffWithoutRollBack(Staff staff);//不回滚
}6. Service implementation:
@Service
public class StaffServiceImpl implements StaffService {
@Autowired
StaffRepository staffRepository; //可以直接注入我们的RersonRepository的Bean。
@Override
//使用@Transactional注解的rollbackFor属性,指定特定异常时,数据回滚。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = {IllegalArgumentException.class})
public Staff saveStaffWithRollBack(Staff staff) {
Staff s = staffRepository.save(staff);
if (staff.getName().equals("张三")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("张三已经存在了,rollback");
}
return s;
}
@Override
public Staff saveStaffWithoutRollBack(Staff staff) {
Staff s = staffRepository.save(staff);
if (staff.getName().equals("张三")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("张三已经存在了,数据不回滚");
}
return s;
}
}7.Controller:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/staff")
public class StaffController {
@Autowired
StaffService staffService;
//测试回滚情况
@RequestMapping("/rollback")
public Staff rollback(Staff staff) {
return staffService.saveStaffWithRollBack(staff);
}
//测试不回滚情况
@RequestMapping("/notrollback")
public Staff noRollBack(Staff staff) {
return staffService.saveStaffWithoutRollBack(staff);
}
}8. Run test:
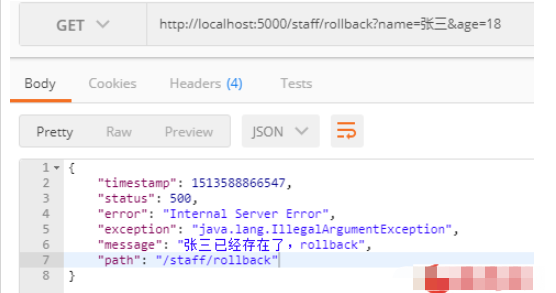
(1) Rollback: http://localhost:5000/staff/rollback?name=张三&age=18
Console:

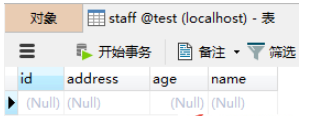
Database:
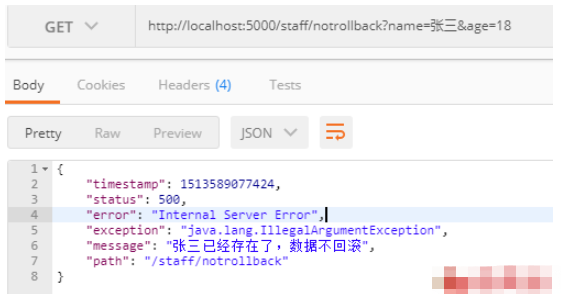
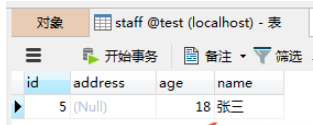
(2) No rollback: http://localhost:5000/staff/notrollback?name=张三&age=18

The above is the detailed content of What is the SpringBoot transaction processing mechanism?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 SpringBoot project building steps
SpringBoot project building steps
 What is the difference between j2ee and springboot
What is the difference between j2ee and springboot
 What are the e-commerce platforms?
What are the e-commerce platforms?
 Why does vue.js report an error?
Why does vue.js report an error?
 How to check website dead links
How to check website dead links
 Can windows.old be deleted?
Can windows.old be deleted?
 What does Metaverse Concept Stock mean?
What does Metaverse Concept Stock mean?
 What should I do if eDonkey Search cannot connect to the server?
What should I do if eDonkey Search cannot connect to the server?
 jquery validate
jquery validate




