How to learn more about ARP protocol
1. MAC definition
MAC is called the hardware address and is the unique identifier of the device in the network, totaling 48 bits. For example, my wireless MAC address is 8C-A9-82-96-F7-66
. The display form in the system is a combination of 6 numbers composed of hexadecimal. For example, the first digit of 8C is 8__c and the number of binary digits is 4X2=8 digits and 8X6=48 digits. Extension content:This address is globally unique. There are no duplicate MAC addresses. If duplicate MAC addresses appear in the switching network, there must be a loop. The loop phenomenon will cause the time connection to be blocked or not connected at all.
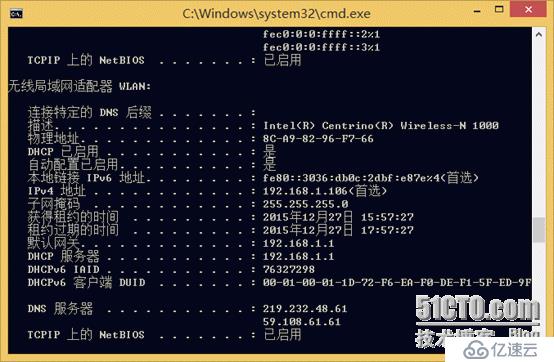
2. PC communication within LAN (IP and MAC)
There is a thing in the world called a computer, a computer There are LOL, CF, haha. The IT world is so great that you can play something called a game. The method of communication between PCs mainly depends on the presence of hardware and the use of MAC addresses and IP addresses.
Example: We have a switch and 2 PCs. How to let the two PCs communicate? It's very simple. The PC is equipped with two addresses of the same network segment.
lap0: 192.168.1.1/24 lap1: 192.168.1.2/24
1> Topology of two separate PCs To the same switch VLAN1
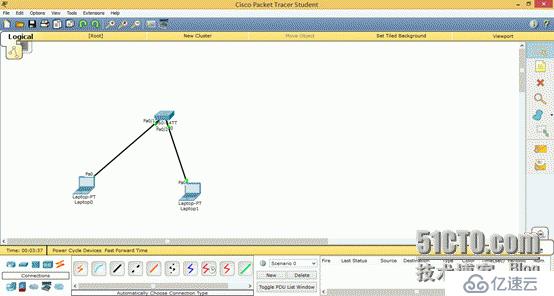
2>lap0 and lap1 ping each other
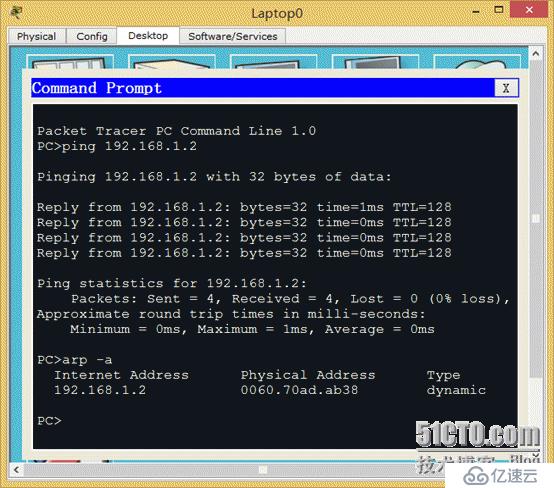
3>Why can lap0 communicate with lap1?
(1) The two laps are in the same network segment (2) In the same VLAN (3) The PC side resolves the relationship between IP and MAC through the ARP protocol. The MAC and IP mapping relationship of lap1 192.168.1.2 has been queried on lap0 through arp -a, so they can communicate with each other. Then on the contrary, lap1 will definitely be able to learn the MAC and IP address of lap0.
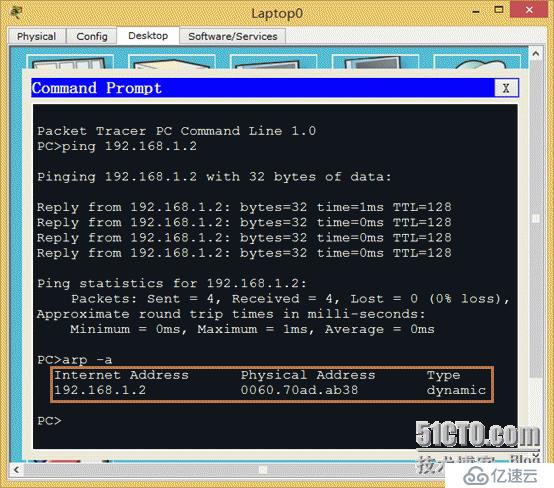
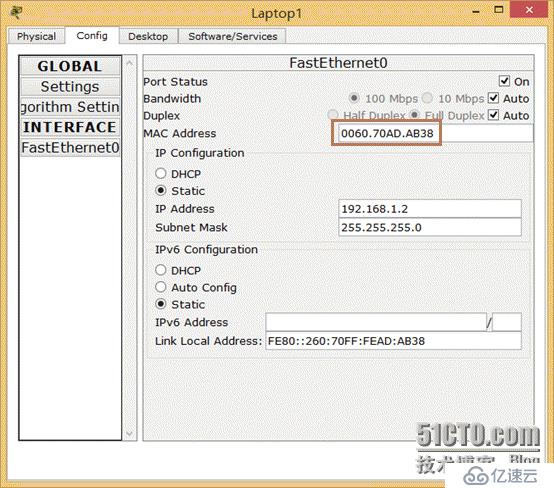
3. Introduction to ARP protocol
The above is quite lively, now let’s introduce it ARP, a common but very important protocol. The full English name of ARP is: Address resolution protocol. ARP provides dynamic mapping between IP and MAC, and the process is automatically completed. When the PC sends a communication request, according to the protocol, its destination address must be a 48-bit MAC address. MAC cannot communicate directly with IP. Then our ARP protocol is needed to do the corresponding conversion work. The following is taken from TCP/IP volume 1 for reference only
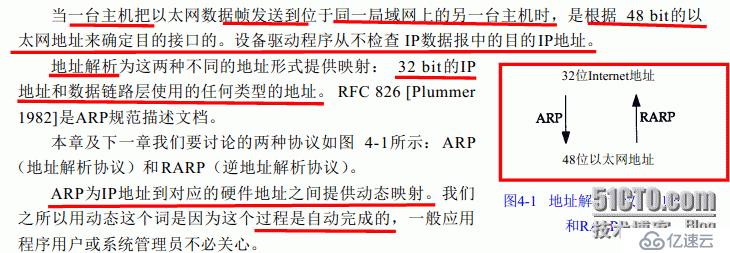
As above in the Ethernet environment:
1>lap0 To communicate with lap1, you need to convert the 32-bit IP address into a 48-bit MAC address.
2>The ARP protocol belongs to a broadcast network, and ARP will broadcast its own request information to the Ethernet network in the form of a broadcast.
3>After lap1 receives the broadcast request, it replies with lap0’s own IP and MAC address. Both parties have established a corresponding relationship
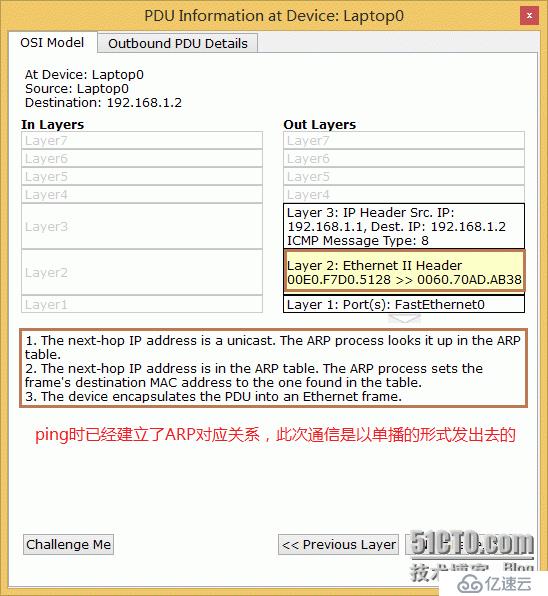
4. Switch MAC correspondence
Communication between PCs needs to be through a layer 2 switch. Implemented, except using the ARP protocol. In addition, each switch port itself has a MAC address. When lap0 goes to ping lap1, after lap0's request frame reaches the switch, it will record it, record the MAC address, and then forward the request to lap1. Such a round-trip request establishes the MAC correspondence table relationship. Layer 2 switches only record the corresponding relationship between MAC and ports. Generally, layer 2 switches only perform high-speed switching. Of course, if there are special needs, they can also perform a series of restriction and binding operations based on MAC.
Corresponding relationship between MAC and port:
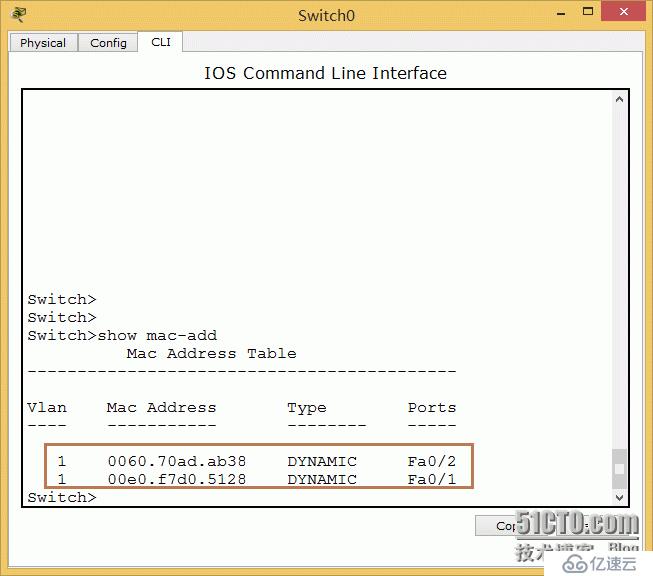
5. MAC and ARP information under the gateway
1> The access switch is connected to a core and added to the gateway |192.168.1.254/24.
2> Let’s analyze it first:
1. First, the switches are interconnected, and the ports learn each other’s port addresses
2. The lap0 and lap1 ping request packets arrive at the gateway, and the core switch establishes a MAC address table (dynamic)
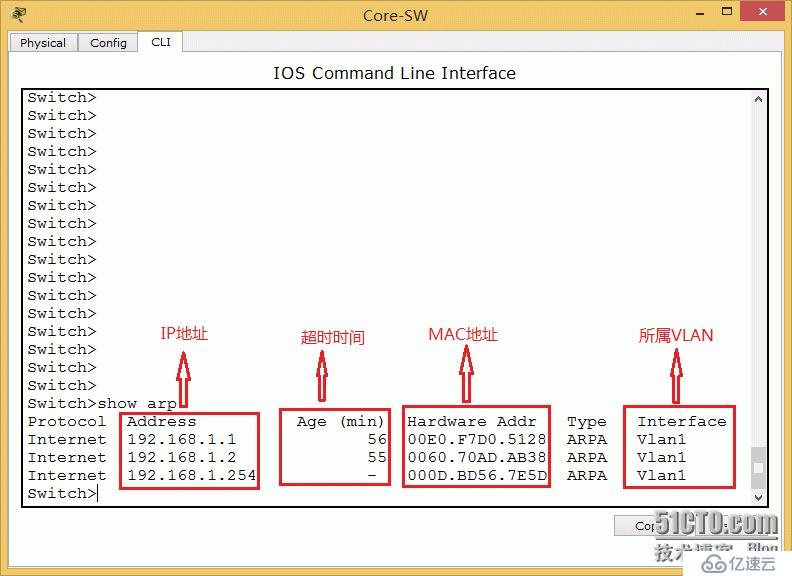
3. At the same time, an ARP entry is established because the gateway is between different network segments. Communication interface
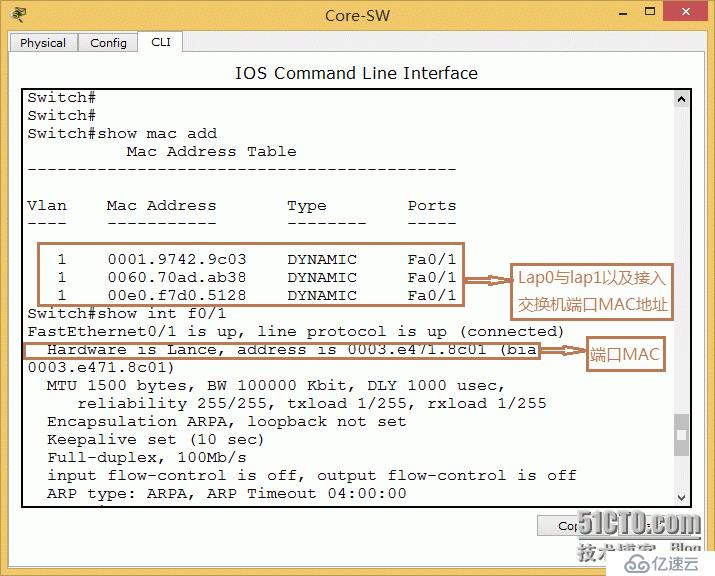
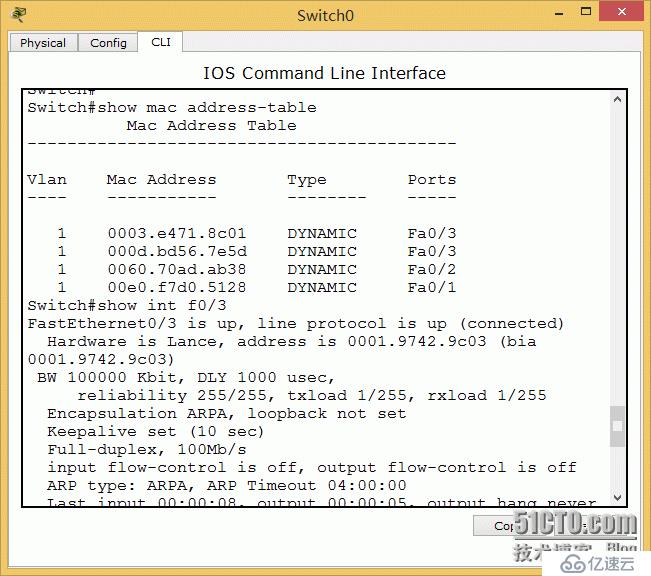
4. Check the MAC address table of the core and core switches.
In core learning, the MAC addresses of lap0 and lap1, as well as the MAC address of the interconnection port of the access switch are learned. Access switch MAC address table: MAC learns the MAC of two PCs, and at the same time, it also learns the onboard MAC address of the core switch and the interconnection port address table. As shown below:
Core switch show mad add
6. Handling ARP spoofing problem in practice
If the Ethernet uses DHCP to automatically obtain an IP address, then enabling dhcp snooping will When it comes to monitoring security, there won't be too many problems. If you use a static IP, troublesome problems such as ARP *** and ARP spoofing may easily occur. Once you understand how it works, solving this type of problem becomes especially easy. The situation I encountered is relatively simple. The server under a certain network segment is sometimes unreachable. After communication, possible network structure problems were ruled out, and it was confirmed that the service single network card was not bound to the network card, and the core implemented HSRP to access dual uplink redundancy. First, eliminate the loop, check that the core spanning tree status is normal, the switch CPU usage is normal, and there are no broadcast packets on the interconnection port of the access switch where the server is located, and there are no sudden large traffic packets, and the loop is eliminated. Next, check the ARP table entry under the server and find that the server gateway ARP entry is abnormal and the MAC address is not the gateway's MAC.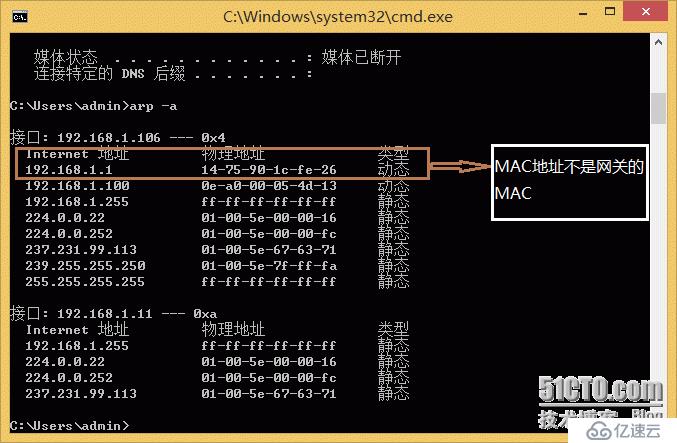
The above is the detailed content of How to learn more about ARP protocol. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 36
36
 110
110


