 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 It was revealed that OpenAI will release a new open source large model. Netizens: GPT replacement?
It was revealed that OpenAI will release a new open source large model. Netizens: GPT replacement?
It was revealed that OpenAI will release a new open source large model. Netizens: GPT replacement?
OpenAI is finally "Open"!
The latest news is that they are preparing to release a new open source language model.
After GPT-2, this is the first time in four years.
Many netizens poked their hands to express their expectations: Are they going to release their own open source replacement?
After all, the best open source model currently is still far from GPT-4. In terms of parameters alone, the difference between the two is three orders of magnitude, one is 20 billion and the other is 1.3 trillion.

OpenAI is going to be Open
In this case, will OpenAI’s move “change the competitive landscape of the entire large model?”.
Many netizens said that the first one to bear the brunt may be the LLaMA large model, the alpaca family.
After all, since the birth of ChatGPT, various open source solutions have emerged in endlessly, but most of them are inspired by the large model of Meta.
For example, Stanford’s Alpaca, Berkeley’s Vicuna, Kaola, and ColossalChat, as well as the domestic Harbin Institute of Technology’s LLaMA fine-tuned model Huatuo based on Chinese medical knowledge... Some of these open source models have even been optimized to be used on mobile phones. equipment operation.
The latest ranking of the large model Chatbot Arena created by UC Berkeley shows that many open source models follow closely behind GPT-4 and Claude.
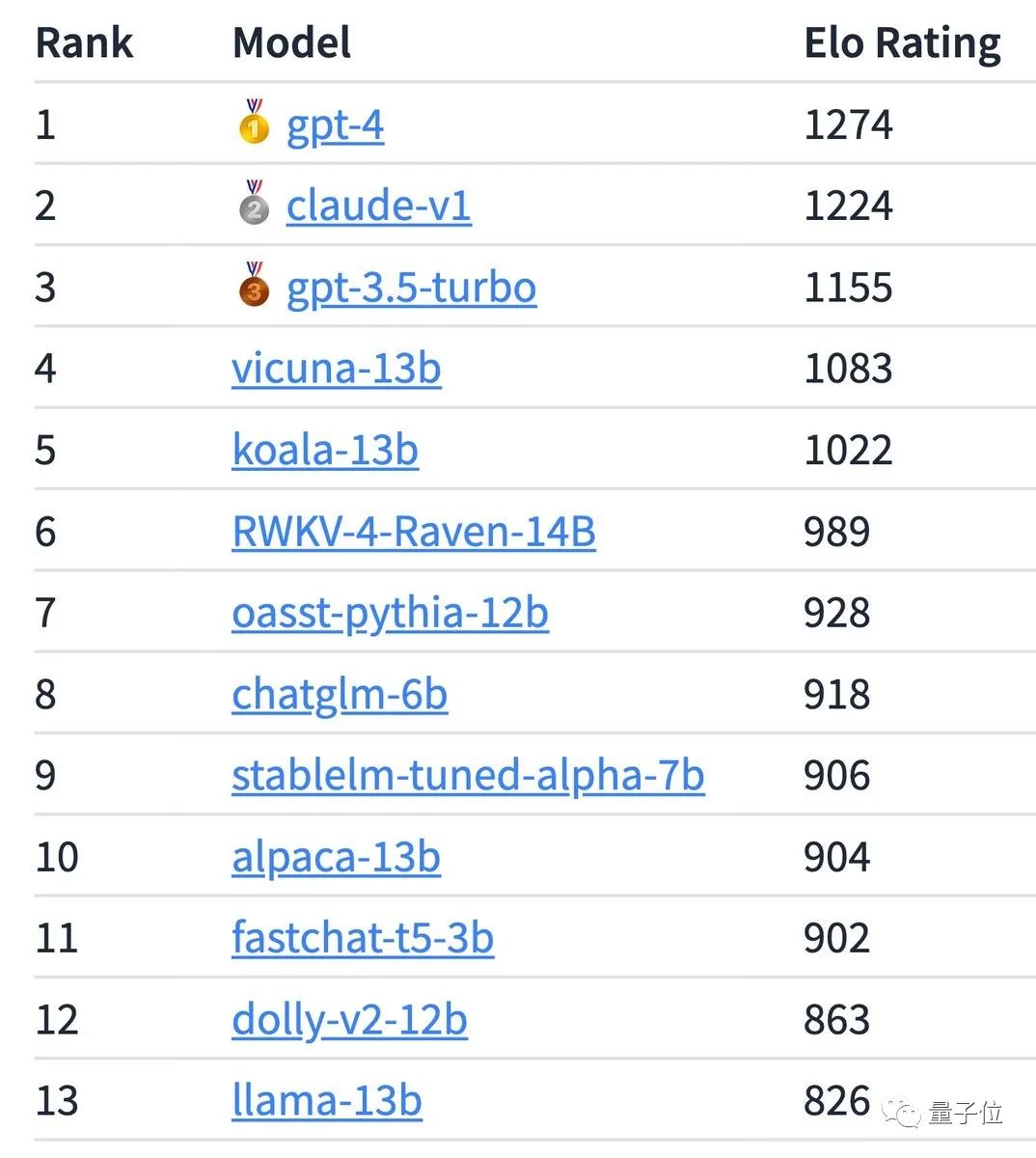
But whether it will be a "replacement" will not be known until the final release.
It is also unclear whether OpenAI will use this model to compete with other similar open source models.
According to The Information, citing people familiar with the matter, it is certain that this new open source model will be unlikely to compete with GPT.
At the same time, someone is naming Google: Now Google is under increasing pressure.

#Open source and moat have also triggered heated discussions.
Open source and moat
Open source or closed source? This is A question.
Some time ago, an internal Google document caused a stir on the Internet. The core point of it was very clear:
Open source large models are developing rapidly and are being Eroding the positions of OpenAI and Google.
And said, "Unless the stance on closed source changes, open source alternatives will eventually eclipse them (including ChatGPT)."
At this point, neither Google nor OpenAI has a moat in this big model arms race.
Many open source problems have been solved, such as running on lower-power devices, scalable personal AI, multi-modality, etc.
Even though OpenAI and Google now have a certain advantage in model quality, this gap is rapidly narrowing.
In the past few weeks, every team in the open source AI field has made continuous progress, whether in terms of models or applications.
For example, the AI startup Together built an open source large model and cloud platform based on LLaMA last month and has now raised US$20 million in seed funding.
This trend has even continued offline, with many people reveling and celebrating the open source movement.
In addition to launching a series of large-scale model tools, "Open Source Center" HuggingFace even held an offline "Woodstock of AI" gathering, attracting more than 5,000 people.
Stability AI, the company behind Stable Diffusion, and Lightning AI, which developed PyTorch Lightning, also plan to hold an open source exchange meeting.
In the eyes of many people, OpenAI and Google have set a bad precedent: the dangers of unmonitored models are real.
While the models of these big tech companies may not be completely replicable, the open source community understands the basic ingredients in these “secret recipes.” But now no one can know its ingredients.
What do you think about this matter?
Reference link:
[1]https://www.reuters.com/technology/openai-readies-new-open-source-ai-model-information-2023-05-15/
[2]https://www.theinformation.com/articles/open-source-ai-is-gaining-on-google-and-chatgpt
[3]https://venturebeat.com/ai/ open-source-ai-continues-to-celebrate-as-big-tech-mulls-over-moats/
The above is the detailed content of It was revealed that OpenAI will release a new open source large model. Netizens: GPT replacement?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
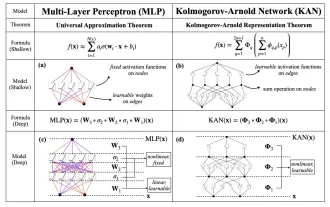
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
Target detection is a relatively mature problem in autonomous driving systems, among which pedestrian detection is one of the earliest algorithms to be deployed. Very comprehensive research has been carried out in most papers. However, distance perception using fisheye cameras for surround view is relatively less studied. Due to large radial distortion, standard bounding box representation is difficult to implement in fisheye cameras. To alleviate the above description, we explore extended bounding box, ellipse, and general polygon designs into polar/angular representations and define an instance segmentation mIOU metric to analyze these representations. The proposed model fisheyeDetNet with polygonal shape outperforms other models and simultaneously achieves 49.5% mAP on the Valeo fisheye camera dataset for autonomous driving
 Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
FP8 and lower floating point quantification precision are no longer the "patent" of H100! Lao Huang wanted everyone to use INT8/INT4, and the Microsoft DeepSpeed team started running FP6 on A100 without official support from NVIDIA. Test results show that the new method TC-FPx's FP6 quantization on A100 is close to or occasionally faster than INT4, and has higher accuracy than the latter. On top of this, there is also end-to-end large model support, which has been open sourced and integrated into deep learning inference frameworks such as DeepSpeed. This result also has an immediate effect on accelerating large models - under this framework, using a single card to run Llama, the throughput is 2.65 times higher than that of dual cards. one
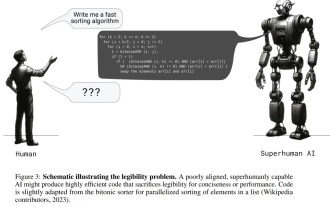 Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
If the answer given by the AI model is incomprehensible at all, would you dare to use it? As machine learning systems are used in more important areas, it becomes increasingly important to demonstrate why we can trust their output, and when not to trust them. One possible way to gain trust in the output of a complex system is to require the system to produce an interpretation of its output that is readable to a human or another trusted system, that is, fully understandable to the point that any possible errors can be found. For example, to build trust in the judicial system, we require courts to provide clear and readable written opinions that explain and support their decisions. For large language models, we can also adopt a similar approach. However, when taking this approach, ensure that the language model generates
 The latest from Oxford University! Mickey: 2D image matching in 3D SOTA! (CVPR\'24)
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:20 PM
The latest from Oxford University! Mickey: 2D image matching in 3D SOTA! (CVPR\'24)
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:20 PM
Project link written in front: https://nianticlabs.github.io/mickey/ Given two pictures, the camera pose between them can be estimated by establishing the correspondence between the pictures. Typically, these correspondences are 2D to 2D, and our estimated poses are scale-indeterminate. Some applications, such as instant augmented reality anytime, anywhere, require pose estimation of scale metrics, so they rely on external depth estimators to recover scale. This paper proposes MicKey, a keypoint matching process capable of predicting metric correspondences in 3D camera space. By learning 3D coordinate matching across images, we are able to infer metric relative
 No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
At the forefront of software technology, UIUC Zhang Lingming's group, together with researchers from the BigCode organization, recently announced the StarCoder2-15B-Instruct large code model. This innovative achievement achieved a significant breakthrough in code generation tasks, successfully surpassing CodeLlama-70B-Instruct and reaching the top of the code generation performance list. The unique feature of StarCoder2-15B-Instruct is its pure self-alignment strategy. The entire training process is open, transparent, and completely autonomous and controllable. The model generates thousands of instructions via StarCoder2-15B in response to fine-tuning the StarCoder-15B base model without relying on expensive manual annotation.



