How to implement elegant parameter verification in Java
1. Introduction
To verify the parameters of the method, the simplest and most violent way to write it is like this:
public static void utilA(String a,BigDecimal b){
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(a)){
System.out.println("a不可为空");
return;
}
if (b == null){
System.out.println("b不可为空");
return;
}
if (b.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) != 1){
System.out.println("b的取值范围不正确");
return;
}
System.out.println("do something");
}There is no problem at all from a functional point of view.
But from the perspective of long-term maintainability of the code, the code reuse rate is low. Once there are too many verification rules, it is difficult to maintain, and it looks clumsy. For engineers with a little pursuit, such a Da Tuo is still quite difficult to accept.
Although there are some solutions such as Preconditions (com.google), it is difficult to adapt to all scenarios, and it is not as comfortable to use as it should be.
2. How to verify parameters elegantly
Spring officially recommends elegant method-level verification with clear semantics (input parameter verification, return value verification)
2.1 Official guidance
Spring official in the SpringBoot document, the solution given for parameter verification (Validation) is as follows:
@Service
@Validated
public class MyBean {
public Archive findByCodeAndAuthor(@Size(min = 8, max = 10) String code,
Author author) {
...
}
}Spring Boot official website document "37. Validation"
In other words, use the JSR-303 specification and directly use annotations for parameter verification.
(JSR-303 is a sub-standard in JAVA EE 6, called Bean Validation, and the official reference implementation is Hibernate Validator)
2.2 Annotation usage instructions
2.2.1. Introduction to annotations
For simple type parameters (non-Bean), use annotations to add constraint rules directly before the parameters. The annotations are as follows:
@AssertTrue / @AssertFalse
Verification applicable fields: boolean
Annotation description: Verify whether the value is true/false
@DecimalMax / @DecimalMin
Validation applicable fields: BigDecimal, BigInteger, String, byte, short, int, long
Annotation: Validation value Whether it is less than or equal to the specified decimal value, please note that there are precision issues with decimals
@Digits
Verification applicable fields: BigDecimal, BigInteger, String, byte, short, int ,long
Annotation: Verify whether the numerical composition of the value is legal
Attribute description: integer: Specifies the number of digits in the integer part. fraction: specifies the number of digits in the fractional part.
@Future / @Past
Validation applicable fields: Date, Calendar
Annotation: Verify whether the value is after/before the current time
Property Description: Public
@Max / @Min
Validation applicable fields: BigDecimal, BigInteger, String, byte, short, int, long
Annotation: Verify whether the value is less than or equal to the specified integer value
Attribute description: Public
Note: It is recommended to use Stirng, Integer type, not recommended to use int type on, because the value submitted by the form cannot be converted to int
@NotNull / @Null
Validation applicable fields: reference data type
Annotation description: Verify whether the value is non-null/empty
Attribute description: Public
@NotBlank Check whether the constraint string is Null and whether the length of the trimmed string is Greater than 0, only for strings, and the leading and trailing spaces will be removed.
@NotEmpty Check whether the constraint element is Null or EMPTY.
@NotBlank and @NotEmpty Difference: Spaces (" ") are legal for NotEmpty, while NotBlank will throw a verification exception
@Pattern
Validation applicable fields: String
Annotation: Verify whether the value is equipped with a regular expression
Attribute description: regexp:regular expression flags: an array specifying Pattern.Flag, representing the related options of the regular expression.
@Size
Verification applicable fields: String, Collection, Map, Array
Annotation: Verify whether the value meets the length requirement
Attribute description: max: specifies the maximum length, min: specifies the minimum length.
@Length(min=, max=): Specially applied to String type
@Valid
Verification applicable fields : Recursively verify the associated object
Note: If the associated object is a collection or array, then the elements in it are verified recursively. If it is a map, the value part is verified. (Whether to perform recursive verification)
Attribute description: None
@Range(min=, max=) The specified element must be within the appropriate range
@CreditCardNumberCredit Card Verification
@Email Verify whether it is an email address. If it is null, no verification is performed and the verification is passed.
@URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)
2.2.2 Use
1. Introduce dependencies
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate.validator/hibernate-validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.1.5.Final</version>
</dependency>2. Add annotations on the corresponding fields. When the method is called, if the actual parameters passed in do not match the constraint rules, a ConstraintViolationException will be thrown directly, indicating that the parameter verification failed.
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty;
/**
* @Author: wangxia
* @Date: 2021/10/20 16:30
*/
public class TestPerson {
@NotEmpty(message = "用户名不能为空")
private String username;
@Min(value = 0,message = "年龄不能小于0岁")
@Max(value =150,message = "年龄不能大于150岁")
private int age;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}3.. For Bean type parameters, add constraint annotations on each field inside the Bean, and then add @Validated or @Valid annotations in front of the method parameters. Example:
@RequestMapping("/")
@RestController
public class TestValidatController {
@PostMapping("/testValid")
public String testValid(@Validated @RequestBody TestPerson testPerson){
return "测试成功";
}
}4. Catch exceptions gracefully. This step can be omitted, but it will be returned directly when requesting, with a 400 exception prompt, which is not very elegant.
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class MethodArgumentNotValidHandel {
@ExceptionHandler(value=MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public JSONObject MethodArgumentNotValidHandler(HttpServletRequest request,
MethodArgumentNotValidException exception) throws Exception
{
JSONObject result=new JSONObject();
result.put("code","fail");
JSONObject errorMsg=new JSONObject();
for (FieldError error : exception.getBindingResult().getFieldErrors()) {
errorMsg.put(error.getField(),error.getDefaultMessage());
}
result.put("msg",errorMsg);
return result;
}
}Add elegantly captured exception prompt:
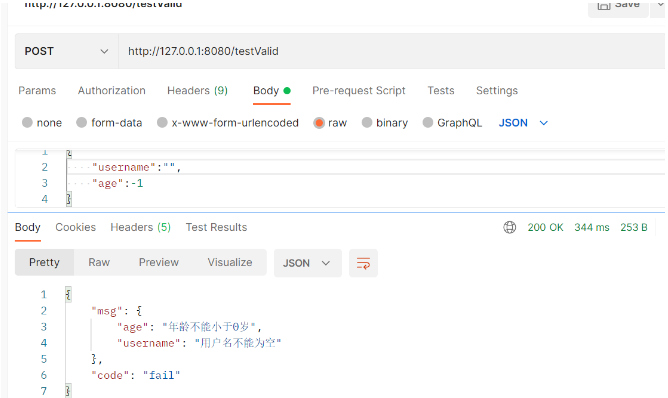
Not add elegantly captured exception prompt:
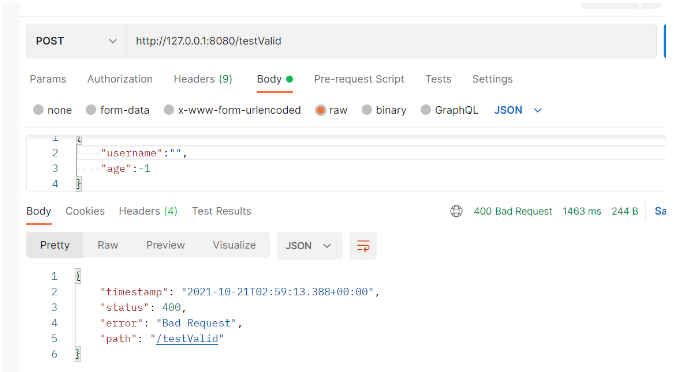
The above is the detailed content of How to implement elegant parameter verification in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




