 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 What is the implementation principle of dictionary in Python virtual machine
What is the implementation principle of dictionary in Python virtual machine
What is the implementation principle of dictionary in Python virtual machine
Dictionary data structure analysis
/* The ma_values pointer is NULL for a combined table
* or points to an array of PyObject* for a split table
*/
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
Py_ssize_t ma_used;
PyDictKeysObject *ma_keys;
PyObject **ma_values;
} PyDictObject;
struct _dictkeysobject {
Py_ssize_t dk_refcnt;
Py_ssize_t dk_size;
dict_lookup_func dk_lookup;
Py_ssize_t dk_usable;
PyDictKeyEntry dk_entries[1];
};
typedef struct {
/* Cached hash code of me_key. */
Py_hash_t me_hash;
PyObject *me_key;
PyObject *me_value; /* This field is only meaningful for combined tables */
} PyDictKeyEntry;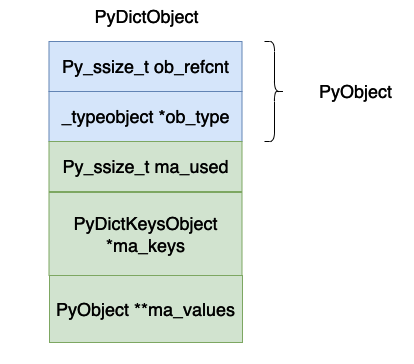
The meaning of each field above is:
- ##ob_refcnt, the reference count of the object.
- ob_type, the data type of the object.
- ma_used, the number of data in the current hash table.
- ma_keys, points to the array holding key-value pairs.
- ma_values, this points to an array of values, but this value is not necessarily used in the specific implementation of cpython, because the objects in the PyDictKeyEntry array in _dictkeysobject can also store values. This The value may only be used when all keys are strings. In this article, the value in PyDictKeyEntry is mainly used to discuss the implementation of the dictionary, so you can ignore this variable.
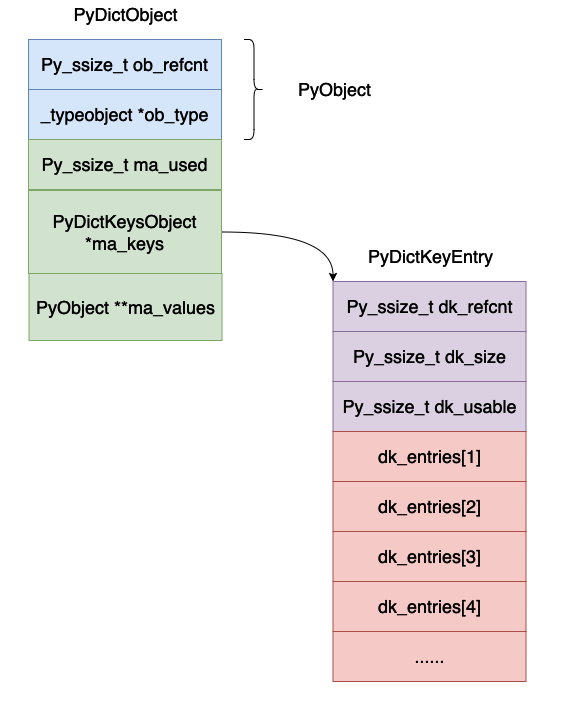
- dk_refcnt, this is also used to represent reference counting. This is related to the dictionary view. The principle is similar to reference counting, so we will ignore it here for now.
- dk_size, this represents the size of the hash table, which must be 2n. In this case, the modular operation can be turned into a bitwise AND operation.
- dk_lookup, this represents the lookup function of the hash table, it is a function pointer.
- dk_usable, indicates how many key-value pairs are available in the current array.
- dk_entries, hash table, where key-value pairs are actually stored.
static PyObject *
dict_new(PyTypeObject *type, PyObject *args, PyObject *kwds)
{
PyObject *self;
PyDictObject *d;
assert(type != NULL && type->tp_alloc != NULL);
// 申请内存空间
self = type->tp_alloc(type, 0);
if (self == NULL)
return NULL;
d = (PyDictObject *)self;
/* The object has been implicitly tracked by tp_alloc */
if (type == &PyDict_Type)
_PyObject_GC_UNTRACK(d);
// 因为还没有增加数据 因此哈希表当中 ma_used = 0
d->ma_used = 0;
// 申请保存键值对的数组 PyDict_MINSIZE_COMBINED 是一个宏定义 值为 8 表示哈希表数组的最小长度
d->ma_keys = new_keys_object(PyDict_MINSIZE_COMBINED);
// 如果申请失败返回 NULL
if (d->ma_keys == NULL) {
Py_DECREF(self);
return NULL;
}
return self;
}
// new_keys_object 函数如下所示
static PyDictKeysObject *new_keys_object(Py_ssize_t size)
{
PyDictKeysObject *dk;
Py_ssize_t i;
PyDictKeyEntry *ep0;
assert(size >= PyDict_MINSIZE_SPLIT);
assert(IS_POWER_OF_2(size));
// 这里是申请内存的位置真正申请内存空间的大小为 PyDictKeysObject 的大小加上 size-1 个PyDictKeyEntry的大小
// 这里你可能会有一位为啥不是 size 个 PyDictKeyEntry 的大小 因为在结构体 PyDictKeysObject 当中已经申请了一个 PyDictKeyEntry 对象了
dk = PyMem_MALLOC(sizeof(PyDictKeysObject) +
sizeof(PyDictKeyEntry) * (size-1));
if (dk == NULL) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return NULL;
}
// 下面主要是一些初始化的操作 dk_refcnt 设置成 1 因为目前只有一个字典对象使用 这个 PyDictKeysObject 对象
DK_DEBUG_INCREF dk->dk_refcnt = 1;
dk->dk_size = size; // 哈希表的大小
// 下面这行代码主要是表示哈希表当中目前还能存储多少个键值对 在 cpython 的实现当中允许有 2/3 的数组空间去存储数据 超过这个数则需要进行扩容
dk->dk_usable = USABLE_FRACTION(size); // #define USABLE_FRACTION(n) ((((n) << 1)+1)/3)
ep0 = &dk->dk_entries[0];
/* Hash value of slot 0 is used by popitem, so it must be initialized */
ep0->me_hash = 0;
// 将所有的键值对初始化成 NULL
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
ep0[i].me_key = NULL;
ep0[i].me_value = NULL;
}
dk->dk_lookup = lookdict_unicode_nodummy;
return dk;
}#define GROWTH_RATE(d) (((d)->ma_used*2)+((d)->ma_keys->dk_size>>1))
- Calculate the size of the new array.
- Create a new array.
- Add the data from the original hash table to the new array (that is, the re-hashing process).
static int
insertion_resize(PyDictObject *mp)
{
return dictresize(mp, GROWTH_RATE(mp));
}
static int
dictresize(PyDictObject *mp, Py_ssize_t minused)
{
Py_ssize_t newsize;
PyDictKeysObject *oldkeys;
PyObject **oldvalues;
Py_ssize_t i, oldsize;
// 下面的代码的主要作用就是计算得到能够大于等于 minused 最小的 2 的整数次幂
/* Find the smallest table size > minused. */
for (newsize = PyDict_MINSIZE_COMBINED;
newsize <= minused && newsize > 0;
newsize <<= 1)
;
if (newsize <= 0) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return -1;
}
oldkeys = mp->ma_keys;
oldvalues = mp->ma_values;
/* Allocate a new table. */
// 创建新的数组
mp->ma_keys = new_keys_object(newsize);
if (mp->ma_keys == NULL) {
mp->ma_keys = oldkeys;
return -1;
}
if (oldkeys->dk_lookup == lookdict)
mp->ma_keys->dk_lookup = lookdict;
oldsize = DK_SIZE(oldkeys);
mp->ma_values = NULL;
/* If empty then nothing to copy so just return */
if (oldsize == 1) {
assert(oldkeys == Py_EMPTY_KEYS);
DK_DECREF(oldkeys);
return 0;
}
/* Main loop below assumes we can transfer refcount to new keys
* and that value is stored in me_value.
* Increment ref-counts and copy values here to compensate
* This (resizing a split table) should be relatively rare */
if (oldvalues != NULL) {
for (i = 0; i < oldsize; i++) {
if (oldvalues[i] != NULL) {
Py_INCREF(oldkeys->dk_entries[i].me_key);
oldkeys->dk_entries[i].me_value = oldvalues[i];
}
}
}
/* Main loop */
// 将原来数组当中的元素加入到新的数组当中
for (i = 0; i < oldsize; i++) {
PyDictKeyEntry *ep = &oldkeys->dk_entries[i];
if (ep->me_value != NULL) {
assert(ep->me_key != dummy);
insertdict_clean(mp, ep->me_key, ep->me_hash, ep->me_value);
}
}
// 更新一下当前哈希表当中能够插入多少数据
mp->ma_keys->dk_usable -= mp->ma_used;
if (oldvalues != NULL) {
/* NULL out me_value slot in oldkeys, in case it was shared */
for (i = 0; i < oldsize; i++)
oldkeys->dk_entries[i].me_value = NULL;
assert(oldvalues != empty_values);
free_values(oldvalues);
DK_DECREF(oldkeys);
}
else {
assert(oldkeys->dk_lookup != lookdict_split);
if (oldkeys->dk_lookup != lookdict_unicode_nodummy) {
PyDictKeyEntry *ep0 = &oldkeys->dk_entries[0];
for (i = 0; i < oldsize; i++) {
if (ep0[i].me_key == dummy)
Py_DECREF(dummy);
}
}
assert(oldkeys->dk_refcnt == 1);
DK_DEBUG_DECREF PyMem_FREE(oldkeys);
}
return 0;
}static void
insertdict_clean(PyDictObject *mp, PyObject *key, Py_hash_t hash,
PyObject *value)
{
size_t i;
size_t perturb;
PyDictKeysObject *k = mp->ma_keys;
// 首先得到 mask 的值
size_t mask = (size_t)DK_SIZE(k)-1;
PyDictKeyEntry *ep0 = &k->dk_entries[0];
PyDictKeyEntry *ep;
i = hash & mask;
ep = &ep0[i];
for (perturb = hash; ep->me_key != NULL; perturb >>= PERTURB_SHIFT) {
// 下面便是遇到哈希冲突时的处理办法
i = (i << 2) + i + perturb + 1;
ep = &ep0[i & mask];
}
assert(ep->me_value == NULL);
ep->me_key = key;
ep->me_hash = hash;
ep->me_value = value;
}The above is the detailed content of What is the implementation principle of dictionary in Python virtual machine. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
XML can be converted to images by using an XSLT converter or image library. XSLT Converter: Use an XSLT processor and stylesheet to convert XML to images. Image Library: Use libraries such as PIL or ImageMagick to create images from XML data, such as drawing shapes and text.
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.





