What is Java's missing feature extension methods
What is an extension method?
An extension method is the ability to "add" methods directly to an existing type without creating a new one. derived type, recompile, or otherwise modify an existing type. When calling an extension method, there is no discernible difference compared to calling the method actually defined in the type.
Why extension methods are needed
Consider implementing this function: after taking out a string containing multiple product IDs from Redis (each product ID is separated by an English comma), first compare the product IDs Remove duplicates (and maintain the order of elements), and finally use commas to connect the product IDs.
Traditional writing method:
Use Stream writing method:
Assume that extension methods can be implemented in Java, and we add the extension method toList for the array (turn the array into a List) , added the extension method toSet for List (turning List into LinkedHashSet), and added the extension method join for Collection (to connect the string forms of elements in the collection using the given connector), then we will be able to write code like this:
I believe you already have the answer to why extension methods are needed at this point:
You can directly enhance the existing class library instead of using tool classes
Compared Use tool classes and use the methods of the type itself to write code more smoothly and more comfortably
The code is easier to read because it is a chain call instead of using static method nesting dolls
How to implement it in Java Extension methods
Let’s first ask about the recently popular ChatGPT:
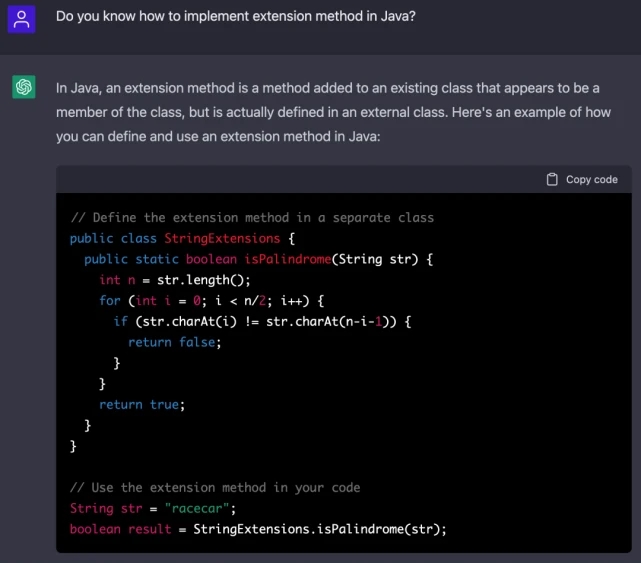
ChatGPT’s view is that in Java, extension methods are provided through tool classes Implemented by static method. So next I will introduce a brand new black technology:
Manifold
Preparation conditions
Manifold and Lombok work similarly, both are compiled through annotation processors processed when. In order to use Manifold effectively, you need to install the Manifold IDEA plug-in in IDEA
and then add annotationProcessorPaths to the maven-compiler-plugin of the project pom:
If you use Lombok in your project, Lombok needs to be added to annotationProcessorPaths:
Writing extension methods
In JDK, the split method of String uses a string as a parameter, that is, String[] split(String). Let's now add an extension method String[] split(char) to String: Split by given characters.
Based on Manifold, write extension methods:
You can find static methods that are essentially tool classes, but there are some requirements:
Tool classes need to use Manifold’s @Extension annotation
In static methods, the parameters of the target type need to be annotated with @This
The package name where the tool class is located needs to end with extensions.the fully qualified class name of the target type
——Students who have used C# will probably smile knowingly. This is the extension method of imitated C#.
Regarding point 3, the reason for this requirement is that Manifold hopes to quickly find extension methods in the project, avoid annotation scanning of all classes in the project, and improve processing efficiency.
Having the ability to extend methods, now we can call it like this:
Amazing! And you can find that System.out.println(numStrs.toString()) actually prints the string form of the array object - not the address of the array object. Browse the decompiled App.class and observe that the extension method call has been replaced by a static method call
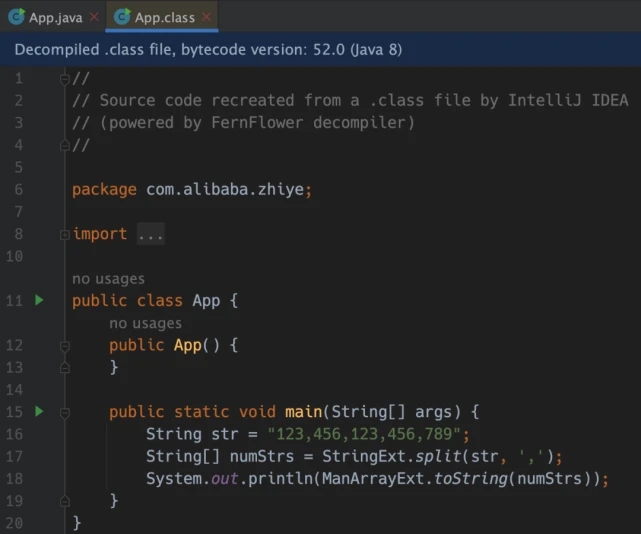
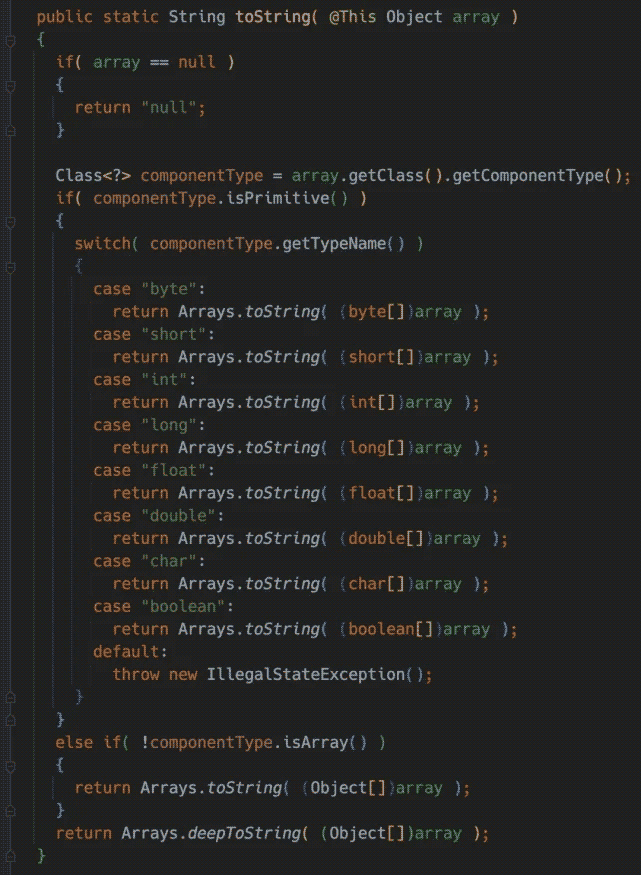
and the toString method of the array uses Manifold to define the array Extension method ManArrayExt.toString(@This Object array):
[Ljava.lang.String;@511d50c0 What, Goodbye, never see you again~
Because extension method calls are replaced with static method calls at compile time, using Manifold's extension method, there is no problem even if the object of the calling method is null, because the processed code passes null as a parameter to the corresponding static method. For example, to extend Collection:
Then when calling:
java.lang.NullPointerException, Goodbye, never see you again~
Array extension method

We see List written like this: @Self is used to indicate what type the annotated value should be. If it is @Self, that is, @Self(false), which represents the annotated value. The value is of the same type as the value of the @This annotation; @Self(true) indicates the type of the elements in the array.
For object arrays, we can see that the toList method returns the corresponding List (T is the type of array element):
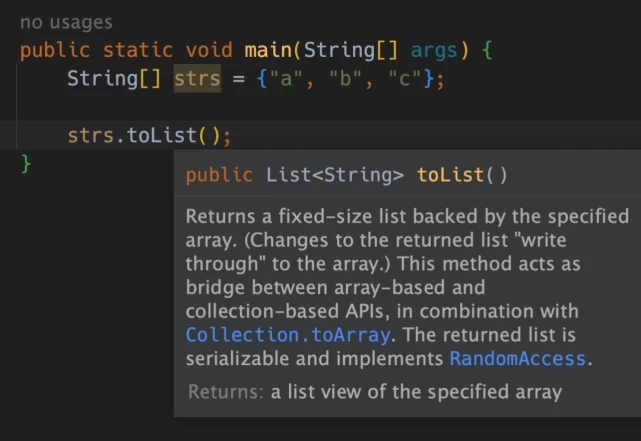
But if it is the original Type array, the return value indicated by IDEA is:
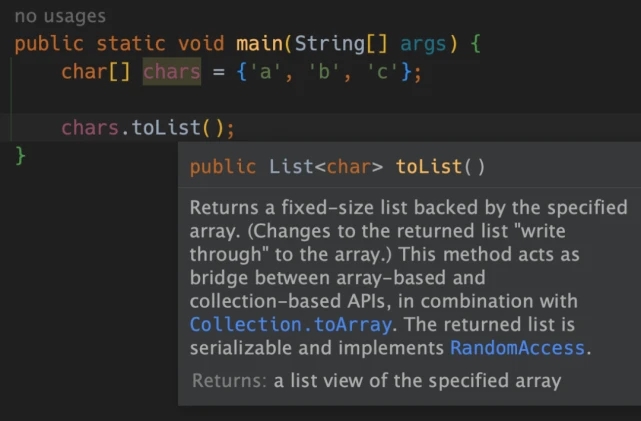
But I am using Java, how can erasure method generics have such a great function as List - So you can only use native types to receive this return value:)
The above is the detailed content of What is Java's missing feature extension methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo




