How to solve nginx+php-fpm service HTTP status code 502
For one of our web projects, due to the increase in new cities, the number of visits has increased and the pressure on the db has increased. As a business party that provides interfaces, a large number of "502" requests have been reported recently by downstream feedback.
502, bad gateway, is usually an error in upstream (here is PHP). For PHP, the common cause of 502 is that the script execution exceeds the timeout setting time, or the timeout setting is too large, causing the PHP process to take a long time It cannot be released and there are no idle worker processes to pick up guests.
Our project is caused by the PHP execution time setting being too short. In this case, you can first increase the PHP execution time appropriately and ensure that 502 is cleared first. Optimization will take more time after all.
There are two options to control php execution time, max_execution_time in php.ini and request_terminate_timeout in php-fpm. request_terminate_timeout can override max_execution_time, so if you don’t want to change the global php.ini, just change php- The configuration of fpm is enough.
Next I will analyze in detail why the execution of the php script exceeds the set time and causes nginx to return 502.
Let’s set the scene first and let the problem reoccur:
nginx and php only start one worker each for easy tracking.
php-fpm's request_terminate_timeout is set to 3s.
Test script test.php
sleep(20); echo 'ok';
go go go:
Visit www.v.com/test.php in the browser, and 404 will appear as expected after 3 seconds. ? ? ? what? ? ?

It’s a bad start, quickly take a look at the nginx configuration file
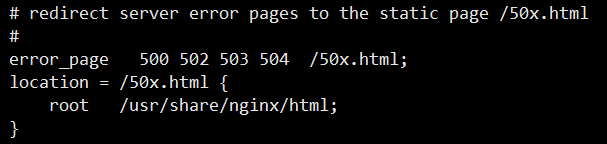
This location configuration is when a 5xx error occurs Jump to a nice-looking interface, but I don’t have the file 50x.html under /usr/share/nginx/html. So I got a 404. Doesn't this affect the accuracy of my judgment of the problem? Just comment it out! Visit again, wait 3 seconds, and finally the 'normal' interface comes out.

The environment is good, let’s follow the routine below. Follow the troubleshooting routine for web problems. Let’s take a look at the error log first:
nginx:
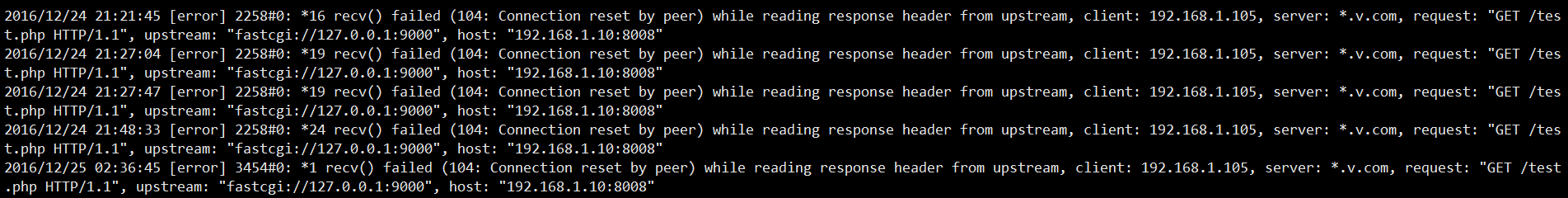
The errors reported are recv() failed (104: connection reset by peer.
recv failed and the connection was reset. Why was the connection reset? Set it? Isn’t it consistent?
We are looking at the error log of php-fpm:
(Note that the php_admin_value[error_log] option in php-fpm specifies the error log of php, which will be overwritten in php.ini. But here we are not looking at php errors, but at php-fpm errors. The error log of php-fpm is specified by the error_log option in php-fpm.conf.)
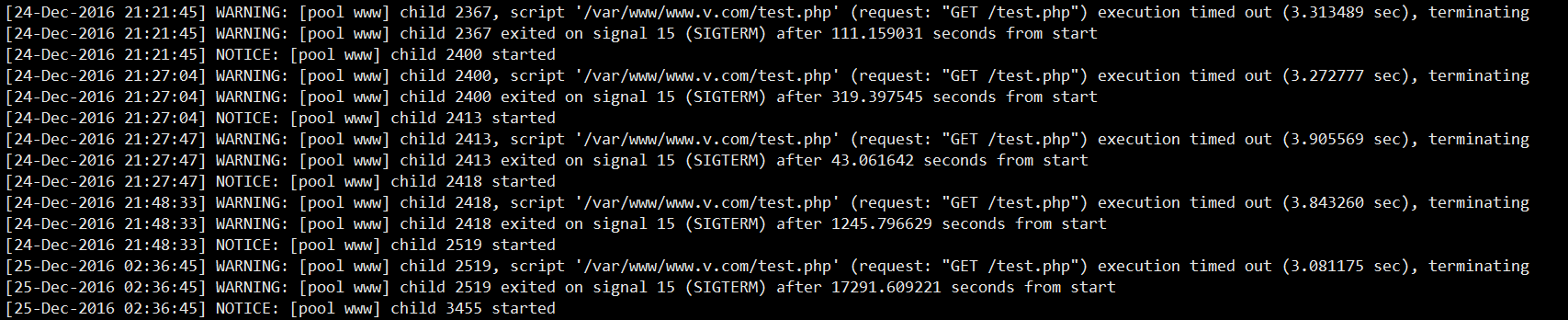
Each request generates 2 warnings and 1 notice:
warning: The script execution timed out and terminated.
warning: The child process received sigterm The signal exited.
Notice: A new child process was started (because I set pm.min_spare_servers = 1)
It seems that if the worker process of php times out, it will not only terminate the script execution , and the worker process will also exit. It seems that the nginx error connection is reset because the php worker process exits (in the tcp connection, if one party is disconnected, it will send rst to the other party)
Through the log We can already know that the execution of the php script times out and the worker sub-process exits, causing nginx to report an error connection reset by peer. Let’s use strace to see the situation of php and nginx:
php:
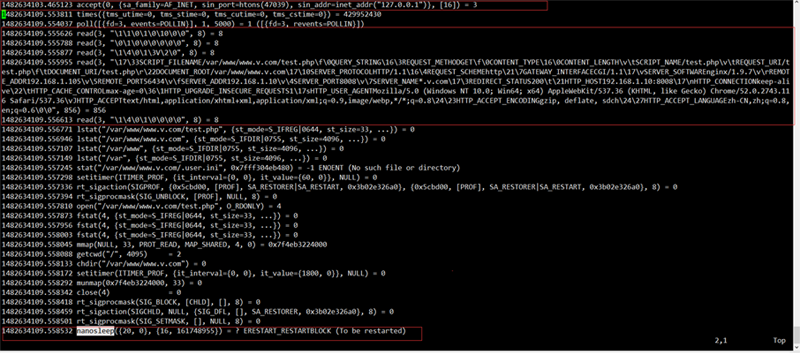
1.Accept an nginx connection request (socket, bind, and listen are all completed in the master). You can see that the port of nginx is 47039, and the data is read from fd0, which is from the standard input. This is stipulated by the fast-cgi protocol. The connected descriptor after accept is 3.
2. Read the data passed by nginx from fd3, in the fastcgi protocol format, and received 856 bytes. Why read5 What about times?
Because the fastcgi protocol data packet is 8-byte aligned and consists of a packet header and a packet body. And it will first send a request packet, including some request id, version, type and other information (the header and body each occupy 8 bytes), and then send a params packet to pass the get parameters and environment variables (the header is 8 bytes) , the packet body becomes longer), and finally a params data packet without a packet body and only a packet header is sent, indicating the end of parameter sending (8 bytes of packet header). So the first three reads are used to read the header and body of the request packet, as well as the header of the params packet. The fourth read is to read the real data, and the last read is to read the header of the last params packet. Therefore, the data transmitted by nginx should be 8 8 8 856 8 = 896 bytes (which can correspond to the transmission bytes of nginx below). Note that if it is post mode, stdin data packets will also be sent.
3. Set sleep for 20s, which is sleep(20) in the php program. After that, because the process is terminated, there will be no more. The strace program also exited.
nginx:
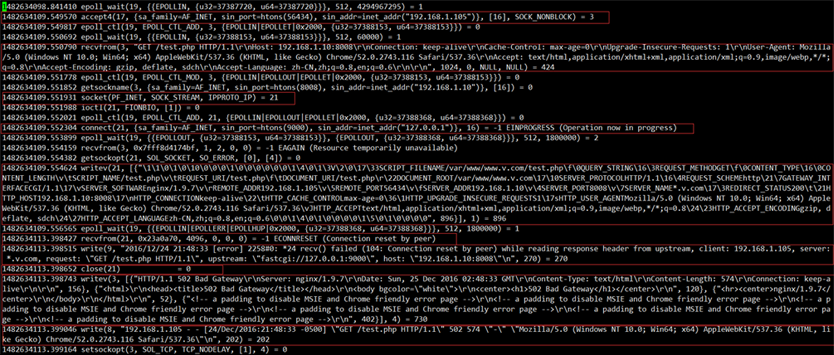

The above is the detailed content of How to solve nginx+php-fpm service HTTP status code 502. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to solve the problem of nginx cross-domain
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:15 AM
How to solve the problem of nginx cross-domain
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:15 AM
There are two ways to solve the Nginx cross-domain problem: modify the cross-domain response header: add directives to allow cross-domain requests, specify allowed methods and headers, and set cache time. Use CORS modules: Enable modules and configure CORS rules that allow cross-domain requests, methods, headers, and cache times.
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.




