How to manually render components to specified elements in Vue3
Convert components to custom elements
Documentation: Vue and Web Components | Vue.js (vuejs.org)
Vue provides good support for Web Components. Components can be converted into custom elements using defineCustomElement. You can then freely insert it into the DOM node.
import { defineCustomElement } from 'vue'
const MyVueElement = defineCustomElement({
// 这里是同平常一样的 Vue 组件选项
props: {},
emits: {},
template: `...`,
// defineCustomElement 特有的:注入进 shadow root 的 CSS
styles: [`/* inlined css */`]
})
// 注册自定义元素
// 注册之后,所有此页面中的 `<my-vue-element>` 标签
// 都会被升级
customElements.define('my-vue-element', MyVueElement)
// 你也可以编程式地实例化元素:
// (必须在注册之后)
document.body.appendChild(
new MyVueElement({
// 初始化 props(可选)
})
)Additionally, it is possible to convert an SFC (Single File Component) into a custom element.
Documentation: sfc as custom element
import { defineCustomElement } from 'vue'
import Example from './Example.ce.vue'
console.log(Example.styles) // ["/* 内联 css */"]
// 转换为自定义元素构造器
const ExampleElement = defineCustomElement(Example)
// 注册
customElements.define('my-example', ExampleElement)It is worth noting that
defineCustomElementwill use Shadow DOM to render the element. This method will cause style isolation, and external styles will not be able to apply to the inside of the component. If you use a component library, or rely on some external styles, remember to import these styles again.
Multiple application instances of Vue
Remember that when creating the project, we used createApp to create an App instance, and then It is mounted in #app. In fact, multiple App instances, that is, multiple Vue applications, can exist in a DOM environment at the same time.
Using this, you can create an App instance again and then mount it on a specific DOM element.
import YouComponent from "./YouComponent.vue";
// 创建一个新的 Vue 应用
const app = createApp(YouComponent);
// 将应用挂载到自定义的 DOM 元素上
app.mount("#you-element");In this way, the component can be rendered normally. The component's provide and inject will be invalid because they do not belong to the original application.
How to communicate between components? You can use custom events, or createEventHook | VueUse. In addition, you can also use the responsiveness principle of Vue3 to create a separate responsive object using
reforreactive, and then reference them in different components to achieve two-way data. Synchronize.
The above is the detailed content of How to manually render components to specified elements in Vue3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite: How to solve the error when using require to dynamically import images in src
May 21, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
vue3+vite:src uses require to dynamically import images and error reports and solutions. vue3+vite dynamically imports multiple images. If vue3 is using typescript development, require will introduce image errors. requireisnotdefined cannot be used like vue2 such as imgUrl:require(' .../assets/test.png') is imported because typescript does not support require, so import is used. Here is how to solve it: use awaitimport
 How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
How to use tinymce in vue3 project
May 19, 2023 pm 08:40 PM
tinymce is a fully functional rich text editor plug-in, but introducing tinymce into vue is not as smooth as other Vue rich text plug-ins. tinymce itself is not suitable for Vue, and @tinymce/tinymce-vue needs to be introduced, and It is a foreign rich text plug-in and has not passed the Chinese version. You need to download the translation package from its official website (you may need to bypass the firewall). 1. Install related dependencies npminstalltinymce-Snpminstall@tinymce/tinymce-vue-S2. Download the Chinese package 3. Introduce the skin and Chinese package. Create a new tinymce folder in the project public folder and download the
 How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
How Vue3 parses markdown and implements code highlighting
May 20, 2023 pm 04:16 PM
Vue implements the blog front-end and needs to implement markdown parsing. If there is code, it needs to implement code highlighting. There are many markdown parsing libraries for Vue, such as markdown-it, vue-markdown-loader, marked, vue-markdown, etc. These libraries are all very similar. Marked is used here, and highlight.js is used as the code highlighting library. The specific implementation steps are as follows: 1. Install dependent libraries. Open the command window under the vue project and enter the following command npminstallmarked-save//marked to convert markdown into htmlnpmins
 How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
How to refresh partial content of the page in Vue3
May 26, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
To achieve partial refresh of the page, we only need to implement the re-rendering of the local component (dom). In Vue, the easiest way to achieve this effect is to use the v-if directive. In Vue2, in addition to using the v-if instruction to re-render the local dom, we can also create a new blank component. When we need to refresh the local page, jump to this blank component page, and then jump back in the beforeRouteEnter guard in the blank component. original page. As shown in the figure below, how to click the refresh button in Vue3.X to reload the DOM within the red box and display the corresponding loading status. Since the guard in the component in the scriptsetup syntax in Vue3.X only has o
 How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
How to use Vue3 reusable components
May 20, 2023 pm 07:25 PM
Preface Whether it is vue or react, when we encounter multiple repeated codes, we will think about how to reuse these codes instead of filling a file with a bunch of redundant codes. In fact, both vue and react can achieve reuse by extracting components, but if you encounter some small code fragments and you don’t want to extract another file, in comparison, react can be used in the same Declare the corresponding widget in the file, or implement it through renderfunction, such as: constDemo:FC=({msg})=>{returndemomsgis{msg}}constApp:FC=()=>{return(
 How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
How to solve the problem that after the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank
May 17, 2023 am 08:19 AM
After the vue3 project is packaged and published to the server, the access page displays blank 1. The publicPath in the vue.config.js file is processed as follows: const{defineConfig}=require('@vue/cli-service') module.exports=defineConfig({publicPath :process.env.NODE_ENV==='production'?'./':'/&
 How to use defineCustomElement to define components in Vue3
May 28, 2023 am 11:29 AM
How to use defineCustomElement to define components in Vue3
May 28, 2023 am 11:29 AM
Using Vue to build custom elements WebComponents is a collective name for a set of web native APIs that allow developers to create reusable custom elements (customelements). The main benefit of custom elements is that they can be used with any framework, even without one. They are ideal when you are targeting end users who may be using a different front-end technology stack, or when you want to decouple the final application from the implementation details of the components it uses. Vue and WebComponents are complementary technologies, and Vue provides excellent support for using and creating custom elements. You can integrate custom elements into existing Vue applications, or use Vue to build
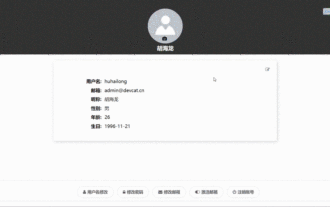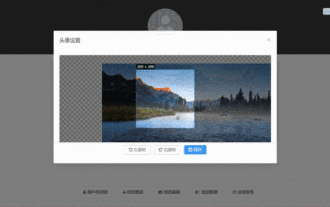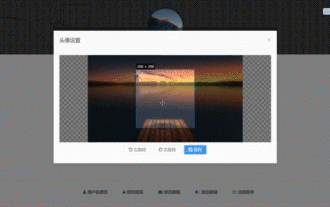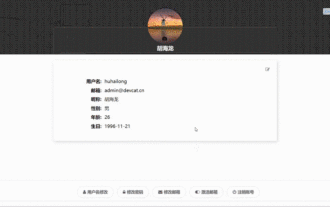 How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
How to select an avatar and crop it in Vue3
May 29, 2023 am 10:22 AM
The final effect is to install the VueCropper component yarnaddvue-cropper@next. The above installation value is for Vue3. If it is Vue2 or you want to use other methods to reference, please visit its official npm address: official tutorial. It is also very simple to reference and use it in a component. You only need to introduce the corresponding component and its style file. I do not reference it globally here, but only introduce import{userInfoByRequest}from'../js/api' in my component file. import{VueCropper}from'vue-cropper&




