##1. Rewrite jump implementation
Nginx: supports URL rewriting and if conditional judgment through the ngx_http_rewrite_module module, but does not support else
Jump: jump from one location to another, the loop can be executed up to 10 times, after which nginx will return a 500 error
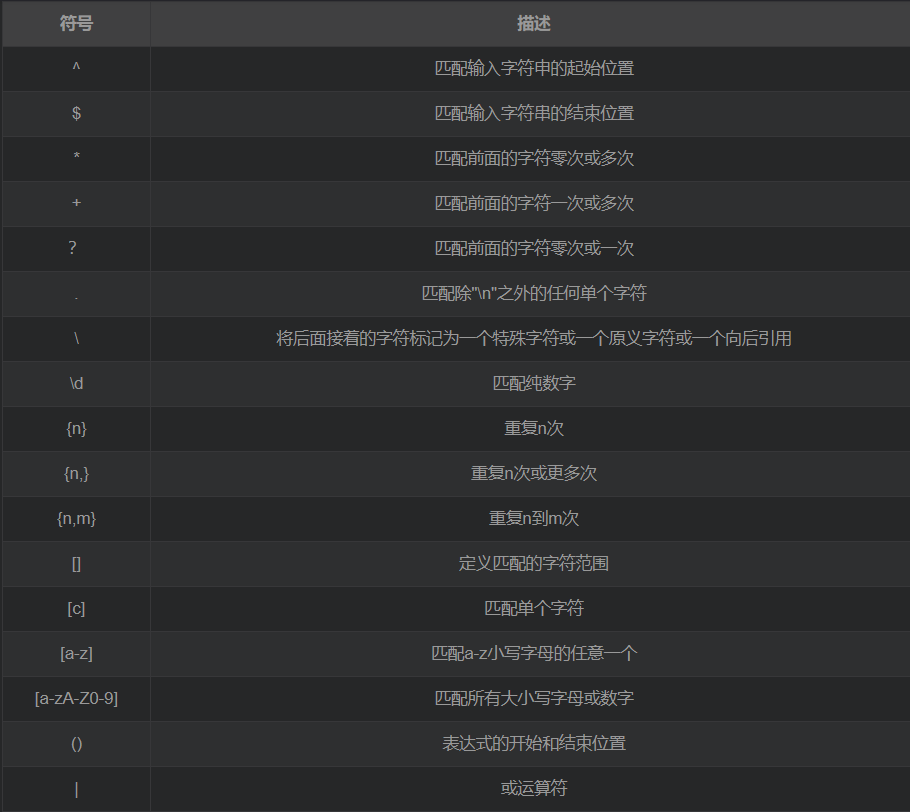
PCRE support: perl compatible regular expression syntax rule matching
Rewrite module set instruction: create new variables and assign values to them
2. Rewrite execution sequence
①Execute the rewriter instruction in the server block
②Execution Location matching
③Execute the rewrite command in the selected location
3. Rewrite jump scenario
Adjust the URL browsed by the user to look more standardized and in line with development and Needs of product personnel
In order to allow search engines to search website content and provide better user experience, companies will disguise dynamic URL addresses as static addresses to provide services
After the URL is changed to a new domain name, the old The access will jump to a new domain name; for example, access to JD.com's 360buy.com will jump to jd.com
Certain business adjustments on the server, such as URL based on special variables, directories, and client information Adjustment, etc.
4. Grammar and flg tag description
Grammar rewrite
[flag];regex: Indicates regular matching rules
replacement: Indicates the content after the jump flag: Indicates the flag mark supported by rewrite flag mark description:
- last: this article After the rule matching is completed, continue to match new location URI rules downwards, generally used in server and if
- break: This rule will terminate when the matching is completed and will no longer match any subsequent rules. , generally used in location
- redirect: Returns 302 temporary redirect, the browser address will display the URL address after the jump
- permanent : Return to 301 permanent redirection, the browser address bar will display the URL address after the jump
5. Nginx commonly used regular expression symbols

6. Location1. Classificationlocation can be roughly divided into the following three categories:
- Exact matching: location = / {…}
- General matching: location / {…}
- Regular matching: location ~ / {…}
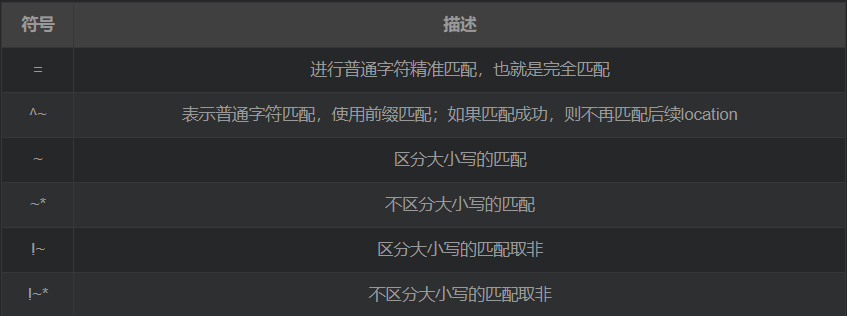
2. Common matching rules

3. Priority
- Exact match first=
- Secondly, prefix matching ^~
- Secondly, regular matching in order in the file ~ or ~*
- Then the prefix matching without any modification, that is, the general matching
- is finally handed over to / general matching, with the lowest priority
4. Example localtion = / {}= is an exact match of /, and no string can be placed after the host name. For example, when accessing / and /xcf, / matches, but /xcf does not. Match location / {}Because all addresses start with /, this rule will match all requests, such as accessing / and /data, then / matches, /data Also matches , but if it is followed by a regular expression, it will be matched with the longest string first (longest match) location /documents/ {} is matched After the address starting with /documents/, you need to continue to search for other locationslocation /documents/abc {} Matches any address starting with /documents/abc. After matching, still To continue searching for other locationsOnly when the regular expressions behind other locations do not match, this one will be usedlocation ^~ /images/ {}Match any address starting with /images/. After matching, stop searching for regular rules and use this location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {}Match all requests ending with gif, jpg, jpegHowever, all images requested under /images/ will be processed by location ^~ /images/, because ^~ has a higher priority, so it arrives This regular rule location /images/abc {}The longest character matches /images/abc, which has the lowest priority. If you continue to search for other locations, you will find ^~ and ~ Existence location ~ /images/abc {}matches those starting with /images/abc, the priority is second, this will only be adopted if the location ^~ /images is removed
location /images/abc/1.html {} Matches the /images/abc/1.html file. If compared with the regular ~ /images/abc/1.html, the regular priority is higher High priority summary: (location = full path) > (location ^~ path) > (location ,* regular sequence) > (location part starting path) > ; (location /) 5. Matching rule definition ① The first required rule: directly matches the website root. Accessing the website homepage through the domain name is more frequent. Use This will speed up the processing, for example, the official website
It can be a static homepage, or it can be forwarded directly to the back-end "application server" - PHP, Apache (the application server is shown in the figure below)
 ##
##
location / {
root
html;
index
index.html index.html;
}Copy after login
location ^~ /static/ {
root /webroot/static/;
}
location ~* \.(html|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
root /webroot/res/ ;
}Copy after login
upstream tomcat_server {
192.168.126.12:80
192.168.126.23:80
}Copy after login
location / {
proxy_ pass http://tomcat_server;Copy after login
1. Compare rewrite and location
Same points: both implement jumpsDifferences: rewrite changes the path to obtain resources within the same domain name Location is to control access or reverse proxy to a class of paths. You can also proxy_pass to other machines
2.rewrite will be written in the location, and the execution sequence
- Execute the rewrite instruction in the server block
- Perform location matching
- Execute the selected location The rewrite directive in
#3. How are the location priorities arranged?
Match a specific file(location = full path) > (location ^~ full path) > (location ~* full path) > (location ~ complete path Path)> (location /)Use directory to match to access a file(location = directory) > (location ^~ directory) > (location ~ directory) > (location ~* directory)> (location /)
4. Why do files and directories only change in case insensitivity?
Regular expression Formula: The purpose is to match files as accurately as possible - try to match as accurately as possible, case-sensitive and accurate, and not distinguish directories - try to match more accurately Exact match, case-sensitive, more precise, higher priorityThe above is the detailed content of Location matching and rewrite jump methods in Nginx. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

 ##
##



