
后端对前端传过来的参数也是需要进行校验的,如果在controller中直接校验需要用大量的if else做判断
以添加用户的接口为例,需要对前端传过来的参数进行校验, 如下的校验就是不优雅的:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("add")
public ResponseEntity<String> add(User user){
if(user.getName()==null) {
return ResponseResult.fail("user name should not be empty");
} else if(user.getName().length()<5 || user.getName().length()>50){
return ResponseResult.fail("user name length should between 5-50");
}
if(user.getAge()< 1 || user.getAge()> 150) {
return ResponseResult.fail("invalid age");
}
// ...
return ResponseEntity.ok("success");
}
}针对这个普遍的问题,Java开者在Java API规范 (JSR303) 定义了Bean校验的标准validation-api,但没有提供实现。
hibernate validation是对这个规范的实现,并增加了校验注解如@Email、@Length等。
Spring Validation是对hibernate validation的二次封装,用于支持spring mvc参数自动校验。
接下来,我们以springboot项目为例,介绍Spring Validation的使用。
本案例使用了 Spring Validation 对参数绑定进行了验证,主要为您提供参数验证的思路。请参考SpringBoot如何封装接口统一错误信息处理,其中包括针对绑定参数检查错误的处理
添加pom依赖:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-validation --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId> </dependency>
单一职责,所以将查询用户的参数封装到UserParam中, 而不是User(数据库实体)本身。
对每个参数字段添加validation注解约束和message。
/**
* user.
*
* @author pdai
*/
@Data
@Builder
@ApiModel(value = "User", subTypes = {AddressParam.class})
public class UserParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@NotEmpty(message = "could not be empty")
private String userId;
@NotEmpty(message = "could not be empty")
@Email(message = "invalid email")
private String email;
@NotEmpty(message = "could not be empty")
@Pattern(regexp = "^(\\d{6})(\\d{4})(\\d{2})(\\d{2})(\\d{3})([0-9]|X)$", message = "invalid ID")
private String cardNo;
@NotEmpty(message = "could not be empty")
@Length(min = 1, max = 10, message = "nick name should be 1-10")
private String nickName;
@NotEmpty(message = "could not be empty")
@Range(min = 0, max = 1, message = "sex should be 0-1")
private int sex;
@Max(value = 100, message = "Please input valid age")
private int age;
@Valid
private AddressParam address;
}使用@Valid或者@Validate注解,参数校验的值放在BindingResult中
/**
* @author pdai
*/
@Slf4j
@Api(value = "User Interfaces", tags = "User Interfaces")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
/**
* http://localhost:8080/user/add .
*
* @param userParam user param
* @return user
*/
@ApiOperation("Add User")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "userParam", type = "body", dataTypeClass = UserParam.class, required = true)
@PostMapping("add")
public ResponseEntity<String> add(@Valid @RequestBody UserParam userParam, BindingResult bindingResult){
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
List<ObjectError> errors = bindingResult.getAllErrors();
errors.forEach(p -> {
FieldError fieldError = (FieldError) p;
log.error("Invalid Parameter : object - {},field - {},errorMessage - {}", fieldError.getObjectName(), fieldError.getField(), fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
});
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("invalid parameter");
}
return ResponseEntity.ok("success");
}
}POST访问添加User的请求
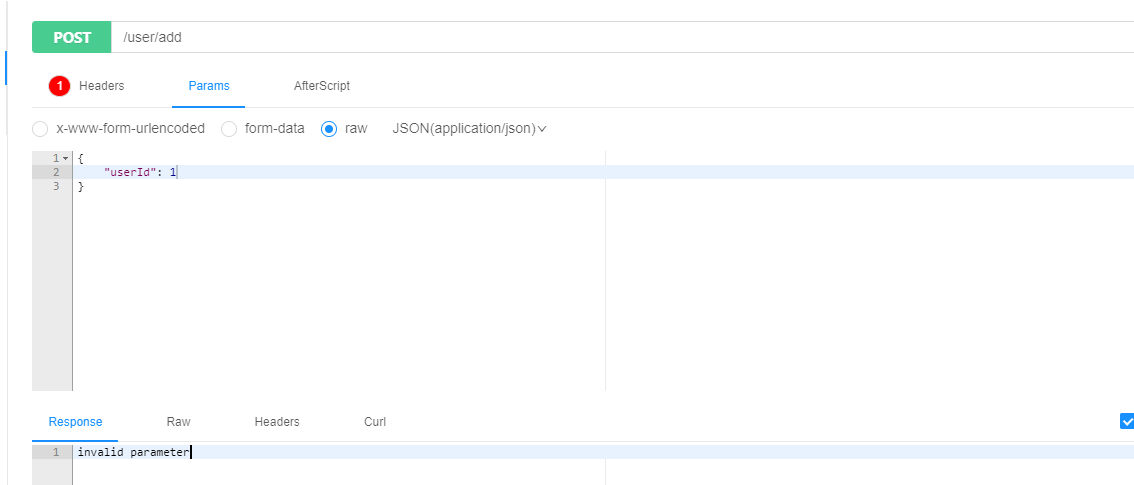
后台输出参数绑定错误信息:(包含哪个对象,哪个字段,什么样的错误描述)
2021-09-16 10:37:05.173 ERROR 21216 --- [nio-8080-exec-8] t.p.s.v.controller.UserController : Invalid Parameter : object - userParam,field - nickName,errorMessage - could not be empty
2021-09-16 10:37:05.176 ERROR 21216 --- [nio-8080-exec-8] t.p.s.v.controller.UserController : Invalid Parameter : object - userParam,field - email,errorMessage - could not be empty
2021-09-16 10:37:05.176 ERROR 21216 --- [nio-8080-exec-8] t.p.s.v.controller.UserController : Invalid Parameter : object - userParam,field - cardNo,errorMessage - could not be empty
(本例只是springboot-validation的简单用例,针对接口统一的错误信息封装请看SpringBoot接口如何统一异常处理
我们再通过一些问题来帮助你更深入理解validation校验。@pdai
上面的例子中,其实存在一个问题,UserParam既可以作为addUser的参数(id为空),又可以作为updateUser的参数(id不能为空),这时候怎么办呢?分组校验登场。
@Data
@Builder
@ApiModel(value = "User", subTypes = {AddressParam.class})
public class UserParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@NotEmpty(message = "could not be empty") // 这里定为空,对于addUser时是不合适的
private String userId;
}这时候可以使用Validation分组
先定义分组(无需实现接口)
public interface AddValidationGroup {
}
public interface EditValidationGroup {
}在UserParam的userId字段添加分组
@Data
@Builder
@ApiModel(value = "User", subTypes = {AddressParam.class})
public class UserParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@NotEmpty(message = "{user.msg.userId.notEmpty}", groups = {EditValidationGroup.class}) // 这里
private String userId;
}controller中的接口使用校验时使用分组
PS: 需要使用@Validated注解
@Slf4j
@Api(value = "User Interfaces", tags = "User Interfaces")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
/**
* http://localhost:8080/user/add .
*
* @param userParam user param
* @return user
*/
@ApiOperation("Add User")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "userParam", type = "body", dataTypeClass = UserParam.class, required = true)
@PostMapping("add")
public ResponseEntity<UserParam> add(@Validated(AddValidationGroup.class){
return ResponseEntity.ok(userParam);
}
/**
* http://localhost:8080/user/add .
*
* @param userParam user param
* @return user
*/
@ApiOperation("Edit User")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "userParam", type = "body", dataTypeClass = UserParam.class, required = true)
@PostMapping("edit")
public ResponseEntity<UserParam> edit(@Validated(EditValidationGroup.class){
return ResponseEntity.ok(userParam);
}
}测试
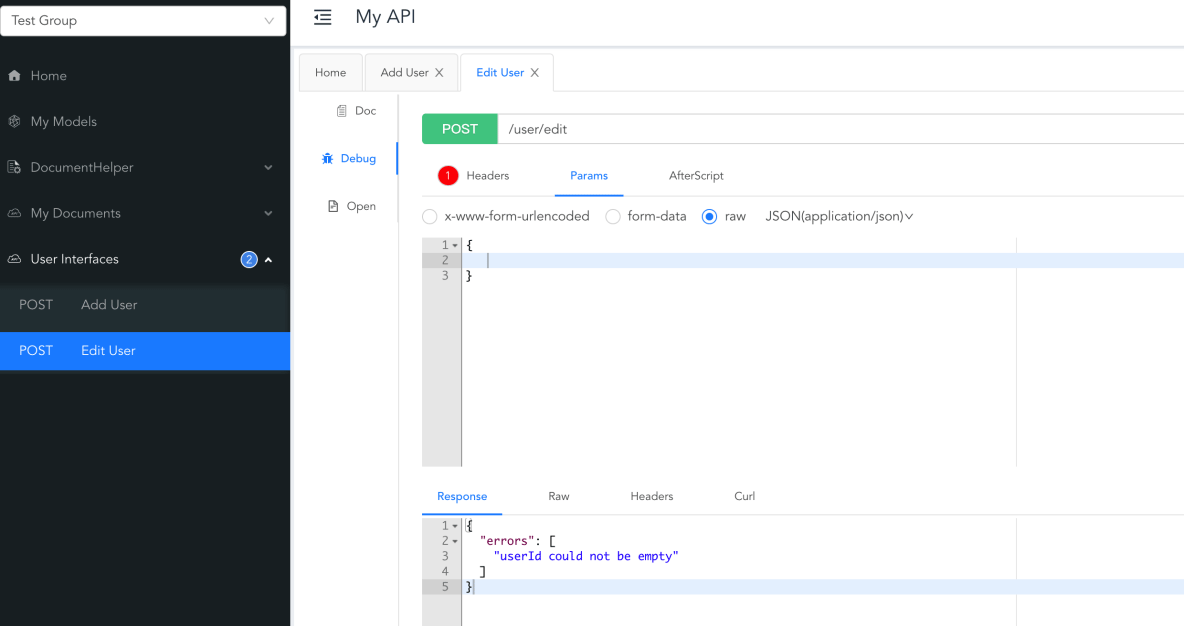
你会注意到,在前面的例子中使用的是@Validate而不是@Valid,你可能会想知道它们之间的不同之处
在检验Controller的入参是否符合规范时,使用@Validated或者@Valid在基本验证功能上没有太多区别。但是在分组、注解地方、嵌套验证等功能上两个有所不同:
分组
@Validated:提供了一个分组功能,可以在入参验证时,根据不同的分组采用不同的验证机制,这个网上也有资料,不详述。JSR-303标准并未包含分组功能。
注解地方
@Validated:可以用在类型、方法和方法参数上。但是不能用在成员属性(字段)上
@Valid:可以用在方法、构造函数、方法参数和成员属性(字段)上
嵌套类型
比如本文例子中的address是user的一个嵌套属性, 只能用@Valid
@Data
@Builder
@ApiModel(value = "User", subTypes = {AddressParam.class})
public class UserParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Valid // 这里只能用@Valid
private AddressParam address;
}从以下三类理解。
JSR303/JSR-349: JSR303是一项标准,只提供规范不提供实现,规定一些校验规范即校验注解,如@Null,@NotNull,@Pattern,位于javax.validation.constraints包下。JSR-349是其的升级版本,添加了一些新特性。
@AssertFalse 被注释的元素只能为false
@AssertTrue 被注释的元素只能为true
@DecimalMax 被注释的元素必须小于或等于{value}
@DecimalMin 被注释的元素必须大于或等于{value}
@Digits 被注释的元素数字的值超出了允许范围(只允许在{integer}位整数和{fraction}位小数范围内)
@Email 被注释的元素不是一个合法的电子邮件地址
@Future 被注释的元素需要是一个将来的时间
@FutureOrPresent 被注释的元素需要是一个将来或现在的时间
@Max 被注释的元素最大不能超过{value}
@Min 被注释的元素最小不能小于{value}
@Negative 被注释的元素必须是负数
@NegativeOrZero 被注释的元素必须是负数或零
@NotBlank 被注释的元素不能为空
@NotEmpty 被注释的元素不能为空
@NotNull 被注释的元素不能为null
@Null 被注释的元素必须为null
@Past 被注释的元素需要是一个过去的时间
@PastOrPresent 被注释的元素需要是一个过去或现在的时间
@Pattern 被注释的元素需要匹配正则表达式"{regexp}"
@Positive 被注释的元素必须是正数
@PositiveOrZero 被注释的元素必须是正数或零
@Size 被注释的元素个数必须在{min}和{max}之间hibernate validation:hibernate validation是对这个规范的实现,并增加了一些其他校验注解,如@Email,@Length,@Range等等
@CreditCardNumber 被注释的元素不合法的信用卡号码
@Currency 被注释的元素不合法的货币 (必须是{value}其中之一)
@EAN 被注释的元素不合法的{type}条形码
@Email 被注释的元素不是一个合法的电子邮件地址 (已过期)
@Length 被注释的元素长度需要在{min}和{max}之间
@CodePointLength 被注释的元素长度需要在{min}和{max}之间
@LuhnCheck 被注释的元素${validatedValue}的校验码不合法, Luhn模10校验和不匹配
@Mod10Check 被注释的元素${validatedValue}的校验码不合法, 模10校验和不匹配
@Mod11Check 被注释的元素${validatedValue}的校验码不合法, 模11校验和不匹配
@ModCheck 被注释的元素${validatedValue}的校验码不合法, ${modType}校验和不匹配 (已过期)
@NotBlank 被注释的元素不能为空 (已过期)
@NotEmpty 被注释的元素不能为空 (已过期)
@ParametersScriptAssert 被注释的元素执行脚本表达式"{script}"没有返回期望结果
@Range 被注释的元素需要在{min}和{max}之间
@SafeHtml 被注释的元素可能有不安全的HTML内容
@ScriptAssert 被注释的元素执行脚本表达式"{script}"没有返回期望结果
@URL 被注释的元素需要是一个合法的URL
@DurationMax 被注释的元素必须小于${inclusive == true ? '或等于' : ''}${days == 0 ? '' : days += '天'}${hours == 0 ? '' : hours += '小时'}${minutes == 0 ? '' : minutes += '分钟'}${seconds == 0 ? '' : seconds += '秒'}${millis == 0 ? '' : millis += '毫秒'}${nanos == 0 ? '' : nanos += '纳秒'}
@DurationMin 被注释的元素必须大于${inclusive == true ? '或等于' : ''}${days == 0 ? '' : days += '天'}${hours == 0 ? '' : hours += '小时'}${minutes == 0 ? '' : minutes += '分钟'}${seconds == 0 ? '' : seconds += '秒'}${millis == 0 ? '' : millis += '毫秒'}${nanos == 0 ? '' : nanos += '纳秒'}spring validation:spring validation对hibernate validation进行了二次封装,在springmvc模块中添加了自动校验,并将校验信息封装进了特定的类中
如果上面的注解不能满足我们检验参数的要求,我们能不能自定义校验规则呢? 可以。
定义注解
package tech.pdai.springboot.validation.group.validation.custom;
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.Payload;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
@Target({ METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER, TYPE_USE })
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = {TelephoneNumberValidator.class}) // 指定校验器
public @interface TelephoneNumber {
String message() default "Invalid telephone number";
Class<?>[] groups() default { };
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default { };
}定义校验器
public class TelephoneNumberValidator implements ConstraintValidator<TelephoneNumber, String> {
private static final String REGEX_TEL = "0\\d{2,3}[-]?\\d{7,8}|0\\d{2,3}\\s?\\d{7,8}|13[0-9]\\d{8}|15[1089]\\d{8}";
@Override
public boolean isValid(String s, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext){
try {
return Pattern.matches(REGEX_TEL, s);
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
}使用
@Data
@Builder
@ApiModel(value = "User", subTypes = {AddressParam.class})
public class UserParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@NotEmpty(message = "{user.msg.userId.notEmpty}", groups = {EditValidationGroup.class})
private String userId;
@TelephoneNumber(message = "invalid telephone number") // 这里
private String telephone;
}The above is the detailed content of How does the SpringBoot interface verify parameters?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




