 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 UCSD, MIT and other Chinese teams teach robot dogs to perceive the 3D world! With the M1 chip, you can climb stairs and cross obstacles.
UCSD, MIT and other Chinese teams teach robot dogs to perceive the 3D world! With the M1 chip, you can climb stairs and cross obstacles.
UCSD, MIT and other Chinese teams teach robot dogs to perceive the 3D world! With the M1 chip, you can climb stairs and cross obstacles.
Recently, researchers from UCSD, IAIFI and MIT institutions used a new neural volumetric memory architecture (NVM) to teach a robot dog to perceive the three-dimensional world.
Using this technology, the robot dog can climb stairs, cross gaps, climb obstacles, etc. through a single neural network - completely autonomously, without the need for a remote control.

I wonder if you’ve noticed the white box on the dog’s back?
It is equipped with Apple’s M1 chip, which is responsible for running the visual processing tasks of the robot dog. Moreover, the team removed it from a Mac.
It is not difficult to see that this robot dog from MIT can easily climb a section of branches in front of it without any effort (basically).
A MacBook with 4 legs?
As we all know, it is very difficult for robot dogs and other legged robots to cross uneven roads.
The more complex the road conditions are, the more obstacles there are that cannot be seen.
In order to solve the problem of "partially observable environment", SOTA's current visual-motion technology connects image channels through frame-stacking.
However, this simple processing method lags far behind current computer vision technology, which can explicitly model optical flow and specific 3D geometries.
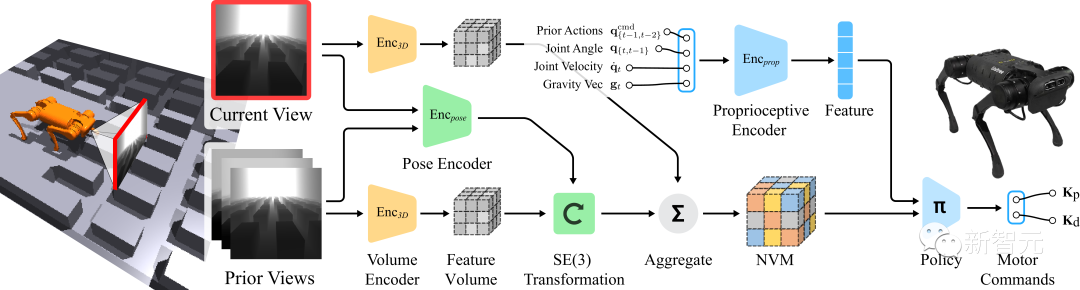
Inspired by this, the team proposed a neural volume memory architecture (NVM) that can fully take into account the SE(3) equivalence of the three-dimensional world.

## Project address: https://rchalyang.github.io/NVM/
Unlike previous methods, NVM is a volumetric format. It aggregates feature volumes from multiple camera views into the robot's egocentric frame, allowing the robot to better understand its surroundings.
The test results show that after using neural volumetric memory (NVM) to train leg movements, the robot's performance on complex terrain is significantly better than previous technologies.
In addition, the results of the ablation experiments show that the content stored in the neural volumetric memory captures enough geometric information to reconstruct the 3D scene.
Experiments in the real world
To validate in different real-world scenarios outside of simulation, the team conducted experiments in indoor and outdoor scenarios All experiments were conducted.

When the robot dog finds that an obstacle suddenly appears in front of it, it will directly choose to avoid it.

There seems to be no problem walking on the rocky ground, although it is still more laborious than on flat ground. Some.

################################################################################################################################################## It's possible to overcome obstacles that are relatively big compared to yourself, but you can still overcome them if you work hard. ######

Using the previous recognition control technology, the puppy’s hind legs obviously made errors in judging the distance. It stepped into a ditch and overturned, which failed.

After adopting the NVM proposed by MIT, the puppy crossed the ditch, stable happiness, success!

# Using the previous recognition control technology, the puppy missed the mark with its first kick, and the dog's head grabbed the ground and failed.

After adopting the NVM proposed by MIT, the puppy walked smoothly through the matrix.

Volume memory for leg movements
Using an egocentric camera perspective is essentially a problem of dealing with "partially-observable environment" (Partially-Observed).
To make the control problem concrete, the robot needs to gather information from previous frames and correctly infer occluded terrain.
During movement, the camera mounted directly on the robot chassis undergoes drastic and sudden position changes.
In this way, in the process of characterizing a series of pictures, it becomes very important that a single frame can be placed in the correct position.
To this end, the concept of neural volume memory (NVM) proposed by the team can convert a series of input visual information into scene features for 3D depiction and then output.
Learning NVM through self-supervision
Although "behavioral cloning goal" Sufficient to generate a good policy, but targeting equivariance of translation and rotation, automatically provides an independent, self-supervised learning objective for neural volumetric memory.
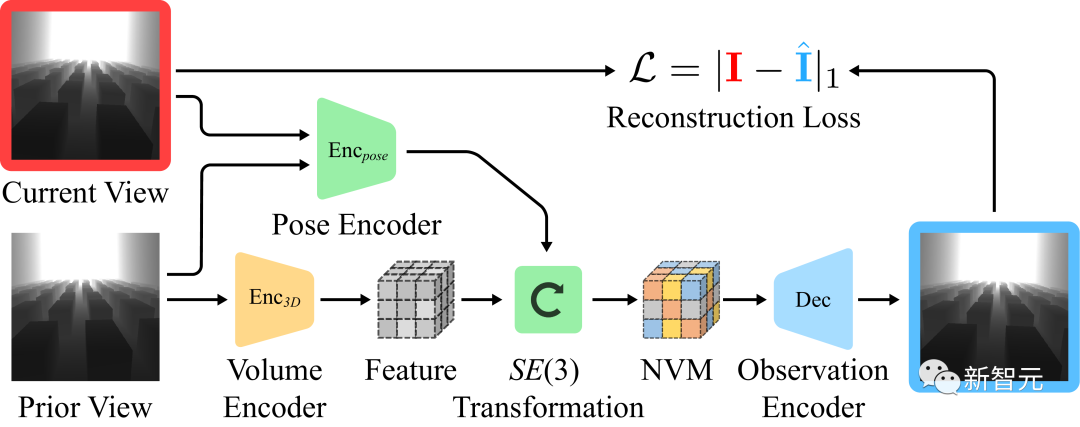
Self-supervised learning: The research team trained an independent decoder. Let it predict visual observations in different frames by taking a visual observation and estimating the transition between two frames.
#As shown in the image above, it can be assumed that the surrounding 3D scene remains unchanged between frames. Since the camera is looking forward, we can normalize the feature volume from previous frames and use it to predict subsequent images.
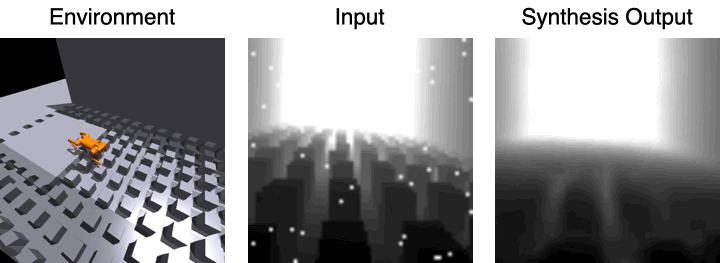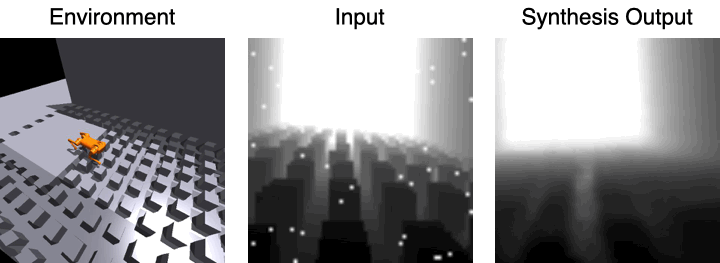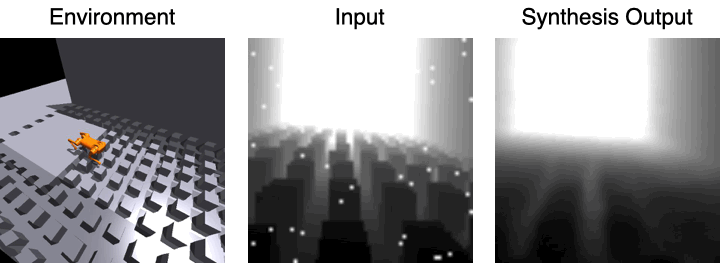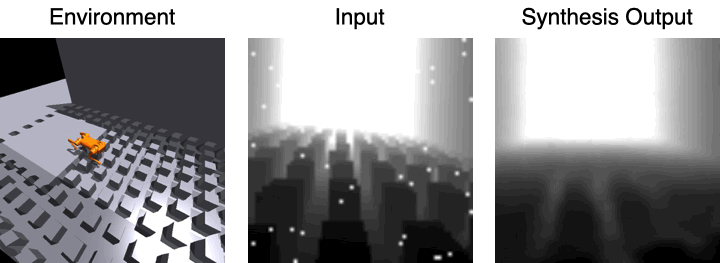
Visual reconstruction of the decoder
The first image shows the robot moving in the environment, and the second image is the input visual observation, The third picture is the visual observation effect using 3D feature volume and estimated picture synthesis.
For the visual observation of the input, the research team applied a large number of data enhancements to the images to improve the robustness of the model.

Ruihan Yan

His research interests are reinforcement learning, machine learning, robotics, etc. Specifically, he wants to build intelligent agents that use information from different sources to make decisions.
Ge Yang

Ge Yang’s research involves two sets of related issues. The first group is to improve learning by revisiting the way we represent knowledge in neural networks and how knowledge is transferred across distributions. The second group looks at reinforcement learning through the lens of theoretical tools such as neural tangent kernels, non-Euclidean geometry, and Hamiltonian dynamics.
Xiaolong Wang
 ##Xiaolong Wang is An Assistant Professor in the ECE Department at UC San Diego. He is a member of the robotics team at the TILOS National Science Foundation Institute for Artificial Intelligence.
##Xiaolong Wang is An Assistant Professor in the ECE Department at UC San Diego. He is a member of the robotics team at the TILOS National Science Foundation Institute for Artificial Intelligence.
He received his PhD in robotics from Carnegie Mellon University and did postdoctoral research at the University of California, Berkeley.
The above is the detailed content of UCSD, MIT and other Chinese teams teach robot dogs to perceive the 3D world! With the M1 chip, you can climb stairs and cross obstacles.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Installing Git software includes the following steps: Download the installation package and run the installation package to verify the installation configuration Git installation Git Bash (Windows only)
 How to solve the complexity of WordPress installation and update using Composer
Apr 17, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
How to solve the complexity of WordPress installation and update using Composer
Apr 17, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
When managing WordPress websites, you often encounter complex operations such as installation, update, and multi-site conversion. These operations are not only time-consuming, but also prone to errors, causing the website to be paralyzed. Combining the WP-CLI core command with Composer can greatly simplify these tasks, improve efficiency and reliability. This article will introduce how to use Composer to solve these problems and improve the convenience of WordPress management.
 How to solve SQL parsing problem? Use greenlion/php-sql-parser!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
How to solve SQL parsing problem? Use greenlion/php-sql-parser!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
When developing a project that requires parsing SQL statements, I encountered a tricky problem: how to efficiently parse MySQL's SQL statements and extract the key information. After trying many methods, I found that the greenlion/php-sql-parser library can perfectly solve my needs.
 How to solve complex BelongsToThrough relationship problem in Laravel? Use Composer!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
How to solve complex BelongsToThrough relationship problem in Laravel? Use Composer!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
In Laravel development, dealing with complex model relationships has always been a challenge, especially when it comes to multi-level BelongsToThrough relationships. Recently, I encountered this problem in a project dealing with a multi-level model relationship, where traditional HasManyThrough relationships fail to meet the needs, resulting in data queries becoming complex and inefficient. After some exploration, I found the library staudenmeir/belongs-to-through, which easily installed and solved my troubles through Composer.
 How to solve the complex problem of PHP geodata processing? Use Composer and GeoPHP!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to solve the complex problem of PHP geodata processing? Use Composer and GeoPHP!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
When developing a Geographic Information System (GIS), I encountered a difficult problem: how to efficiently handle various geographic data formats such as WKT, WKB, GeoJSON, etc. in PHP. I've tried multiple methods, but none of them can effectively solve the conversion and operational issues between these formats. Finally, I found the GeoPHP library, which easily integrates through Composer, and it completely solved my troubles.
 Solve CSS prefix problem using Composer: Practice of padaliyajay/php-autoprefixer library
Apr 17, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Solve CSS prefix problem using Composer: Practice of padaliyajay/php-autoprefixer library
Apr 17, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
I'm having a tricky problem when developing a front-end project: I need to manually add a browser prefix to the CSS properties to ensure compatibility. This is not only time consuming, but also error-prone. After some exploration, I discovered the padaliyajay/php-autoprefixer library, which easily solved my troubles with Composer.
 git software installation tutorial
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
git software installation tutorial
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
Git Software Installation Guide: Visit the official Git website to download the installer for Windows, MacOS, or Linux. Run the installer and follow the prompts. Configure Git: Set username, email, and select a text editor. For Windows users, configure the Git Bash environment.
 The latest tutorial on how to read the key of git software
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
The latest tutorial on how to read the key of git software
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
This article will explain in detail how to view keys in Git software. It is crucial to master this because Git keys are secure credentials for authentication and secure transfer of code. The article will guide readers step by step how to display and manage their Git keys, including SSH and GPG keys, using different commands and options. By following the steps in this guide, users can easily ensure their Git repository is secure and collaboratively smoothly with others.



