How to use the second-level cache of Mybatis in Java
Overview and classification of cache
Overview
Cache is a piece of memory space that saves temporary data
Why use Cache
Read the data from the data source (database or file) and store it in the cache. When retrieving it, obtain it directly from the cache, which can reduce the number of interactions with the database, which can improve the performance of the program. Performance!
Applicability of cache
Suitable for cache: frequently queried but not frequently modified (eg: provinces, cities, category data), the accuracy of the data has no impact on the final result Big
Not suitable for caching: frequently changing data, sensitive data (for example: stock market prices, bank exchange rates, money in bank cards), etc.
MyBatis Cache Category
Level 1 cache: It is the cache of the sqlSession object. It comes with it (no configuration required) and cannot be uninstalled (if you don’t want to use it). The life cycle of the first level cache is consistent with sqlSession.
Second level cache: It is the cache of SqlSessionFactory. As long as the SqlSession created by the same SqlSessionFactory shares the contents of the second-level cache, it can operate the second-level cache. If we want to use the second-level cache, we need to manually enable it ourselves (configuration is required).
Use of second-level cache
1. Enable the second-level cache in the core configuration file of mybatis
<!--**因为 cacheEnabled 的取值默认就为 true**,所以这一步可以省略不配置。为 true 代表开启二级缓存;为 false 代表不开启二级缓存。 -->
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>2. Configure the use of the second-level cache in the Dao mapping file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.UserDao">
<!--配置二级缓存-->
<cache/>
<select id="findAll" resultType="user">
select * from t_user
</select>
<delete id="deleteById" parameterType="int">
delete from t_user where uid=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>3. The Pojo class for second-level caching must implement the Serializable interface
public class User implements Serializable {
private int uid;
private String username;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
private String address;
// 省略setter,getter,构造...等方法
}4. Test the use of second-level cache
Test code
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws Exception{
// 1.加载mybatis核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2.创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 3.构建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is);
// 4.获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 5.获得dao接口的代理对象
UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
// 6.执行sql语句,得到结果
List<User> list = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println("user = " + user);
}
sqlSession.close();//清除一级缓存
System.out.println("分割线----------------------------------");
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserDao userDao2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserDao.class);
List<User> userList2 = userDao2.findAll();
for (User user : userList2) {
System.out.println(user);
}
// 7.释放资源
sqlSession2.close();
}- Test results:
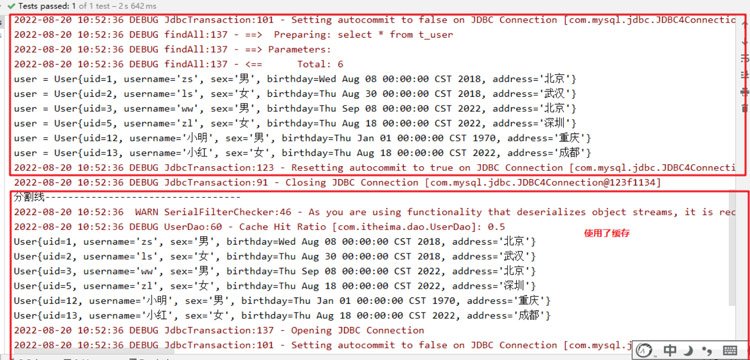
#- After the above test, we found that two queries were executed, and after executing the first query, we turned off the first-level cache and then went to When executing the second query, we found that no SQL statement was issued to the database, so the data at this time can only come from what we call the second-level cache.
5. Test to turn off the second-level cache
-Test code
@Test
public void testFindAll() throws Exception{
// 1.加载mybatis核心配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2.创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 3.构建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is);
// 4.获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 5.获得dao接口的代理对象
UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
// 6.执行sql语句,得到结果
List<User> list = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println("user = " + user);
}
sqlSession.close();//清除一级缓存
System.out.println("分割线----------------------------------");
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserDao userDao2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserDao.class);
userDao2.deleteById(5);// 关闭二级缓存
List<User> userList2 = userDao2.findAll();
for (User user : userList2) {
System.out.println(user);
}
// 7.释放资源
sqlSession2.close();
}-Test result
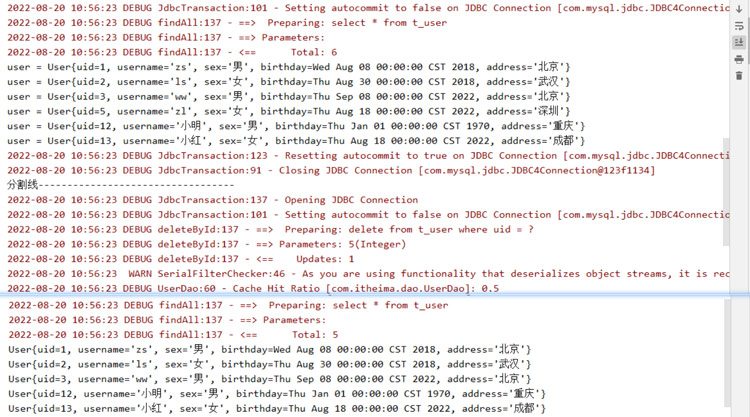
After the above Testing, we found that two queries were executed, and after executing the first query, we closed the first-level cache and the second-level cache. When we executed the second query, we found that a sql statement was issued to the database, so The data at this time comes from the database, not the cache.
The above is the detailed content of How to use the second-level cache of Mybatis in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is




