
1. Build database and tables
1. Database demo1 puts a user table
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of user
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('1', 'aa');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('2', 'bb');2. Database demo2 Put a role table
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for role
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of role
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `role` VALUES ('1', 'CC');
INSERT INTO `role` VALUES ('2', 'DD');2. Pom.xml introduces the package
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>mysql</groupid> <artifactid>mysql-connector-java</artifactid> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>mysql</groupid> <artifactid>mysql-connector-java</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupid> <artifactid>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactid> <version>2.0.1</version> </dependency> <!-- aop --> <dependency> <groupid>org.aspectj</groupid> <artifactid>aspectjweaver</artifactid> </dependency> <!-- alibaba druid--> <dependency> <groupid>com.alibaba</groupid> <artifactid>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactid> <version>1.1.10</version> </dependency> <!-- dynamic--> <dependency> <groupid>com.typesafe.dynamicdatasource</groupid> <artifactid>dynamic-data-source_2.11</artifactid> </dependency>
3. Use the generator plug-in to generate Entity classes of user and role tables, mapper.java, mapper.xml
User.java Role.java UserMapper.java RoleMapper.java UserMapper.xml RoleMapper.xml
4. Configure application.yml
server: port: 8088 mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml spring: datasource: db1: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT username: root password: root type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #驱动包 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #初始连接数 initial-size: 5 #最小空闲数 min-idle: 5 #最大活动数 max-active: 20 #等待超时时间 max-wait: 60000 #配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000 # 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000 #验证数据库连接的查询语句,MYSQL是select 1 validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL #空闲时测试,testOnBorrow和testOnReturn在生产环境一般是不开启的,主要是性能考虑。失效连接主要通过testWhileIdle保证 test-while-idle: true test-on-borrow: false test-on-return: false #打开PSCache,并指定每个链接上的PSCache大小 pool-prepared-statements: true max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20 #配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,‘wall'用于防火墙,此处是filter修改的地方 filters: stat,wall #通过connectproperties属性来打开mergesql功能:慢sql记录 connection-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000 #合并多个DruidDataSource useGlobalDataSourceStat: true db2: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT username: root password: root type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #驱动包 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver #初始连接数 initial-size: 5 #最小空闲数 min-idle: 5 #最大活动数 max-active: 20 #等待超时时间 max-wait: 60000 #配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000 # 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000 #验证数据库连接的查询语句,MYSQL是select 1 validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL #空闲时测试,testOnBorrow和testOnReturn在生产环境一般是不开启的,主要是性能考虑。失效连接主要通过testWhileIdle保证 test-while-idle: true test-on-borrow: false test-on-return: false #打开PSCache,并指定每个链接上的PSCache大小 pool-prepared-statements: true max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20 #配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,‘wall'用于防火墙,此处是filter修改的地方 filters: stat,wall #通过connectproperties属性来打开mergesql功能:慢sql记录 connection-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000 #合并多个DruidDataSource useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
5. Start class scanning mapper.java file
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.example.demo.dao")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}6. Define DataSourceConfig, import the configuration in application.yml into DataSource, and inject it into the bean
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
//从配置文件配置数据源
@Primary
@Bean(name="datasource1")
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.db1")
public DataSource dataSource1(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//从配置文件配置数据源
@Bean(name="datasource2")
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.db2")
public DataSource dataSource2(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//动态数据源 进行数据源切换
@Bean(name="dynamicDataSource")
public DataSource dynamicDataSource(){
DynamicDataSource dynamicDatasource=new DynamicDataSource();
//设置默认数据源
dynamicDatasource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dataSource1());
//配置多数据源
Map<object> dsMap=new HashMap();
dsMap.put("datasource1",dataSource1());
dsMap.put("datasource2",dataSource2());
//将多数据源放到数据源池中
dynamicDatasource.setTargetDataSources(dsMap);
return dynamicDatasource;
}
}</object>7. Define the dynamic data source switching class DynamicDataSourceContextHolder
public class DynamicDataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<string> contextHolder=new ThreadLocal();
//设置数据源名称
public static void setDB(String dbType){
contextHolder.set(dbType);
}
//获取数据源名称
public static String getDB(){
return contextHolder.get();
}
//清除数据源名
public static void clearDB(){
contextHolder.remove();
}
}</string>8. Define the dynamic data source class DynamicDataSource
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDB();
}
}9. Define the mybatis configuration class and put DynamicDataSource into SqlSessionFactoryBean
@EnableTransactionManagement
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Resource(name = "dynamicDataSource")
private DataSource dynamicDataSource;
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource);//将动态数据源bean配置到sqlsessionfactory
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mapper/*.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dynamicDataSource);
}
}10. Define for Switch the annotation TargetDataSource of the data source
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TargetDataSource {
String value() default "datasource1";
}11. Define the aspect DynamicDataSourceAspect, which is used to intercept the annotation and perform the data source switching function
@Aspect
@Component
public class DynamicDataSourceAspect {
@Before("@annotation(targetDataSource)")
public void beforeSwitchDS(JoinPoint point,TargetDataSource targetDataSource){
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDB(targetDataSource.value());
}
@After("@annotation(targetDataSource)")
public void afterSwitchDS(JoinPoint point,TargetDataSource targetDataSource){
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.clearDB();
}
}12. Test class Test
@RestController
public class Test {
@Autowired
private RoleMapper roleMapper;
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//未使用TargetDataSource注解,则使用默认数据源,即datasource1
@RequestMapping("/ds1")
public String selectDataSource1(){
return userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1).toString();
}
//使用了注解,则数据源为注解中指定的datasource2
@RequestMapping("/ds2")
@TargetDataSource("datasource2")
public String selectDataSource2(){
return roleMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1).toString();
}
}Test
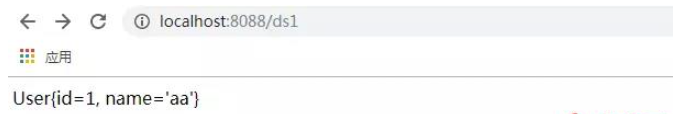
1. Enter
http://localhost:8088/ds1
Return
↓
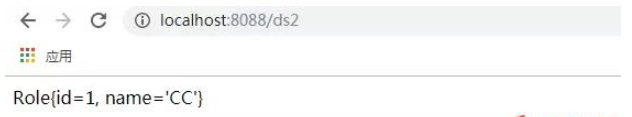
##2. Enter
http://localhost:8088/ds2
↓
The above is the detailed content of How to use mybatis+druid to configure dynamic data sources in springboot. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 mybatis first level cache and second level cache
mybatis first level cache and second level cache
 SpringBoot project building steps
SpringBoot project building steps
 What is the difference between ibatis and mybatis
What is the difference between ibatis and mybatis
 How to configure database connection in mybatis
How to configure database connection in mybatis
 What is the working principle and process of mybatis
What is the working principle and process of mybatis
 What are the differences between hibernate and mybatis
What are the differences between hibernate and mybatis
 What is the difference between j2ee and springboot
What is the difference between j2ee and springboot
 html file opens blank
html file opens blank
 How to cancel automatic renewal at Station B
How to cancel automatic renewal at Station B




