How to configure Nginx for NodeJS application load balancing
Load balancing can allocate user requests to multiple servers for processing, thereby achieving access support for a large number of users. The load balancing architecture is shown in the figure:
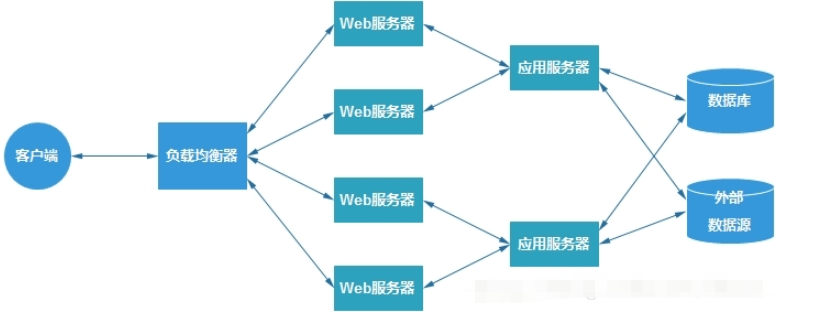
For complex web applications, using nginx for front-end load balancing is a matter of course.
Below, we use nginx for load balancing of nodejs applications.
1. Configure nginx
Modify nginx.conf:
upstream sample {
server 127.0.0.1:3000;
server 127.0.0.1:3001;
keepalive 64;
}
server {
listen 80;
....
server_name 127.0.0.1;
....
location / {
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header x-real-ip $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header x-forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header x-forwarded-proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header host $http_host;
proxy_set_header x-nginx-proxy true;
proxy_set_header connection "";
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass http://sample;
}
}There is a node.js server on port 3000 and port 3001. These two servers are doing the same thing. work. In the upstream section, two node.js servers are configured. In addition, we also set proxy_pass as an http request proxy.
2. Build nodejs server
var http = require('http');
var morgan = require('morgan');
var server1 = http.createserver(function (req, res) {
console.log("request for: " + req.url + "-- port 3000 ");
res.writehead(200, {'content-type': 'text/plain'});
res.end('hello node.js\n');
}).listen(3000, "127.0.0.1");
var server2 = http.createserver(function (req, res) {
console.log("request for: " + req.url + "-- port 3001 ");
res.writehead(200, {'content-type': 'text/plain'});
res.end('hello node.js\n');
}).listen(3001, "127.0.0.1");
server1.once('listening', function() {
console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1:3000/');
});
server2.once('listening', function() {
console.log('server running at http://127.0.0.1:3001/');
});3. Access nginx server
Now we can access
You can see to the following output:
server running at http://127.0.0.1:3000/ server running at http://127.0.0.1:3001/ request for: /-- port 3001 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3000 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3001 request for: /-- port 3000 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3001 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3000 request for: /-- port 3001 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3000 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3001 request for: /-- port 3000 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3001 request for: /favicon.ico-- port 3000
The above is the detailed content of How to configure Nginx for NodeJS application load balancing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
How to run nginx apache
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
To get Nginx to run Apache, you need to: 1. Install Nginx and Apache; 2. Configure the Nginx agent; 3. Start Nginx and Apache; 4. Test the configuration to ensure that you can see Apache content after accessing the domain name. In addition, you need to pay attention to other matters such as port number matching, virtual host configuration, and SSL/TLS settings.
 How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How to create a mirror in docker
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:27 AM
Steps to create a Docker image: Write a Dockerfile that contains the build instructions. Build the image in the terminal, using the docker build command. Tag the image and assign names and tags using the docker tag command.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".




