 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 How to solve the problem of using SpringBoot ApplicationListener event listening interface
How to solve the problem of using SpringBoot ApplicationListener event listening interface
How to solve the problem of using SpringBoot ApplicationListener event listening interface
Let’s reproduce the problem. Look at the code below to see if there is a problem and how to solve it:
@RequestMapping("verify")
@RestController
@DependsOn({"DingAppInfoService","CloudChatAppInfoService"})
public class LoginAction {
@Qualifier("ElderSonService")
@Autowired
private ElderSonService elderSonService;
@Qualifier("EmployeeService")
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Qualifier("UserThreadPoolTaskExecutor")
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor userThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
private static AuthRequest ding_request = null;
private static RongCloud cloud_chat = null;
private static TokenResult register = null;
private static final ThreadLocal<String> USER_TYPE = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 注意不能在bean的生命周期方法上添注@CheckAppContext注解
*/
@PostConstruct
public void beforeVerifySetContext() {
AppContext.fillLoginContext();
Assert.hasText(AppContext.getAppLoginDingId(), "初始化app_login_ding_id错误");
Assert.hasText(AppContext.getAppLoginDingSecret(), "初始化app_login_ding_secret错误");
Assert.hasText(AppContext.getAppLoginReturnUrl(), "初始化app_login_return_url错误");
Assert.hasText(AppContext.getCloudChatKey(), "初始化cloud_chat_key错误");
Assert.hasText(AppContext.getCloudChatSecret(), "初始化cloud_chat_secret错误");
if (!(StringUtils.hasText(AppContext.getCloudNetUri()) || StringUtils.hasText(AppContext.getCloudNetUriReserve()))) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("初始化cloud_net_uri与cloud_net_uri_reserve错误");
}
ding_request = new AuthDingTalkRequest(
AuthConfig.builder().
clientId(AppContext.getAppLoginDingId()).
clientSecret(AppContext.getAppLoginDingSecret()).
redirectUri(AppContext.getAppLoginReturnUrl()).build());
cloud_chat = RongCloud.getInstance(AppContext.getCloudChatKey(), AppContext.getCloudChatSecret());
}
.....以下API方法无所影响......
}What may be puzzling is the code of the initialization method in the controller component:
public static void fillLoginContext() {
DingAppInfo appInfo = SpringContextHolder.getBean(DingAppInfoService.class).findAppInfo(APP_CODE);
setDingVerifyInfo(appInfo);
CloudChatAppInfo cloudChatAppInfo = SpringContextHolder.getBean(CloudChatAppInfoService.class).findAppInfo(APP_CODE);
setCloudChatInfo(cloudChatAppInfo);
}
public static void setDingVerifyInfo(DingAppInfo dingAppInfo){
if (dingAppInfo.checkKeyWordIsNotNull(dingAppInfo)) {
put(APP_LOGIN_DING_ID, dingAppInfo.getApp_id());
put(APP_LOGIN_DING_SECRET, dingAppInfo.getApp_secret());
put(APP_LOGIN_RETURN_URL, dingAppInfo.getApp_return_url());
}
}
public static void setCloudChatInfo(CloudChatAppInfo cloudChatAppInfo){
if (cloudChatAppInfo.checkKeyWordIsNotNull(cloudChatAppInfo)){
put(CLOUD_CHAT_KEY,cloudChatAppInfo.getCloud_key());
put(CLOUD_CHAT_SECRET,cloudChatAppInfo.getCloud_secret());
put(CLOUD_NET_URI,cloudChatAppInfo.getCloud_net_uri());
put(CLOUD_NET_URI_RESERVE,cloudChatAppInfo.getCloud_net_uri_reserve());
}
}You can find here that actually pouring some project customized data into the local thread ThreadLocal
Solution idea (actually this is not the solution, but it can also be done at the cost of high performance):
Design a listener and a publisher in the method of request entry Perform aspect processing. The aspect checks the AppContext object data. If it is empty, the event will be published. If it is not empty, enter the method:
Event prototype:
public class AppContextStatusEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public AppContextStatusEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
public AppContextStatusEvent(Object source, Clock clock) {
super(source, clock);
}
}Listener:
@Component
public class AppContextListener implements ApplicationListener<AppContextStatusEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(AppContextStatusEvent event) {
if ("FillAppContext".equals(event.getSource())) {
AppContext.fillLoginContext();
} else if ("CheckAppContextLogin".equals(event.getSource())) {
boolean checkContext = AppContext.checkLoginContext();
if (!checkContext) {
AppContext.fillLoginContext();
}
}
}
}Publisher (aspect class):
@Aspect
@Component("AppContextAopAutoSetting")
public class AppContextAopAutoSetting {
@Before("@annotation(com.lww.live.ApplicationListener.CheckAppContextLogin)")
public void CheckContextIsNull(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("-----------aop---------CheckAppContextLogin---------start-----");
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
boolean value = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(CheckAppContextLogin.class).value();
if (value){
boolean checkContext = AppContext.checkLoginContext();
if (!checkContext){
SpringContextHolder.pushEvent(new AppContextStatusEvent("FillAppContext"));
}
}
}
@After("@annotation(com.lww.live.ApplicationListener.CheckAppContextLogin)")
public void CheckContextIsNull(){
System.out.println("-----------aop---------CheckAppContextLogin---------end-----");
SpringContextHolder.pushEvent(new AppContextStatusEvent("CheckAppContextLogin"));
}
}Then the AOP aspect class captures the annotation:
@Inherited
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface CheckAppContextLogin {
boolean value() default false;
String info() default "";
}It is not difficult to find that we check first in the pre- and post-enhancement methods of the aspect. AppContext data integrity, and then fill in the data. In this way, it can be achieved if we annotate @CheckAppContextLogin on every request method. However, the problem is that other data except the filled methods are too difficult to maintain, the cost of aspect hijacking agents is too high, and the frequency of checking data is too high.
Correct solution:
Divide according to the business function of the data, because it mainly realizes the filling of two objects. Even if these data are lost, the member variables of the same controller component They are all the same object, and they are all initialized during initialization, so subsequent switching requests will not affect their ability to implement business:
private static AuthRequest ding_request = null; private static RongCloud cloud_chat = null;
We can ask the front end to pass us the current user in the interceptor The user type and unique identifier are used to encapsulate the user-customized data for each request (to reduce the method chain library check operation called within the request):
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String token = (String) request.getSession().getAttribute("token");
String user_type = (String) request.getSession().getAttribute("user_type");
if (StringUtils.hasText(token) && StringUtils.hasText(user_type)) {
Context context = new Context();
if (Objects.equals(user_type, "elder_son")) {
ElderSon elderSon = elderSonService.getElderSonByElderSonId(token);
context.setContextByElderSon(elderSon);
return true;
} else if (Objects.equals(user_type, "employee")) {
Employee employee = employeeService.getEmployeeById(token);
context.setContextByEmployee(employee);
return true;
}
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(user_type)) {
response.sendRedirect("/verify/login?user_type=" + user_type);
return false;
}
return false;
}Finally, don’t forget to remove the ThreadLocal reference:
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
AppContext.clear();
HandlerInterceptor.super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex);
}So the actual scenario is actually solved, the core is the business, and the code simplicity is just an incidental requirement.
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the problem of using SpringBoot ApplicationListener event listening interface. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How Springboot integrates Jasypt to implement configuration file encryption
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
How Springboot integrates Jasypt to implement configuration file encryption
Jun 01, 2023 am 08:55 AM
Introduction to Jasypt Jasypt is a java library that allows a developer to add basic encryption functionality to his/her project with minimal effort and does not require a deep understanding of how encryption works. High security for one-way and two-way encryption. , standards-based encryption technology. Encrypt passwords, text, numbers, binaries... Suitable for integration into Spring-based applications, open API, for use with any JCE provider... Add the following dependency: com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter2. 1.1Jasypt benefits protect our system security. Even if the code is leaked, the data source can be guaranteed.
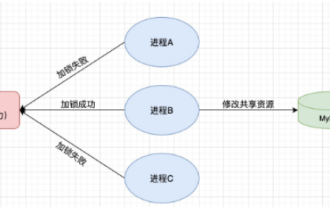 How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
How to use Redis to implement distributed locks in SpringBoot
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:16 AM
1. Redis implements distributed lock principle and why distributed locks are needed. Before talking about distributed locks, it is necessary to explain why distributed locks are needed. The opposite of distributed locks is stand-alone locks. When we write multi-threaded programs, we avoid data problems caused by operating a shared variable at the same time. We usually use a lock to mutually exclude the shared variables to ensure the correctness of the shared variables. Its scope of use is in the same process. If there are multiple processes that need to operate a shared resource at the same time, how can they be mutually exclusive? Today's business applications are usually microservice architecture, which also means that one application will deploy multiple processes. If multiple processes need to modify the same row of records in MySQL, in order to avoid dirty data caused by out-of-order operations, distribution needs to be introduced at this time. The style is locked. Want to achieve points
 How SpringBoot integrates Redisson to implement delay queue
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
How SpringBoot integrates Redisson to implement delay queue
May 30, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
Usage scenario 1. The order was placed successfully but the payment was not made within 30 minutes. The payment timed out and the order was automatically canceled. 2. The order was signed and no evaluation was conducted for 7 days after signing. If the order times out and is not evaluated, the system defaults to a positive rating. 3. The order is placed successfully. If the merchant does not receive the order for 5 minutes, the order is cancelled. 4. The delivery times out, and push SMS reminder... For scenarios with long delays and low real-time performance, we can Use task scheduling to perform regular polling processing. For example: xxl-job Today we will pick
 How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
How to solve the problem that springboot cannot access the file after reading it into a jar package
Jun 03, 2023 pm 04:38 PM
Springboot reads the file, but cannot access the latest development after packaging it into a jar package. There is a situation where springboot cannot read the file after packaging it into a jar package. The reason is that after packaging, the virtual path of the file is invalid and can only be accessed through the stream. Read. The file is under resources publicvoidtest(){Listnames=newArrayList();InputStreamReaderread=null;try{ClassPathResourceresource=newClassPathResource("name.txt");Input
 Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Comparison and difference analysis between SpringBoot and SpringMVC
Dec 29, 2023 am 11:02 AM
SpringBoot and SpringMVC are both commonly used frameworks in Java development, but there are some obvious differences between them. This article will explore the features and uses of these two frameworks and compare their differences. First, let's learn about SpringBoot. SpringBoot was developed by the Pivotal team to simplify the creation and deployment of applications based on the Spring framework. It provides a fast, lightweight way to build stand-alone, executable
 How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
How SpringBoot customizes Redis to implement cache serialization
Jun 03, 2023 am 11:32 AM
1. Customize RedisTemplate1.1, RedisAPI default serialization mechanism. The API-based Redis cache implementation uses the RedisTemplate template for data caching operations. Here, open the RedisTemplate class and view the source code information of the class. publicclassRedisTemplateextendsRedisAccessorimplementsRedisOperations, BeanClassLoaderAware{//Declare key, Various serialization methods of value, the initial value is empty @NullableprivateRedisSe
 How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
How to implement Springboot+Mybatis-plus without using SQL statements to add multiple tables
Jun 02, 2023 am 11:07 AM
When Springboot+Mybatis-plus does not use SQL statements to perform multi-table adding operations, the problems I encountered are decomposed by simulating thinking in the test environment: Create a BrandDTO object with parameters to simulate passing parameters to the background. We all know that it is extremely difficult to perform multi-table operations in Mybatis-plus. If you do not use tools such as Mybatis-plus-join, you can only configure the corresponding Mapper.xml file and configure The smelly and long ResultMap, and then write the corresponding sql statement. Although this method seems cumbersome, it is highly flexible and allows us to
 How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
How to get the value in application.yml in springboot
Jun 03, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
In projects, some configuration information is often needed. This information may have different configurations in the test environment and the production environment, and may need to be modified later based on actual business conditions. We cannot hard-code these configurations in the code. It is best to write them in the configuration file. For example, you can write this information in the application.yml file. So, how to get or use this address in the code? There are 2 methods. Method 1: We can get the value corresponding to the key in the configuration file (application.yml) through the ${key} annotated with @Value. This method is suitable for situations where there are relatively few microservices. Method 2: In actual projects, When business is complicated, logic





