Redis transaction instance analysis
Usage in Redis
Redis implements transaction functions through multi, exec, discard, and watch.
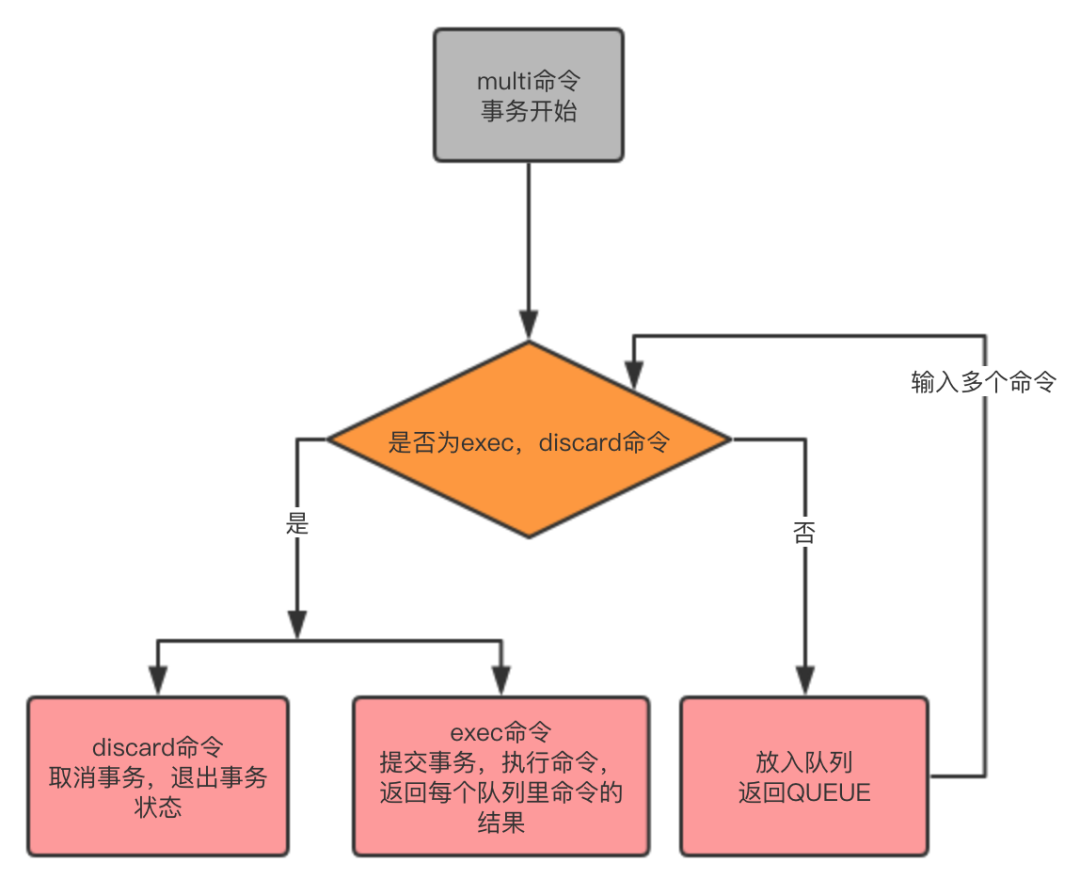
multi: start transaction
exec: commit transaction and execute
discard: cancel transaction
watch: Monitor any number of keys before the transaction starts
> multi OK > set bookName "Redis" QUEUED > get bookName QUEUED > sadd tag "Redis" "New Book" QUEUED > smembers tag QUEUED > exec 1) OK 2) "Redis" 3) (integer) 2 4) 1) "Redis" 2) "New Book"
Start transaction
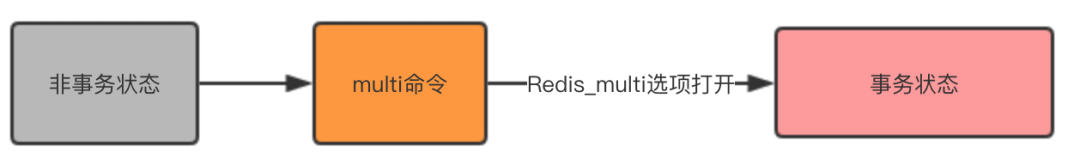
> multi OK
This command turns on the Redis_multi option , let the client change from non-transactional state to transactional state
Command enqueue
> set bookName "Redis" QUEUED > get bookName QUEUED > sadd tag "Redis" "New Book" QUEUED > smembers tag QUEUED
The Redis command will not be executed immediately, but will first enter an advanced First out of the transaction queue until the transaction is committed. QUEUED indicates that this command has been entered into the transaction queue.
Execute transactions
> exec 1) OK 2) "Redis" 3) (integer) 2 4) 1) "Redis" 2) "New Book"
When executing the exec command, Redis executes the commands in the transaction queue in a first-in, first-out manner according to the transaction queue saved by the client: the first command to be queued Executed first, and the last command enqueued is executed last. After executing the exec command, Redis stores the results in the reply queue and sends the queue to the client. The client exits from the transaction state and a transaction is completed.
discard command
> multi OK > set author "lisi" QUEUED > discard OK > get author (nil)
discard is a command to cancel a transaction, indicating that the transaction has been cancelled. When the client ends the transaction state and returns to the non-transaction state, the Redis_multi option needs to be turned off.
watch command
# Redis 客户端1 > watch letter OK > multi OK > set letter a QUEUED > exec (nil) # Redis 客户端2 > set letter b OK # Redis 客户端1 > get letter "b"
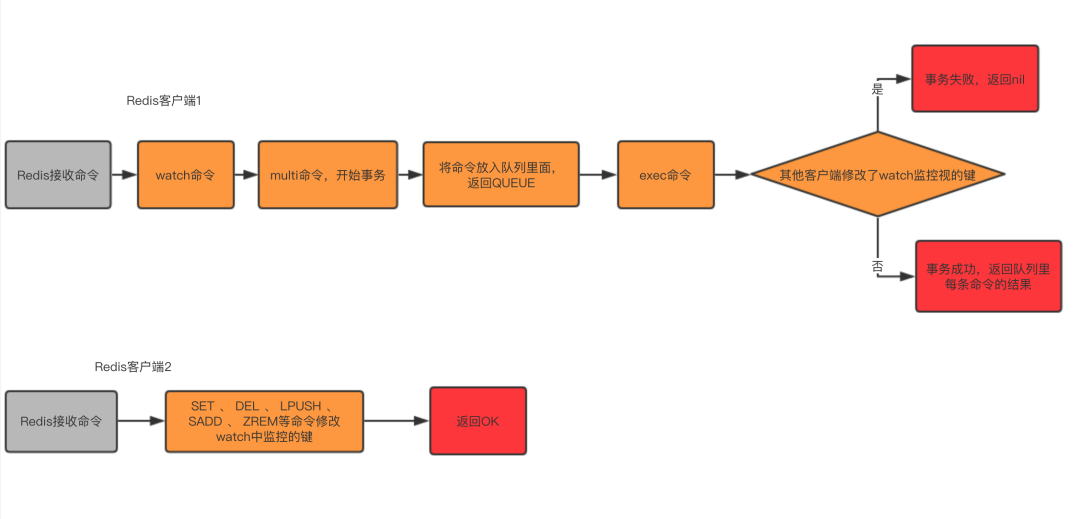
When client 1 enters the transaction, the watch sets the letter key and sets its value to a, but the transaction has not yet submit. Client 2 sets the value of letter to b. After client 1 commits the transaction, the result returned is nil, but by calling the get command, the value of letter can be obtained as b. This means that when the letter key is changed by another client, the transaction will be canceled, will not be executed, and will fail.
The watch command monitors any number of keys before the transaction starts: when calling the excel command to execute a transaction, if any of the monitored keys has been modified by other clients, the entire transaction will no longer be executed and will return directly. fail.
Transaction exception
Command error
> set letter ac QUEUED > get letter ac (error) ERR wrong number of arguments for 'get' command > exec (error) EXECABORT Transaction discarded because of previous errors.
Command exception in the transaction is a syntax error and will cause the transaction to fail to be executed.
Runtime exception
> multi OK > lpush books "Redis" QUEUED > incr books QUEUED > lpush books "Python" QUEUED > lrange books 0 -1 QUEUED > exec 1) (integer) 1 2) (error) WRONGTYPE Operation against a key holding the wrong kind of value 3) (integer) 2 4) 1) "Python" 2) "Redis"
The above example is that the transaction encountered a failure in the middle of execution, because the incr command cannot be performed on a string. After the transaction encounters a command execution failure, subsequent The command continues to execute, so the value of books continues to be set. This exception can only be avoided by programmers in their code.
ACID of transactions
Atomicity
Atomic means that either they execute successfully together or they fail together and are rolled back. All APIs provided by Redis are atomic operations. Then the Redis transaction only needs to guarantee atomicity in a batch of operations. However, in the case of runtime exceptions, if an exception occurs in a command in a transaction, other commands will continue to be executed. There is no rollback mechanism for the transaction, so the Redis transaction is not guaranteed to be atomic. sexual.
Consistency
Transaction exception
If the command error occurs, the transaction cannot be executed. If it is a runtime exception, Redis will include the error in the return result and will not affect subsequent execution. , so the transaction is consistent.
The Redis process is terminated
In pure memory mode, Redis does not perform persistence. After restarting, the database is blank, so it is transactionally consistent.
In RDB mode, the transaction will not perform the work of saving the RDB file in the middle. The RDB work may start only after the transaction is completed. Therefore, the Redis process is killed during transaction execution, and no matter how successful it is, it will not be saved to the RDB file, so it is consistent.
In AOF mode, part of the transaction statement is written to the AOF file and saved successfully. Incomplete transactions are saved to the AOF file. When restarting Redis, check that the AOF file is incomplete, and Redis exits with an error. This incomplete transaction needs to be deleted before the restart can be successful, so it is consistent.
In AOF mode, transactions are not written to the AOF file, so after restarting the Redis database is the latest data successfully saved to the AOF file. There is no data for this transaction, so it is consistent.
Isolation
Redis is a single-process program, and it guarantees that the transaction will not be interrupted when executing the transaction. The transaction can run until all commands in the transaction queue are executed. So transactions are isolated.
Persistence
In pure memory mode, transactions are definitely not persistent.
In RDB mode, the server may fail during the period after the transaction is executed and before the RDB file is updated, so transactions in RDB mode are not durable.
In AOF mode, add the command to the AOF file, but writing the file will not be written to the disk immediately, but will be stored in the buffer first. So there is a very small interval between data being saved to disk. Transactions in this mode are not durable either.
The above is the detailed content of Redis transaction instance analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




