How to solve the problem of using Pipelining to speed up queries in Redis
Request/Response protocols and RTT
Redis is a client-server mode TCP service, also known as the implementation of the Request/Response protocol.

This means that usually the completion of a request follows the following two steps:
Client sends an operation command to the Server, Read the Server's response value from the TCP socket. Generally speaking, this is a blocking method.
Server executes the operation command and then returns the response value to the Client
For example
Client: INCR X Server: 1 Client: INCR X Server: 2 Client: INCR X Server: 3 Client: INCR X Server: 4
Clients and Servers are connected through the network. Network connections can be very fast (such as a local loopback network) or very slow (such as a network that spans multiple hosts). No matter what the network is like, it takes a certain amount of time for a data packet to go from the Client to the Server, and then the corresponding value is returned from the Server to the Client.
This time is called RTT (Round Trip Time). When a Client needs to perform multiple consecutive requests (such as adding many elements to a list, or clearing many key-value pairs in Redis), how does RTT affect performance? This is also very convenient to calculate. For example, if the RTT time is 250ms (assuming the Internet connection is very slow), even if the server can handle 100k requests per second, it can only accept up to 4 requests per second.
If it is a loopback network, the RTT will be particularly short (for example, the author's 127.0.0.1, the RTT response time is 44ms), but it will also consume a lot of money when performing multiple consecutive write operations. .
Actually, we have other ways to reduce consumption in this scenario, are you happy? Surprise?
Redis Pipelining
There is a feature in a Request/Response style service: even if the Client does not receive the previous response value, it can continue to send new requests. . This feature means that we do not need to wait for the server's response. We can send many operation commands to the server first, and then read all the server's response values at once.
This method is called Pipelining technology, which has been widely used in recent decades. For example, the implementation of multiple POP3 protocols supports this feature, which greatly improves the speed of downloading new emails from the server.
Redis has supported this technology very early, so no matter what version you are running, you can use the pipelining technology. For example, here is one using the netcat tool:
$ (printf "PING\r\nPING\r\nPING\r\n"; sleep 1) | nc localhost 6379 +PONG +PONG +PONG
Now we don’t need to pay RTT for each request, but send three operation commands at once. In order to facilitate intuitive understanding, let’s take the previous instructions and use the pipelining technology. The implementation sequence is as follows:
Client: INCR X Client: INCR X Client: INCR X Client: INCR X Server: 1 Server: 2 Server: 3 Server: 4
Highlight (knock on the blackboard): When the client uses pipeliningWhen sending an operation command, the server will force the use of memory to arrange the response results. Therefore, when using pipelining to send a large number of operation commands, it is best to determine a reasonable number of commands and send them to the server in batches. For example, send 10k operation commands and read the response results. Send another 10k operation commands, and so on... Although the time consumption is almost the same, the additional memory consumption will be the maximum value required for the arrangement response result of these 10k operation commands. (To prevent memory exhaustion, choose a reasonable value)
It’s not just a matter of RTT
Pipeliningis not the only way to reduce consumption caused by RTT , but it does help you greatly increase the number of commands executed per second. The truth of the matter is: from the perspective of accessing the corresponding data structure and generating the reply result, not using pipelining is indeed very cheap; but from the perspective of socket I/O, it is just the opposite. . Because this involves read() and write() calls, you need to switch from user mode to kernel mode. This kind of context switching will be particularly time-consuming.
Once pipelining technology is used, many operation commands will perform read operations from the same read() call, and a large number of reply results will be distributed to The write operation is performed in the same write() call. Based on this, as the length of the pipeline increases, the number of queries executed per second initially increases almost linearly until it is 10 times the baseline without using pipelining technology, as shown below:
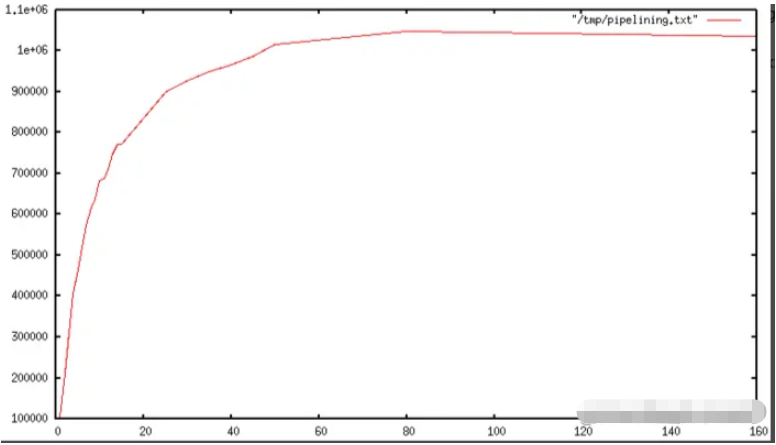
Some real world code example
is not translated, basically it means using pipelining to improve the performance by 5 times.
Pipelining VS Scripting
Redis Scripting(2.6+版本可用),通过使用在Server端完成大量工作的脚本Scripting,可以更加高效的解决大量pipelining用例。使用脚本Scripting的最大好处就是在读和写的时候消耗更少的性能,使得像读、写、计算这样的操作更加快速。(当client需要写操作之前获取读操作的响应结果时,pepelining就显得相形见拙。) 有时候,应用可能需要在使用pipelining时,发送 EVAL 或者 EVALSHA 命令,这是可行的,并且Redis明确支持这么这种SCRIPT LOAD命令。(它保证可可以调用 EVALSHA 而不会有失败的风险)。
Appendix: Why are busy loops slow even on the loopback interface?
读完全文,你可能还会感到疑问:为什么如下的Redis测试基准 benchmark 会执行这么慢,甚至在Client和Server在一个物理机上也是如此:
FOR-ONE-SECOND:
Redis.SET("foo","bar")
END毕竟Redis进程和测试基准benchmark在相同的机器上运行,并且这是没有任何实际的延迟和真实的网络参与,不就是消息通过内存从一个地方拷贝到另一个地方么? 原因是进程在操作系统中并不是一直运行。真实的情景是系统内核调度,调度到进程运行,它才会运行。比如测试基准benchmark被允许运行,从Redis Server中读取响应内容(与最后一次执行的命令相关),并且写了一个新的命令。这时命令将在回环网络的套接字中,但是为了被Redis Server读取,系统内核需要调度Redis Server进程(当前正在系统中挂起),周而复始。所以由于系统内核调度的机制,就算是在回环网络中,仍然会涉及到网络延迟。 简言之,在网络服务器中衡量性能时,使用回环网络测试并不是一个明智的方式。应该避免使用此种方式来测试基准。
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the problem of using Pipelining to speed up queries in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




