Redis command processing example source code analysis
This article is based on the community version of Redis 4.0.8
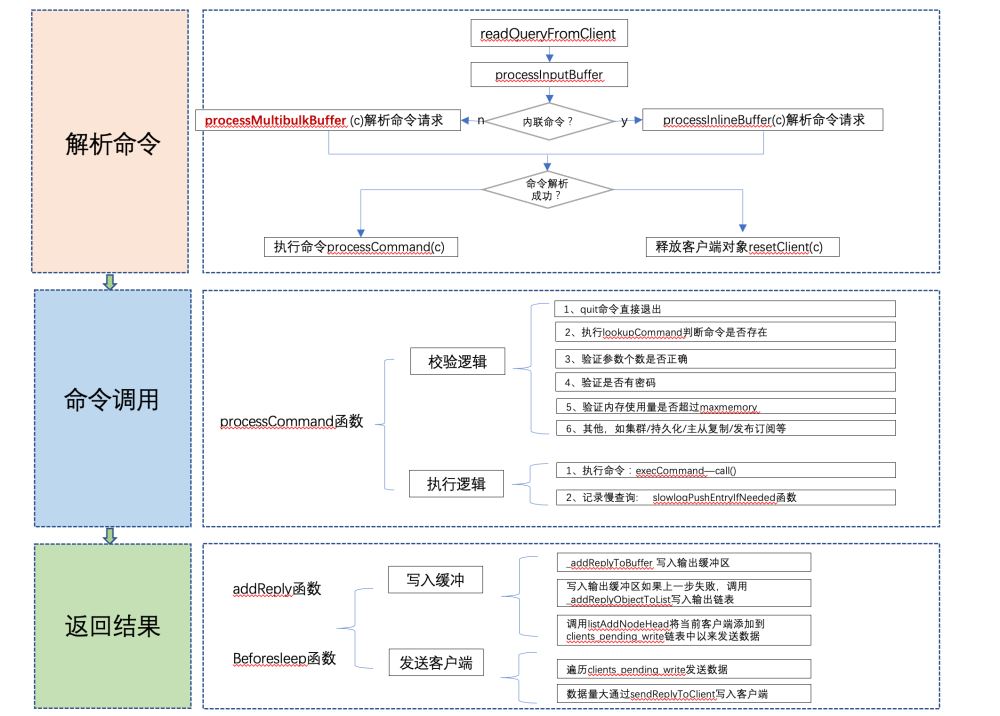
1. Command analysis
The command request received by the Redis server is first stored in the client object The querybuf input buffer then parses the various parameters of the command request and stores them in the argv and argc fields of the client object.
The entry function for the client to parse the command request is readQueryFromClient, which reads the socket data and stores it in the input buffer of the client object, and calls the function processInputBuffer to parse the command request.
Note: Inline command: Use the telnet session to enter the command
void processInputBuffer(client *c) {
......
//循环遍历输入缓冲区,获取命令参数,调用processMultibulkBuffer解析命令参数和长度
while(sdslen(c->querybuf)) {
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_INLINE) {
if (processInlineBuffer(c) != C_OK) break;//处理telnet方式的内联命令
} else if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK) {
if (processMultibulkBuffer(c) != C_OK) break; //解析命令参数和长度暂存到客户端结构体中
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown request type");
}
}
}
//解析命令参数和长度暂存到客户端结构体中
int processMultibulkBuffer(client *c) {
//定位到行尾
newline = strchr(c->querybuf,'\r');
//解析命令请求参数数目,并存储在客户端对象的c->multibulklen字段
serverAssertWithInfo(c,NULL,c->querybuf[0] == '*');
ok = string2ll(c->querybuf+1,newline-(c->querybuf+1),&ll);
c->multibulklen = ll;
pos = (newline-c->querybuf)+2;//记录已解析命令的请求长度resp的长度
/* Setup argv array on client structure */
//分配请求参数存储空间
c->argv = zmalloc(sizeof(robj*)*c->multibulklen);
// 开始循环解析每个请求参数
while(c->multibulklen) {
......
newline = strchr(c->querybuf+pos,'\r');
if (c->querybuf[pos] != '$') {
return C_ERR;
ok = string2ll(c->querybuf+pos+1,newline-(c->querybuf+pos+1),&ll);
pos += newline-(c->querybuf+pos)+2;
c->bulklen = ll;//字符串参数长度暂存在客户端对象的bulklen字段
//读取该长度的参数内容,并创建字符串对象,同时更新待解析参数multibulklen
c->argv[c->argc++] =createStringObject(c->querybuf+pos,c->bulklen);
pos += c->bulklen+2;
c->multibulklen--;
}2. Command call
When the value of multibulklen is updated to 0, it means that the parameter parsing is completed. Start calling processCommand to process the command. There is a lot of verification logic before processing the command, as follows:
void processInputBuffer(client *c) {
......
//调用processCommand来处理命令
if (processCommand(c) == C_OK) {
......
}
}
//处理命令函数
int processCommand(client *c) {
//校验是否是quit命令
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr,"quit")) {
addReply(c,shared.ok);
c->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
return C_ERR;
}
//调用lookupCommand,查看该命令是否存在
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
if (!c->cmd) {
flagTransaction(c);
addReplyErrorFormat(c,"unknown command '%s'",
(char*)c->argv[0]->ptr);
return C_OK;
//检查用户权限
if (server.requirepass && !c->authenticated && c->cmd->proc != authCommand)
{
addReply(c,shared.noautherr);
//还有很多检查,不一一列举,比如集群/持久化/复制等
/* 真正执行命令 */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand)
queueMultiCommand(c);
//将结果写入outbuffer
addReply(c,shared.queued);
}
// 调用execCommand执行命令
void execCommand(client *c) {
call(c,CMD_CALL_FULL);//调用call执行命令
//调用execCommand调用call执行命令
void call(client *c, int flags) {
start = ustime();
c->cmd->proc(c);//执行命令
duration = ustime()-start;
//如果是慢查询,记录慢查询
if (flags & CMD_CALL_SLOWLOG && c->cmd->proc != execCommand) {
char *latency_event = (c->cmd->flags & CMD_FAST) ?
"fast-command" : "command";
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded(latency_event,duration/1000);
//记录到慢日志中
slowlogPushEntryIfNeeded(c,c->argv,c->argc,duration);
//更新统计信息:当前命令执行时间和调用次数
if (flags & CMD_CALL_STATS) {
c->lastcmd->microseconds += duration;
c->lastcmd->calls++;3. Return result
The result returned by Redis is not directly returned to the client, but written first Enter the output buffer (buf field) or output linked list (reply field)
int processCommand(client *c) {
......
//将结果写入outbuffer
addReply(c,shared.queued);
......
}
//将结果写入outbuffer
void addReply(client *c, robj *obj) {
//调用listAddNodeHead将客户端添加到服务端结构体的client_pending_write链表,以便后续能快速查找出哪些客户端有数据需要发送
if (prepareClientToWrite(c) != C_OK) return;
//然后添加字符串到输出缓冲区
if (_addReplyToBuffer(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr)) != C_OK)
//如果添加失败,则添加到输出链表中
_addReplyObjectToList(c,obj);
}The addReply function only temporarily stores the data to be sent to the client in the output linked list or output buffer, then when will the data be sent to What about the client? The answer is the beforesleep function called when the event loop is turned on. This function specifically performs some operations that are not very time-consuming, such as deleting expired keys, returning command replies to the client, etc.
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
......
/* Handle writes with pending output buffers. */
handleClientsWithPendingWrites();
}
//回复客户端命令函数
int handleClientsWithPendingWrites(void) {
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_write);
listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE;
listDelNode(server.clients_pending_write,ln);
/* 发送客户端数据 */
if (writeToClient(c->fd,c,0) == C_ERR) continue;
/* If there is nothing left, do nothing. Otherwise install
* the write handler. */
//如果数据量很大,一次性没有发送完成,则进行添加文件事件,监听当前客户端socket文件描述符的可写事件即可
if (clientHasPendingReplies(c) &&
aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, c->fd, AE_WRITABLE,
sendReplyToClient, c) == AE_ERR)
{
freeClientAsync(c);
}
}
return processed;The above is the detailed content of Redis command processing example source code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1375
1375
 52
52
 How is the redis cluster implemented
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
How is the redis cluster implemented
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:27 PM
Redis cluster is a distributed deployment model that allows horizontal expansion of Redis instances, and is implemented through inter-node communication, hash slot division key space, node election, master-slave replication and command redirection: inter-node communication: virtual network communication is realized through cluster bus. Hash slot: divides the key space into hash slots to determine the node responsible for the key. Node election: At least three master nodes are required, and only one active master node is ensured through the election mechanism. Master-slave replication: The master node is responsible for writing requests, and the slave node is responsible for reading requests and data replication. Command redirection: The client connects to the node responsible for the key, and the node redirects incorrect requests. Troubleshooting: fault detection, marking off line and re-
 How is the key unique for redis query
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:03 PM
How is the key unique for redis query
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:03 PM
Redis uses five strategies to ensure the uniqueness of keys: 1. Namespace separation; 2. HASH data structure; 3. SET data structure; 4. Special characters of string keys; 5. Lua script verification. The choice of specific strategies depends on data organization, performance, and scalability requirements.
 How to handle redis transactions
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:24 PM
How to handle redis transactions
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:24 PM
Redis transactions ensure atomicity, consistency, isolation, and persistence (ACID) properties, and operate as follows: Start a transaction: Use the MULTI command. Record command: Execute any number of Redis commands. Commit or rollback transactions: Use the EXEC command to commit the transaction, or the DISCARD command to rollback transactions. Commit: If there is no error, the EXEC command commits the transaction and all commands are applied atomically to the database. Rollback: If there is an error, the DISCARD command rolls back the transaction, all commands are discarded, and the database status remains unchanged.
 How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
To view all keys in Redis, there are three ways: use the KEYS command to return all keys that match the specified pattern; use the SCAN command to iterate over the keys and return a set of keys; use the INFO command to get the total number of keys.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Redis Ordered Sets (ZSets) are used to store ordered elements and sort by associated scores. The steps to use ZSet include: 1. Create a ZSet; 2. Add a member; 3. Get a member score; 4. Get a ranking; 5. Get a member in the ranking range; 6. Delete a member; 7. Get the number of elements; 8. Get the number of members in the score range.
 How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
To view the Redis version number, you can use the following three methods: (1) enter the INFO command, (2) start the server with the --version option, and (3) view the configuration file.
 How to optimize memory with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
How to optimize memory with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:24 PM
To optimize Redis memory usage, you can take the following steps: Use appropriate data structures such as hash tables, lists, compressed lists, or hash tables. Enable compression to compress duplicate data. Use object sharing to store similar objects. Limit the number of keys and group the relative keys using hash tags. Delete expired keys and use persistence to prevent data loss. Use RDB or AOF as a persistence method to monitor memory usage and use a Redis memory server. Use space-efficient data structures, disable lazy expiration, and control the number of compressed list entries in zset.




