How to use redis bit operations
The redis test code in this article is based on the following environment:
Operating system: Mac OS 64 bit
Version: Redis 5.0.7 64 bit
Running mode: standalone mode
redis bit operation
reids bit operation is also called bit array operation and bitmap. It provides four commands: SETBIT, GETBIT, BITCOUNT, and BITTOP for operating binary bit arrays.
Let’s take a look at a basic operation example
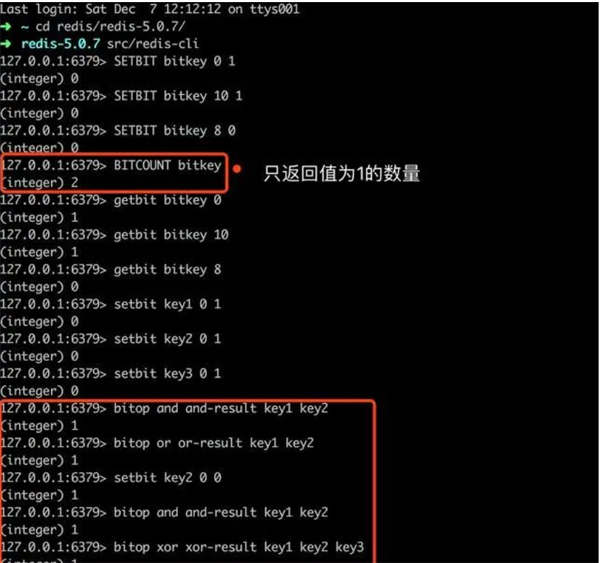
SETBIT
Syntax: SETBIT key offset value
That is: Command key offset 0/1
The setbit command is used to write the binary bit setting value of the specified offset in the bit array, The offset starts counting from 0, and only 1 or 0 is allowed to be written. If a value other than 0 and 1 is written, the writing fails:

GETBIT
Syntax: GETBIT key offset
That is: Command key offset
The gitbit command is used to obtain Binary value at the specified offset in the bit array:

BITCOUNT
Syntax: BITCOUNT key
That is: Command key
The bitcount command is used to get the number of binary bits with a value of 1 in the bit array of the specified key. Before we wrote the offset 0 has a value of 1, offset 10 has a value of 1, and offset 8 has a value of 0:

BITOP
Syntax: BITOP operation destkey key [key...]
That is: Command operation result target key key1 key2...
bitop The command can perform and (bitwise AND), or (bitwise OR), xor (bitwise exclusive OR) operations on the keys of multiple bit arrays, and set the operation results to destkey:

Underlying data structure analysis
SDS is a data structure in redis, called Simple Dynamic String, and it is a binary Safe, in most cases strings in redis are stored using SDS.
Data structure of SDS:
struct sdshdr { #记录buff数组中已使用字节的数量 #也是SDS所保存字符串的长度 int len; #记录buff数组中未使用字节的数量 int free; #字节数组,字符串就存储在这个数组里 char buff[]; }Data storage example:
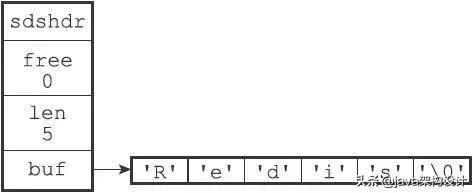
## Advantages of #SDS:
- Hongmeng official strategic cooperation and co-construction - HarmonyOS technology community
- Time complexity is O(1)
- Prevent buffer overflow
- Reduce the number of memory reallocations required when modifying the string length
- Binary safe API operation
- Compatible with some C string functions
The bit array in redis is stored in the String string data format, and the string object uses the SDS simple dynamic string data structure mentioned above.
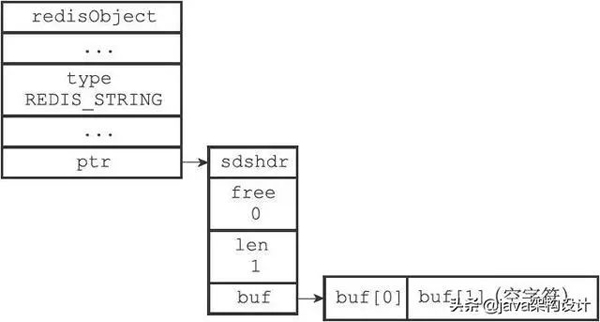 Picture source "Redis Design and Implementation"
Picture source "Redis Design and Implementation"
Everyone knows that a byte is stored with 8 binary bits, that is 8 0s or 1s, that is, one byte can store decimal numbers from 0 to 127, which includes all numbers, English upper and lower case letters, and punctuation marks.
1Byte=8bitBit array In the redis storage world, each byte is also 8 bits, and the initial value is:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
The bit operation is to set 0 or 1 on the corresponding offset offset, for example, set the third bit to 1, that is:
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 #对应redis操作即: setbit key 3 1
Based on this, if you want to set the offset to 13 The position is set to 1, that is:
setbit key 13 1 #对应redis中的存储为: 0 0 1 0 | 0 0 0 0 | 0 0 0 0 | 1 0 0 0
##GETBIT command time complexity O(1)
STEBIT command time complexity O(1)
BITCOUNT command time complexity O(n)
The time complexity of the BITOP command is O(n), O(n2)
Let’s look at why the time complexity of the GETBIT and SETBIT commands is O(1). When we When executing a SETBIT key 10086 1 value, reids are calculated as follows:
Get which byte to be written in the bit array: 10086÷8=1260, which needs to be written to the subscript of the bit array The byte of 1260Gets the number of this byte to be written: 10086 mod 8 = 6. It needs to be written to the index of this byte which is 6, that is, the 7th bit.Through these two calculation methods, you can clearly see that GETBIT and SETBIT of bit operations are constant calculations, so their time complexity is O(1).
The BITCOUNT command needs to traverse all the elements of the entire bit array to calculate how many elements have a value of 1. Of course, redis will have a set of complex optimization algorithms for executing the bitcount command on bits with big data, but the core The idea is still the same, it is nothing more than reducing the number of partial traversal queries. If 128 bits are explicitly used as one traversal, then the number of times he needs to traverse is equal to all the digits divided by 128.
The BITTOP command has different execution methods according to different operations. For example, for AND operation, you need to check the bit value is 1.
Storage Space Calculation
Based on the above introduction, we can know how to calculate the memory size occupied by using the Redis-based bit array data structure to store data. For example, if there are 10 billion data, then the byte array it requires:
1000000000÷8÷1024÷1024≈119.21MB
That is, only about 119MB of memory is needed to store 1 billion data Space, this is no problem at all for the 16G and 32G cluster versions of redis that are now available.
It should be noted that if the amount of your data is not large, then don’t make the starting offset very large. This will also take up space. For example, we only need to store a few hundred pieces of data, but The offset is very large, which will cause a lot of waste of memory space.
Application scenarios
In actual project development, there are many businesses that are suitable to be implemented using redis bits.
User sign-in scenario
The daily date string is used as a key, the user ID is used as the offset, and the daily user sign-in status is counted, and the total user sign-in number
Statistics on the number of active users
User daily activity, monthly activity, retention rate, etc. can be stored using redis bit arrays, or use the daily date as the key. Write when the user is active Enter offset as the bit value 1 of the user ID.
The same goes for monthly living expenses.
Whether the user is online and the total number of people online
Use the same bit array, set the bit offset of the user ID mapping to 1 to indicate online, and to 0 Indicates offline. This can realize user online and offline queries and statistics of the total number of people online
The global message prompt of users in the APP is a red dot
Now most APPs have in-site With the message function, when there is a message, a small red dot will be prompted, indicating that the user has new messages.
The above is the detailed content of How to use redis bit operations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




