What are the ways to establish the Redis master-slave architecture?
Master-slave environment construction
Redis instances are all master nodes by default, so we need to modify some configurations to build a master-slave architecture. The master-slave architecture of redis is relatively simple to build. Redis Three ways are provided to build a master-slave architecture, which we will introduce later. Before introducing, we must first understand the characteristics of the master-slave architecture: In the master-slave architecture, there is a master node (master) and at least one slave node (slave). ), and data replication is one-way, it can only be copied from the master node to the slave node, not from the slave node to the master node.
How to establish the master-slave architecture
There are three ways to establish the master-slave architecture:
In Redis. Add the slaveof {masterHost} {masterPort} command to the conf configuration file, which will take effect when the Redis instance is started.
Add the --slaveof {masterHost} {masterPort} parameter after the redis-server startup command
Use the command directly in the redis-cli interactive window: slaveof {masterHost} {masterPort}
The above three methods can build Redis For the master-slave architecture, we will demonstrate the first method and try the other two methods by ourselves. Since it is a demonstration, we will start two Redis instances locally instead of starting redis instances on multiple machines. We will prepare a port. For the master node instance of 6379, prepare an instance of the slave node with port 6480. Name the redis instance configuration file of port 6480 6480.conf and add the slaveof statement in it. Add the following statement at the end of the configuration file.
slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379
Start two redis instances respectively. After starting, they will automatically establish a master-slave relationship. Regarding the principle behind this, we will talk in detail later. First, let’s verify whether our master-slave architecture is established. Successfully, we first add a new piece of data on the 6379 master node:
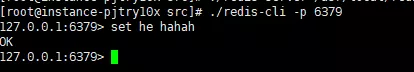
The master node adds new data
and then obtain the data on the 6480 slave node:
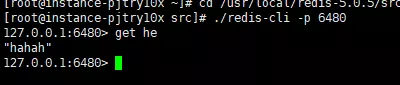
slave node obtains data
It can be seen that we have successfully obtained the new value on the master node on the slave node, indicating the master-slave architecture. It has been set up successfully. We use the info replication command to view the information of the two nodes. Let’s first look at the information of the master node.
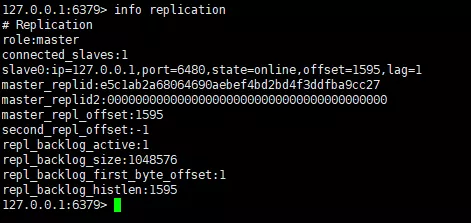
master info replication
It can be seen that the instance role of port 6379 is master, there is an instance being connected, and there is other running information. We Let's take a look at the redis instance information of port 6480.
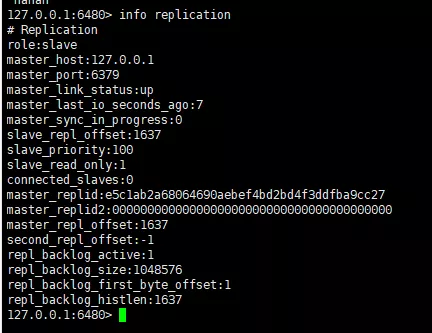
slave info replication
It can be observed that the two nodes record object information between each other, and this information will be used during data replication. One thing needs to be explained here. By default, the slave node is read-only and does not support writing. It is not recommended to enable writing. We can verify it and write a piece of data on the 6480 instance.
127.0.0.1:6480> set x 3 (error) READONLY You can't write against a read only replica. 127.0.0.1:6480>
The prompt is read-only and does not support write operations. Of course, we can also modify the configuration. In the configuration file, the replica-read-only yes configuration item is used to control read-only from the server. Why only Can it be read-only? Because we know that replication is one-way, and data can only be sent from the master to the slave node. If writing is enabled on the slave node, then the data of the slave node is modified, and the master node cannot sense it. The slave node The data cannot be copied to the master node, which will cause data inconsistency, so it is recommended that the slave node be read-only.
Disconnection of the master-slave architecture
The disconnection of the master-slave architecture is also the slaveof command. Execute the slaveof no one command on the slave node to disconnect from the master node. To open the following relationship, we execute the slaveof no one command on node 6480.
127.0.0.1:6480> slaveof no one OK 127.0.0.1:6480> info replication # Replication role:master connected_slaves:0 master_replid:a54f3ba841c67762d6c1e33456c97b94c62f6ac0 master_replid2:e5c1ab2a68064690aebef4bd2bd4f3ddfba9cc27 master_repl_offset:4367 second_repl_offset:4368 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1 repl_backlog_histlen:4367 127.0.0.1:6480>
After executing the slaveof no one command, the role of the 6480 node is immediately restored to master. Let's take a look again and see that it is still connected to the 6379 instance. We add a new key-value on the 6379 node.
127.0.0.1:6379> set y 3 OK
Get y on the 6480 node
127.0.0.1:6480> get y (nil) 127.0.0.1:6480>
Cannot get y on the 6480 node, because the 6480 node has been disconnected from the 6379 node, and there is no master-slave relationship, slaveof command Not only can the connection be disconnected, but also the master server can be switched. The command is slaveof {newMasterIp} {newMasterPort}. We make 6379 the slave node of 6480 and execute the slaveof 127.0.0.1 6480 command on the 6379 node. Let's take a look at 6379 info replication.
127.0.0.1:6379> info replication # Replication role:slave master_host:127.0.0.1 master_port:6480 master_link_status:up master_last_io_seconds_ago:2 master_sync_in_progress:0 slave_repl_offset:4367 slave_priority:100 slave_read_only:1 connected_slaves:0 master_replid:99624d4b402b5091552b9cb3dd9a793a3005e2ea master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 master_repl_offset:4367 second_repl_offset:-1 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:4368 repl_backlog_histlen:0 127.0.0.1:6379>
6379 The role of the node is already slave, and the master node is 6480. We can look at the info replication of the 6480 node.
127.0.0.1:6480> info replication # Replication role:master connected_slaves:1 slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6379,state=online,offset=4479,lag=1 master_replid:99624d4b402b5091552b9cb3dd9a793a3005e2ea master_replid2:a54f3ba841c67762d6c1e33456c97b94c62f6ac0 master_repl_offset:4479 second_repl_offset:4368 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1 repl_backlog_histlen:4479 127.0.0.1:6480>
There is information about 6379 slave nodes on the 6480 node. It can be seen that the slaveof command has helped us complete the switch of the main server.
复制技术的原理
redis 的主从架构好像很简单一样,我们就执行了一条命令就成功搭建了主从架构,并且数据复制也没有问题,使用起来确实简单,但是这背后 redis 还是帮我们做了很多的事情,比如主从服务器之间的数据同步、主从服务器的状态检测等,这背后 redis 是如何实现的呢?接下来我们就一起看看。
数据复制原理
我们执行完 slaveof 命令之后,我们的主从关系就建立好了,在这个过程中, master 服务器与 slave 服务器之间需要经历多个步骤,如下图所示:

redis 复制原理
slaveof 命令背后,主从服务器大致经历了七步,其中权限验证这一步不是必须的,为了能够更好的理解这些步骤,就以我们上面搭建的 redis 实例为例来详细聊一聊各步骤。
1、保存主节点信息
在 6480 的客户端向 6480 节点服务器发送 slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379 命令时,我们会立马得到一个 OK。
127.0.0.1:6480> slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379 OK 127.0.0.1:6480>
这时候数据复制工作并没有开始,数据复制工作是在返回 OK 之后才开始执行的,这时候 6480 从节点做的事情是将给定的主服务器 IP 地址 127.0.0.1 以及端口 6379 保存到服务器状态的 masterhost 属性和 masterport 属性里面。
2、建立 socket 连接
在 slaveof 命令执行完之后,从服务器会根据命令设置的 IP 地址和端口,跟主服务器创建套接字连接, 如果从服务器能够跟主服务器成功的建立 socket 连接,那么从服务器将会为这个 socket 关联一个专门用于处理复制工作的文件事件处理器,这个处理器将负责后续的复制工作,比如接受全量复制的 RDB 文件以及服务器传来的写命令。同样主服务器在接受从服务器的 socket 连接之后,将为该 socket 创建一个客户端状态,这时候的从服务器同时具有服务器和客户端两个身份,从服务器可以向主服务器发送命令请求而主服务器则会向从服务器返回命令回复。
3、发送 ping 命令
从服务器与主服务器连接成功后,做的第一件事情就是向主服务器发送一个 ping 命令,发送 ping 命令主要有以下目的:
检测主从之间网络套接字是否可用
检测主节点当前是否可接受处理命令
在发送 ping 命令之后,正常情况下主服务器会返回 pong 命令,接受到主服务器返回的 pong 回复之后就会进行下一步工作,如果没有收到主节点的 pong 回复或者超时,比如网络超时或者主节点正在阻塞无法响应命令,从服务器会断开复制连接,等待下一次定时任务的调度。
4、身份验证
从服务器在接收到主服务器返回的 pong 回复之后,下一步要做的事情就是根据配置信息决定是否需要身份验证:
如果从服务器设置了 masterauth 参数,则进行身份验证
如果从服务器没有设置 masterauth 参数,则不进行身份验证
在需要身份验证的情况下,从服务器将就向主服务器发送一条 auth 命令,命令参数为从服务器 masterauth 选项的值,举个例子,如果从服务器的配置里将 masterauth 参数设置为:123456,那么从服务器将向主服务器发送 auth 123456 命令,身份验证的过程也不是一帆风顺的,可能会遇到以下几种情况:
从服务器通过 auth 命令发送的密码与主服务器的 requirepass 参数值一致,那么将继续进行后续操作,如果密码不一致,主服务将返回一个 invalid password 错误
如果主服务器没有设置 requirepass 参数,那么主服务器将返回一个 no password is set 错误
所有的错误情况都会令从服务器中止当前的复制工作,并且要从建立 socket 开始重新发起复制流程,直到身份验证通过或者从服务器放弃执行复制为止。
5. Send port information
After the authentication is passed, the slave server will execute the REPLCONF listening command and send the listening port number of the slave server to the master server, for example in our example The listening port of the slave server is 6480, then the slave server will send the REPLCONF listening 6480 command to the master server. After the master server receives this command, it will record the port number in the slave_listening_port attribute of the client status corresponding to the slave server. It is the port value we see in the master server's info replication.
6. Data replication
Data replication is the most complicated part. It is completed by the psync command. The slave server will send a psync command to the master server to process the data. Synchronization, before the redis version 2.8, the sync command was used. In addition to the different commands, the replication method was also very different. Before the redis version 2.8, full replication was used, which would cause problems for the master node and the network. A lot of overhead. After redis version 2.8, data synchronization will be divided into full synchronization and partial synchronization.
-
Full copy: Generally used in the initial copy scenario. Regardless of the old or new version of redis, a full copy will be performed when the slave server connects to the master service for the first time. It will copy the master All the data of the node is sent to the slave node at once. When the data is large, it will cause a lot of overhead on the master node and the network. Early versions of redis only support full replication, which is not an efficient data replication method
Partial replication: used to handle data loss scenarios caused by network interruptions and other reasons in master-slave replication. When the slave node connects to the master node again, if conditions permit, the master node will make up for the loss. Send the missing data to the slave node. Because the reissued data is far smaller than the full amount of data, it can effectively avoid the excessive overhead of full copying. Partial copying is a major optimization of the old version of copying, effectively avoiding unnecessary full copying operations
The reason why redis can support full copy and partial copy is mainly to optimize the sync command. After redis version 2.8, a new psync command is used. The command format is: psync {runId} {offset}. These two The meaning of each parameter:
runId: the id of the master node running
-
offset: the offset of the data copied from the current slave node
Maybe you are unfamiliar with the runid and offset above, it doesn’t matter, let’s take a look at the following three concepts first:
1. Copy offset
The master and slave nodes participating in replication will maintain their own replication offsets respectively: every time the master server transmits N bytes of data to the slave server, it adds N to the value of its own offset. Each time the slave server receives N bytes of data transmitted by the master server, it adds N to its own offset value. By comparing the replication offsets of the master and slave servers, you can know whether the data of the master and slave servers are consistent. If the offsets of the master and slave servers are always the same, then the master and slave data are consistent. On the contrary, if the offsets of the master and slave servers are consistent, If the transfer amount is not the same, it means that the master and slave servers are not in a consistent data state. For example, when there are multiple slave servers, a certain server goes offline during the transmission process, as shown in the following figure:
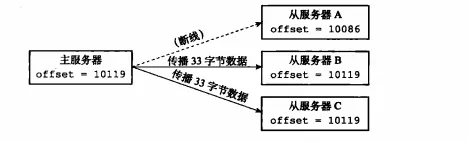
Offset is inconsistent
Because slave server A is offline due to network reasons during data transmission, causing the offset to be inconsistent with the master server, then when slave server A restarts and matches After the master server is successfully connected, re-send the psync command to the master server. At this time, should the data replication be performed in full or in part? If partial replication is performed, how can the master compensate for the data lost by slave A during the disconnection period? ?The answers to these questions are in the replication backlog buffer.
2. Replication backlog buffer
The replication backlog buffer is a fixed-length queue saved on the primary node. The default size is 1MB. When the primary node is connected The slave node (slave) is created. At this time, when the master node (master) responds to the write command, it will not only send the command to the slave node, but also write it to the replication backlog buffer, as shown in the following figure:
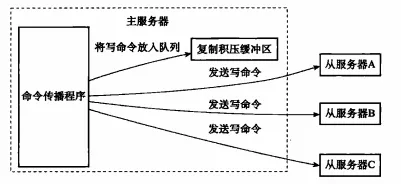
Replication Backlog Buffer
Therefore, the replication backlog buffer of the main server will store a part of the recently propagated write commands, and the replication backlog buffer will be the Each byte records the corresponding replication offset. So when the slave server reconnects to the master server, the slave server sends its own replication offset offset to the master server through the psync command. The master server will use this replication offset to decide what data synchronization operation to perform on the slave server:
If the data after the slave server's replication offset still exists in the replication backlog buffer, the master server will perform partial replication operations on the slave server
如果从服务器的复制偏移量之后的数据不存在于复制积压缓冲区里面,那么主服务器将对从服务器执行全量复制操作
3、服务器运行ID
每个 Redis 节点启动后都会动态分配一个 40 位的十六进制字符串作为运行 ID,运行 ID 的主要作用是用来唯一识别 Redis 节点,我们可以使用 info server 命令来查看
127.0.0.1:6379> info server # Server redis_version:5.0.5 redis_git_sha1:00000000 redis_git_dirty:0 redis_build_id:2ef1d58592147923 redis_mode:standalone os:Linux 3.10.0-957.27.2.el7.x86_64 x86_64 arch_bits:64 multiplexing_api:epoll atomicvar_api:atomic-builtin gcc_version:4.8.5 process_id:25214 run_id:7b987673dfb4dfc10dd8d65b9a198e239d20d2b1 tcp_port:6379 uptime_in_seconds:14382 uptime_in_days:0 hz:10 configured_hz:10 lru_clock:14554933 executable:/usr/local/redis-5.0.5/src/./redis-server config_file:/usr/local/redis-5.0.5/redis.conf 127.0.0.1:6379>
这里面有一个run_id 字段就是服务器运行的ID
在熟悉这几个概念之后,我们可以一起探讨 psync 命令的运行流程,具体如下图所示:
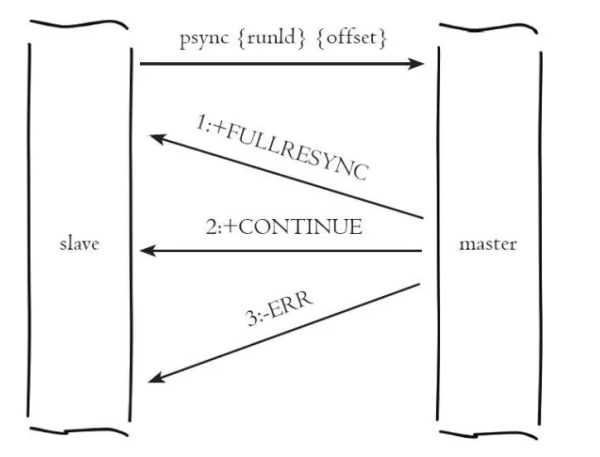
psync 运行流程
psync 命令的逻辑比较简单,整个流程分为两步:
1、从节点发送 psync 命令给主节点,参数 runId 是当前从节点保存的主节点运行ID,参数offset是当前从节点保存的复制偏移量,如果是第一次参与复制则默认值为 -1。
2、主节点接收到 psync 命令之后,会向从服务器返回以下三种回复中的一种:
回复 +FULLRESYNC {runId} {offset}:表示主服务器将与从服务器执行一次全量复制操作,其中 runid 是这个主服务器的运行 id,从服务器会保存这个id,在下一次发送 psync 命令时使用,而 offset 则是主服务器当前的复制偏移量,从服务器会将这个值作为自己的初始化偏移量
回复 +CONTINUE:那么表示主服务器与从服务器将执行部分复制操作,从服务器只要等着主服务器将自己缺少的那部分数据发送过来就可以了
回复 +ERR:那么表示主服务器的版本低于 redis 2.8,它识别不了 psync 命令,从服务器将向主服务器发送 sync 命令,并与主服务器执行全量复制
7、命令持续复制
当主节点把当前的数据同步给从节点后,便完成了复制的建立流程。主从服务器之间的连接不会中断,因为主节点会持续发送写命令到从节点,以确保主从数据的一致性。
经过上面 7 步就完成了主从服务器之间的数据同步,由于这篇文章的篇幅比较长,关于全量复制和部分复制的细节就不介绍了,全量复制就是将主节点的当前的数据生产 RDB 文件,发送给从服务器,从服务器再从本地磁盘加载,这样当文件过大时就需要特别大的网络开销,不然由于数据传输比较慢会导致主从数据延时较大,部分复制就是主服务器将复制积压缓冲区的写命令直接发送给从服务器。
心跳检测
心跳检测是发生在主从节点在建立复制后,它们之间维护着长连接并彼此发送心跳命令,便以后续持续发送写命令,主从心跳检测如下图所示:
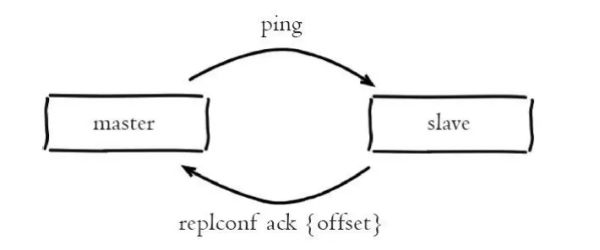
主从心跳检测
主从节点彼此都有心跳检测机制,各自模拟成对方的客户端进行通信,主从心跳检测的规则如下:
默认情况下,主节点会每隔 10 秒向从节点发送 ping 命令,以检测从节点的连接状态和是否存活。可通过修改 redis.conf 配置文件里面的 repl-ping-replica-period 参数来控制发送频率
从节点在主线程中每隔 1 秒发送 replconf ack {offset} 命令,给主节点 上报自身当前的复制偏移量,这条命令除了检测主从节点网络之外,还通过发送复制偏移量来保证主从的数据一致
主节点根据 replconf 命令判断从节点超时时间,体现在 info replication 统 计中的 lag 信息中,我们在主服务器上执行 info replication 命令:
127.0.0.1:6379> info replication # Replication role:master connected_slaves:1 slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6480,state=online,offset=25774,lag=0 master_replid:c62b6621e3acac55d122556a94f92d8679d93ea0 master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 master_repl_offset:25774 second_repl_offset:-1 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1 repl_backlog_histlen:25774 127.0.0.1:6379>
可以看出 slave0 字段的值最后面有一个 lag,lag 表示与从节点最后一次通信延迟的秒数,正常延迟应该在 0 和 1 之间。如果超过 repl-timeout 配置的值(默认60秒),则判定从节点下线并断开复制客户端连接,如果从节点重新恢复,心跳检测会继续进行。
主从拓扑架构
Redis 的主从拓扑结构可以支持单层或多层复制关系,根据拓扑复杂性可以分为以下三种:一主一从、一主多从、树状主从架构。
一主一从结构
一主一从结构是最简单的复制拓扑结构,我们前面搭建的就是一主一从的架构,架构如图所示:
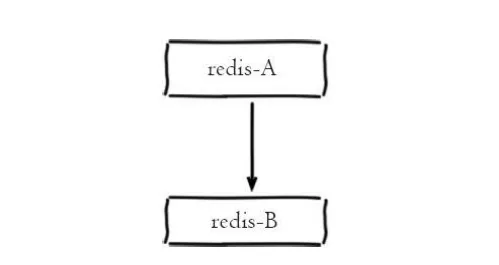
一主一从架构
One master and one slave architecture
is used to provide failover support from the slave node when the master node goes down. When the application write command concurrency is high and persistence is required, it can Only enable AOF on the slave node, which not only ensures data security but also avoids the performance interference of persistence on the master node. But there is a pit here that requires your attention, that is, when the master node turns off the persistence function, avoid automatic restart if the master node goes offline. Because the master node has not turned on the persistence function before, the data set will be empty after automatic restart. At this time, if the slave node continues to copy the master node, the slave node data will also be cleared, and the meaning of persistence will be lost. The safe approach is to execute slaveof no one on the slave node to disconnect the replication relationship with the master node, and then restart the master node to avoid this problem.
One master and multiple slaves architecture One master and multiple slaves architecture is also called star topology. One master and multiple slaves architecture is shown in the figure below:
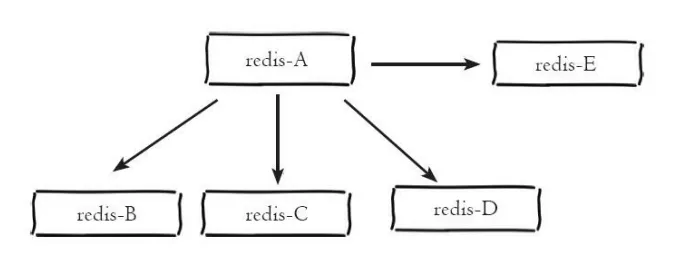
一Master-multiple-slave architecture
One-master-multiple-slave architecture can achieve separation of reading and writing to reduce the pressure on the master server. For scenarios with a large proportion of reads, read commands can be sent to slave nodes to share the pressure on the master node. At the same time, if you need to execute some time-consuming read commands during daily development, such as keys, sort, etc., you can execute them on one of the slave nodes to prevent slow queries from blocking the master node and affecting the stability of online services. For scenarios with high write concurrency, multiple slave nodes will cause the master node to send write commands multiple times, excessively consuming network bandwidth, and also increasing the load on the master node and affecting service stability.
Tree master-slave architecture
The tree master-slave architecture is also called the tree topology architecture. The tree master-slave architecture is shown in the following figure:
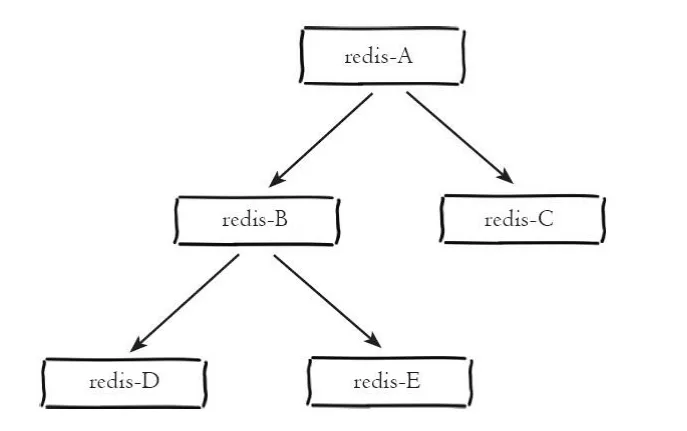
Tree-like master-slave architecture
The tree-like master-slave architecture allows the slave node to not only copy the master section data, but also serve as the master node of other slave nodes to continue to copy to the lower levels. . It solves the shortcomings of the one-master-multi-slave architecture and introduces the replication intermediate layer, which can effectively reduce the load of the master node and the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the slave nodes. As shown in the architecture diagram, after data is written to node A, it will be synchronized to nodes B and C. Node B then synchronizes the data to nodes D and E. The data is replicated layer by layer. In order to avoid interference with the performance of the master node, the master node can adopt a tree master-slave structure when it needs to mount multiple slave nodes to reduce its load pressure.
The above is the detailed content of What are the ways to establish the Redis master-slave architecture?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
To view all keys in Redis, there are three ways: use the KEYS command to return all keys that match the specified pattern; use the SCAN command to iterate over the keys and return a set of keys; use the INFO command to get the total number of keys.
 How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
How to view the version number of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
To view the Redis version number, you can use the following three methods: (1) enter the INFO command, (2) start the server with the --version option, and (3) view the configuration file.
 What to do if redis-server can't be found
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
What to do if redis-server can't be found
Apr 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
Steps to solve the problem that redis-server cannot find: Check the installation to make sure Redis is installed correctly; set the environment variables REDIS_HOST and REDIS_PORT; start the Redis server redis-server; check whether the server is running redis-cli ping.
 How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
How to use redis zset
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
Redis Ordered Sets (ZSets) are used to store ordered elements and sort by associated scores. The steps to use ZSet include: 1. Create a ZSet; 2. Add a member; 3. Get a member score; 4. Get a ranking; 5. Get a member in the ranking range; 6. Delete a member; 7. Get the number of elements; 8. Get the number of members in the score range.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.




