How to realize the identification and exchange of hot and cold data in Redis
Background
The Redis hybrid storage product is a hybrid storage product independently developed by Alibaba Cloud that is fully compatible with the Redis protocol and features.
By storing part of the cold data on the disk, while ensuring that most access performance does not decrease, user costs are greatly reduced and the memory limit on the data volume of a Redis single instance is exceeded.
Among them, the identification and exchange of hot and cold data are key factors in the performance of hybrid storage products.
Definition of hot and cold data
In Redis hybrid storage, the ratio of memory to disk is freely selectable by the user:
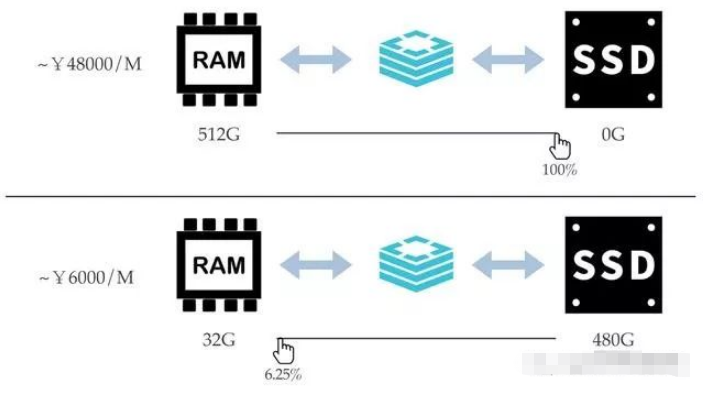
Redis Hybrid storage instances consider all Keys as hot data, ensuring that the performance of all Key access requests is efficient and consistent at the expense of a small amount of memory. For the Value part, when there is insufficient memory, the instance itself will select part of the value based on recent access time, access frequency, Value size and other dimensions as cold data and asynchronously store it on the disk in the background until the memory is less than the specified threshold.
In the Redis hybrid storage instance, we consider all Keys as hot data and save them in memory for the following two considerations:
Key access Frequency is much higher than Value.
As a KV database, normal access requests need to first search for the Key to confirm whether the Key exists. To confirm that a key does not exist, you need to check the set of all Keys in some form. Retaining all key values for in-memory data structures can ensure that the search speed is exactly the same as that of pure memory data structures.
The size ratio of Key is very low.
In a general business model, even if it is an ordinary string type, its Value is generally several times larger than the Key. For collection objects such as Set, List, Hash, etc., the value formed by the sum of all members is several orders of magnitude larger than the key.
Therefore, there are two main applicable scenarios for Redis hybrid storage instances:
Uneven data access and the existence of hotspot data;
The memory is not enough to store all the data, and the Value is large (relative to the Key)
Identification of hot and cold data
When there is insufficient memory, the instance will calculate the weight of the value based on recent access time, access frequency, value size and other dimensions, store the value with the lowest weight on the disk and delete it from the memory.
The pseudo code is as follows:

In the most ideal situation, we would like to be able to accurately calculate the current lowest value. However, the hot and cold degree of a value changes dynamically according to the access situation, and the time consumption of recalculating the hot and cold weights of all values every time is completely unacceptable.
When the memory is full, Redis itself will eliminate data according to the elimination strategy set by the user, and writing hot data from memory to disk can also be considered an "elimination" process. Considering performance, accuracy and user understanding, we use an approximate calculation method similar to Redis when identifying hot and cold data. We support multiple strategies and reduce CPU and memory consumption by randomly sampling a small part of the data, and utilize sampling through the eviction pool. historical information to help improve accuracy.
The schematic diagram of the hit rate of Redis's approximate elimination algorithm is shown under different versions and configurations of different numbers of sampling samples. Data points that have been eliminated are colored light gray, data points that have not been eliminated are gray, and data points added during the test are colored green.
Cold and hot data exchange
Redis mixed storage hot and cold data exchange process is completed in the background IO thread.
Hot data->Cold data
Asynchronous method:
The main thread generates data when the memory is close to the maximum A series of data swapping tasks;
The background thread executes these data swapping tasks and notifies the main thread after completion;
The main thread updates Release the value in the memory and update the value in the data dictionary in the memory to a simple meta-information;
Synchronization method:
When writing If the incoming traffic is too large, the asynchronous method cannot swap out the data in time, which may cause the memory to exceed the maximum specification. The main thread will directly perform the data swapping task to achieve the purpose of current limiting in disguise.
Cold data->Hot data
Asynchronous method:
The main thread first judges the command before executing it Whether all the values involved are in memory;
If not, generate a data loading task, suspend the client, and the main thread continues to process other client requests;
The background thread performs the data loading task and notifies the main thread after completion;
The main thread updates the value in the data dictionary in memory and wakes up the previously suspended client. end, processing its request.
Synchronization method:
In the Lua script, during the specific command execution phase, if a value is found to be stored on the disk, the main thread will execute it directly Data loading tasks ensure that the semantics of Lua scripts and commands remain unchanged.
The above is the detailed content of How to realize the identification and exchange of hot and cold data in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to view all keys in redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
To view all keys in Redis, there are three ways: use the KEYS command to return all keys that match the specified pattern; use the SCAN command to iterate over the keys and return a set of keys; use the INFO command to get the total number of keys.
 How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to implement the underlying redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Redis uses hash tables to store data and supports data structures such as strings, lists, hash tables, collections and ordered collections. Redis persists data through snapshots (RDB) and append write-only (AOF) mechanisms. Redis uses master-slave replication to improve data availability. Redis uses a single-threaded event loop to handle connections and commands to ensure data atomicity and consistency. Redis sets the expiration time for the key and uses the lazy delete mechanism to delete the expiration key.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.




