 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 The geo module in Nginx and how to use it to configure load balancing
The geo module in Nginx and how to use it to configure load balancing
The geo module in Nginx and how to use it to configure load balancing
The geo directive uses the ngx_http_geo_module module. By default, nginx loads this module unless --without-http_geo_module is configured manually.
ngx_http_geo_module module can be used to create variables whose values depend on the client ip address.
geo directive
Syntax: geo [$address] $variable { ... }
Default value: —
Configuration section: http
Definition from the specified variable Get the client's ip address. By default, nginx gets the client IP address from the $remote_addr variable, but it can also be obtained from other variables. For example,
geo $remote_addr $geo {
default 0;
127.0.0.1 1;
}
geo $arg_ttlsa_com $geo {
default 0;
127.0.0.1 1;
}If the value of this variable cannot represent a legal IP address, then nginx will use the address "255.255.255.255".
nginx describes the address through cidr or address segment, and supports the following parameters:
delete: delete the specified network
if If the client address cannot match any defined address, nginx will use the default value. CIDR can use "0.0.0.0/0" to replace the default value.
include: Contains a file that defines addresses and values, and can contain multiple files.
proxy: Define trusted address. When the request comes from a trusted address, nginx will obtain the address information with the help of its "X-Forwarded-For" header. Compared with ordinary addresses, trusted addresses are detected sequentially.
proxy_recursive: Enable recursive address search. If recursive lookup is turned off, nginx will use the last address in "x-forwarded-for" instead of the original client address when the client address matches a trusted address. If recursive search is enabled, when the client address matches a trusted address, nginx will use the last address in "x-forwarded-for" that does not match any trusted address to replace the original client address.
ranges: Define the address in the form of an address segment. This parameter must be placed first. To speed up loading of the address library, addresses should be defined in ascending order.
geo $country {
default zz;
include conf/geo.conf;
delete 127.0.0.0/16;
proxy 192.168.100.0/24;
proxy 2001:0db8::/32;
127.0.0.0/24 us;
127.0.0.1/32 ru;
10.1.0.0/16 ru;
192.168.1.0/24 uk;
}vim conf/geo.conf
10.2.0.0/16 ru; 192.168.2.0/24 ru;
Address segment example:
geo $country {
ranges;
default zz;
127.0.0.0-127.0.0.0 us;
127.0.0.1-127.0.0.1 ru;
127.0.0.1-127.0.0.255 us;
10.1.0.0-10.1.255.255 ru;
192.168.1.0-192.168.1.255 uk;
}The geo command mainly assigns values to variables based on ip. Therefore, only IP or network segments can be defined under the geo block, otherwise an error will be reported.
geo module implements global load balancing
server1 : 192.168.6.101
server2 : 192.168.6.102
server3 : 192.168.6.121
Test machine 1 ip: 192.168.6.2
Test machine 2 ip: 192.168.6.8
Test machine 3 ip: 192.168.6.189
1. Compile and install nginx on each server, I don’t have much said!
I have not changed the configurations of server1 and server2. I only changed the homepage, which is good for testing!
server1 :
shell $> cd /usr/local/nginx/html shell $> rm index.html shell $> echo "192.168.6.101" > index.html
server2:
shell $> cd /usr/local/nginx/html shell $> rm index.html shell $> echo "192.168.6.102" > index.html
Get their services up
shell $> /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
2 .Modify the configuration of server3`
shell $> cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/ shell $> vim nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
geo $geo {
default default;
192.168.6.189/32 uk;
192.168.6.8/32 us;
#这里的子网码是 32 是因为,我是单网段测试,如果你有vlan,你可以是24 例如
# 192.168.0.0/24 tw
}
upstream uk.server {
server 192.168.6.101;
}
upstream us.server {
server 192.168.6.102;
}
upstream default.server {
server 192.168.6.121:8080;
}
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.6.121;
index index.html index.htm;
root html;
location / {
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header host $host;
proxy_set_header x-real-ip $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header x-forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://$geo.server$request_uri;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 8080;
server_name 192.168.6.121;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
3. Test, open the browser on test machine 1 and enter
http://192.168.6.121
display
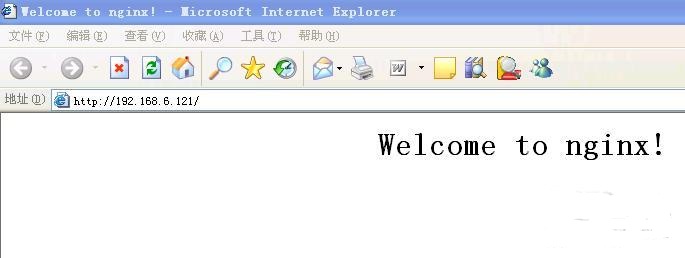
Because the IP address of test machine 1 is 192.168.6.2 according to nginx configuration, it is obvious that he accesses server3 port 8080! Because I modified the index.html of server1 server2
Open the browser on test machine 2~Enter
http://192.168.6.121
display
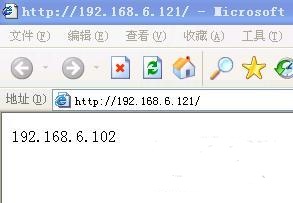
Open the browser on test machine 3 ~ enter
http://192.168.6.121
The ip of test machine 3 is 192.168.6.189
Display:
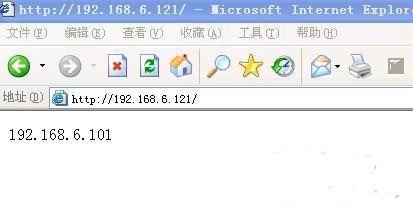
Obviously, load balancing plays a role~~~
In this way, the three servers can be placed in different IDC computer rooms. Then just synchronize the data~ The advantage of this is that it saves the trouble with DNS, because smart DNS will sometimes parse the other party's DNS address when parsing according to the visiting IP, and match it to a server. If the other party He is a Netcom user. The Telecom DNS he uses will directly match him to the Telecom server, nginx, and match the server based on the access IP. In this way, as long as we collect the IP segments in each region, it will be fine.
The above is the detailed content of The geo module in Nginx and how to use it to configure load balancing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
How to start nginx in Linux
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:51 PM
Steps to start Nginx in Linux: Check whether Nginx is installed. Use systemctl start nginx to start the Nginx service. Use systemctl enable nginx to enable automatic startup of Nginx at system startup. Use systemctl status nginx to verify that the startup is successful. Visit http://localhost in a web browser to view the default welcome page.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to solve nginx403
Apr 14, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to fix Nginx 403 Forbidden error? Check file or directory permissions; 2. Check .htaccess file; 3. Check Nginx configuration file; 4. Restart Nginx. Other possible causes include firewall rules, SELinux settings, or application issues.
 How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
How to check whether nginx is started?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:48 PM
In Linux, use the following command to check whether Nginx is started: systemctl status nginx judges based on the command output: If "Active: active (running)" is displayed, Nginx is started. If "Active: inactive (dead)" is displayed, Nginx is stopped.
 How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
How to solve nginx403 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
The server does not have permission to access the requested resource, resulting in a nginx 403 error. Solutions include: Check file permissions. Check the .htaccess configuration. Check nginx configuration. Configure SELinux permissions. Check the firewall rules. Troubleshoot other causes such as browser problems, server failures, or other possible errors.
 How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
How to solve nginx304 error
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Answer to the question: 304 Not Modified error indicates that the browser has cached the latest resource version of the client request. Solution: 1. Clear the browser cache; 2. Disable the browser cache; 3. Configure Nginx to allow client cache; 4. Check file permissions; 5. Check file hash; 6. Disable CDN or reverse proxy cache; 7. Restart Nginx.



