What are the persistence methods of Redis?
Why is persistence needed?
Normally all redis data is stored in memory. Once the database fails and is restarted, all data will be lost, even in redis cluster or redis The recovery of master-slave synchronization data in sentinel mode still takes some time.

The persistence function can effectively avoid data loss caused by process exit. Data recovery can be achieved by using the previously persisted files during the next restart.
After using Redis persistence, the data will be stored on the disk. When performing incremental synchronization of the database, the time required is much less than that of performing full synchronization. Data recovery from failures plays a very important role in a production environment!
There are two options for Redis data persistence
There are two options for Redis persistence:
RDB is a snapshot data storage that periodically saves all Redis data at the current point in time to disk.
AOF is an append-based storage method that records Redis write operations to the disk in real time.
What are the differences between these two solutions? Let me explain them one by one~
1. RDB persistence
When the writing of Redis triggers the RDB persistence condition (it can also be triggered by manually executing the dgsave command), the Redis main process forks a child process to create a temporary RDB storage file. After the file creation is completed, the temporary File rename replaces the original RDB file. The RDB file is a single file that is very suitable for disaster recovery backup and recovery of data. Restoring the database through the RDB file takes less time. Usually, it only takes about 20 seconds to load a 1G snapshot file into the memory.
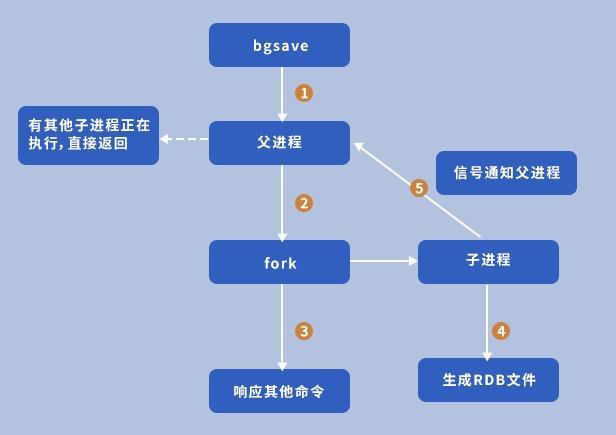
Disadvantages:
RDB persistence will only save Redis data periodically, when the next storage has not been triggered yet If Redis crashes, all data in the memory will be lost.
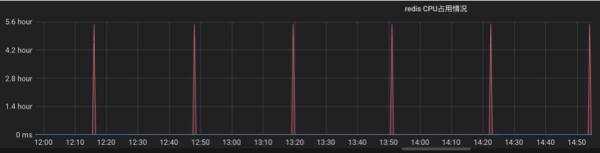
In addition, when the amount of data is large, the operation of forking the sub-process consumes a lot of CPU. As shown in the monitoring chart below, the RDB persistence triggered every 1800s will consume a lot of CPU for Redis. Soaring. Second-long blocking may occur during the fork child process.
Parameters:

save option If configured as empty save "", it will be closed RDB persistence. You can configure multiple trigger conditions for turning on RDB persistence. For example, 1 write triggers a snapshot within 900 seconds/10 writes triggers a snapshot within 300 seconds. This can be freely configured according to your own Redis writing conditions. Balance performance with data security.
It is recommended to enable stop-writes-on-bgsave-error. When an error occurs in redis bgsave, the client's request will be rejected. Bgsave failure is usually caused by insufficient disk or memory space, and monitoring is required to improve data security.
2. AOF persistence
AOF achieves persistence by saving commands for Redis write operations. Using AOF for persistence, the security of Redis data will be greatly improved. Improved, up to 1 second of data loss in case of abnormal downtime. The write operations of Redis are recorded in the AOF file. The format of the file is clear and easy to understand and can be easily modified for convenient data reconstruction.
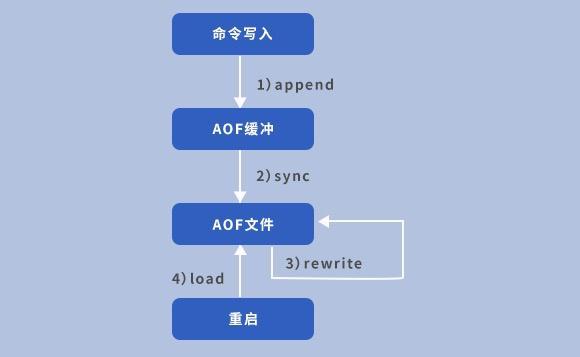
Disadvantages:
As redis writes increase, the AOF storage file will become larger and larger, which will affect the database Data recovery time and disk space, etc., so we need to configure AOF rewriting to reduce the size of the AOF file. Here we can use the default two trigger condition configurations or we can manually call the BGREWRITEAOF command to trigger.
Parameters:

appendonly sets whether to enable AOF persistence.
appendfsync has three persistence modes: always/everysec/no, which takes into account the speed and security of data storage and is configured as everysec, which synchronizes data to the disk every second.
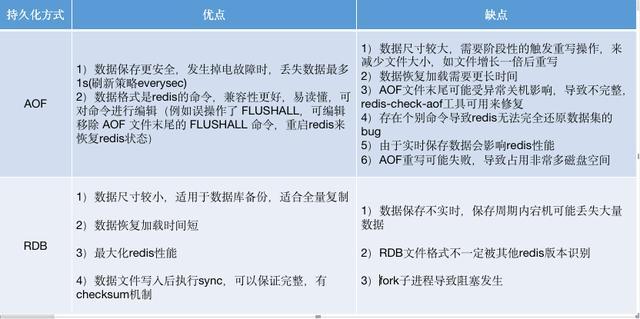
3. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of RDB and AOF persistence
Both methods have their own merits. Let’s compare the two redis data persistence methods:
4. When selecting
Redis will first check whether the AOF file exists, and if it does not exist, try to load the RDB file.
Under different circumstances, depending on the amount of data, application requirements for data security, budget constraints, etc., various persistence strategies will be used in actual production environments. This sentence can be rewritten as: You can choose not to use persistence, or you can choose to use separate RDB or AOF persistence, or you can enable RDB and AOF persistence at the same time.
PS: The choice of persistence must be considered together with the master-slave strategy of Redis, because master-slave replication and persistence also have the function of data backup, and the host master and slave slave can independently choose the persistence solution.
The above is the detailed content of What are the persistence methods of Redis?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1393
1393
 52
52
 1207
1207
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)




