 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 LLM inference is 3 times faster! Microsoft releases LLM Accelerator: using reference text to achieve lossless acceleration
LLM inference is 3 times faster! Microsoft releases LLM Accelerator: using reference text to achieve lossless acceleration
LLM inference is 3 times faster! Microsoft releases LLM Accelerator: using reference text to achieve lossless acceleration
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, new products and technologies such as ChatGPT, New Bing, and GPT-4 have been released one after another. Basic large models will play an increasingly important role in many applications.
Most of the current large language models are autoregressive models. Autoregression means that the model often uses word-by-word output when outputting, that is, when outputting each word, the model needs to use the previously output words as input. This autoregressive mode usually restricts the full utilization of parallel accelerators during output.
In many application scenarios, the output of a large model is often very similar to some reference texts, such as in the following three common scenarios:
1. Retrieval enhanced generation
When retrieval applications such as New Bing respond to user input, they will first return some information related to the user input. Relevant information is then used to summarize the retrieved information using a language model, and then answers the user input. In this scenario, the model's output often contains a large number of text fragments from the search results.
2. Use cached generation
#In the process of large-scale deployment of language models, historical input and output will is cached. When processing new input, the retrieval application looks for similar input in the cache. Therefore, the output of the model is often very similar to the corresponding output in the cache.
3. Generation in multi-turn conversations
When using applications such as ChatGPT, users often use models based on The output repeatedly requested modifications. In this multi-turn dialogue scenario, the multiple outputs of the model often have only a small amount of change and a high degree of repetition.
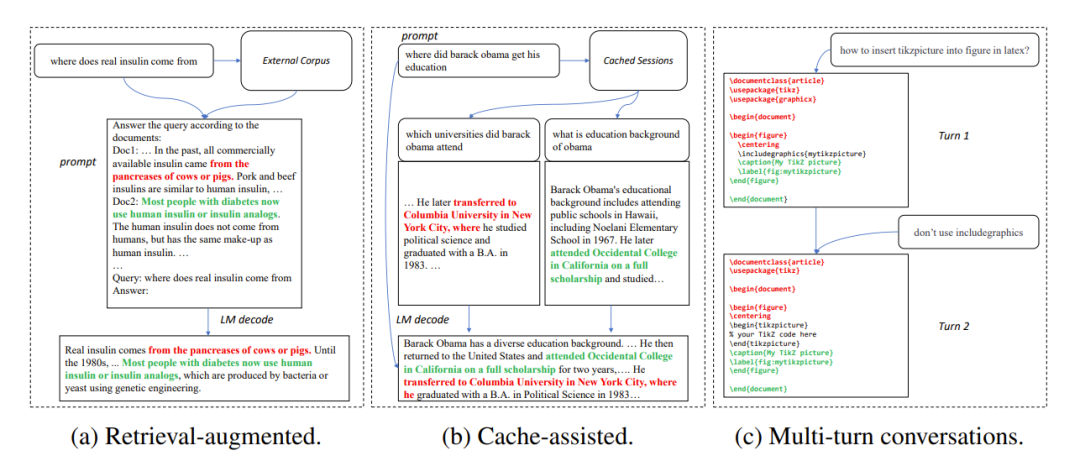
Figure 1: Common scenarios where the output of a large model is similar to the reference text
Based on the above observations, the researchers used the repeatability of reference text and model output as a focus to break through the autoregressive bottleneck, hoping to improve the utilization of parallel accelerators, accelerate large language model inference, and then A method LLM Accelerator is proposed that uses the repetition of output and reference text to output multiple words in one step.
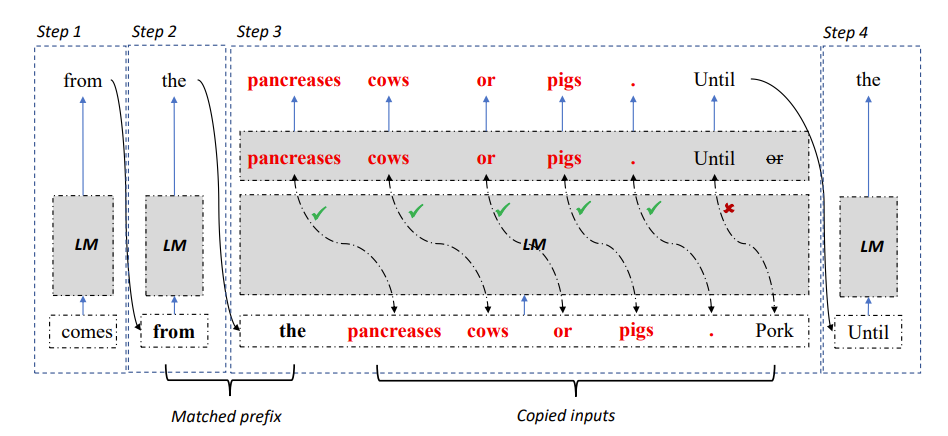
Figure 2: LLM Accelerator decoding algorithm
Specifically, at each decoding step, let the model first match the existing output results and the reference text. If a reference text is found to match the existing output, then the model is likely to postpone the existing reference text to continue output. .
Therefore, the researchers added subsequent words of the reference text as input to the model, so that one decoding step can output multiple words.
In order to ensure the accuracy of input and output, the researchers further compared the words output by the model with the words input from the reference document. If the two are inconsistent, the incorrect input and output results will be discarded.
The above method can ensure that the decoding results are completely consistent with the baseline method, and can increase the number of output words in each decoding step, thereby achieving lossless acceleration of large model inference.
LLM Accelerator does not require additional auxiliary models, is simple to use, and can be easily deployed in various application scenarios.
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.04487.pdf
Project Link: https://github.com/microsoft/LMOps
Using LLM Accelerator, there are two hyperparameters that need to be adjusted.
The first is the number of matching words between the output required to trigger the matching mechanism and the reference text: the longer the number of matching words, the more accurate it is, which can better ensure that the words copied from the reference text are correct output and reduce inaccuracies. Necessary triggering and computation; shorter matches, fewer decoding steps, potentially faster speedup.
The second is the number of words copied each time: the more words copied, the greater the acceleration potential, but it may also cause more incorrect output to be discarded, which wastes computing resources. Researchers have found through experiments that more aggressive strategies (matching single word triggers, copying 15 to 20 words at a time) can often achieve better acceleration ratios.
In order to verify the effectiveness of LLM Accelerator, the researchers conducted experiments on retrieval enhancement and cache-assisted generation, and constructed experimental samples using the MS-MARCO paragraph retrieval data set.
In the retrieval enhancement experiment, the researchers used the retrieval model to return the 10 most relevant documents for each query, and then spliced them into the query as model input. These 10 documents were used as Reference text.
In the cache-assisted generation experiment, each query generates four similar queries, and then uses the model to output the corresponding query as the reference text.
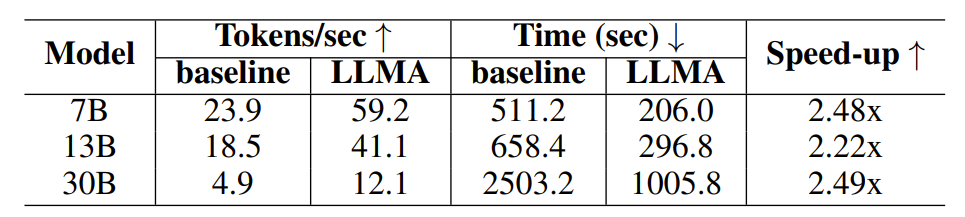
Table 1: Time comparison under retrieval enhanced generation scenario
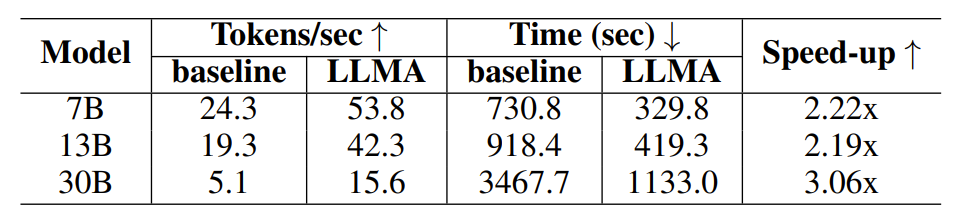
Table 2: Time comparison in the generation scenario using cache
The researchers used the output of the Davinci-003 model obtained through the OpenAI interface as the target output to obtain high-quality output. After obtaining the required input, output and reference text, the researchers conducted experiments on the open source LLaMA language model.
Since the output of the LLaMA model is inconsistent with the Davinci-003 output, the researchers used a goal-oriented decoding method to test the speedup ratio under the ideal output (Davinci-003 model result) .
The researchers used Algorithm 2 to obtain the decoding steps required to generate the target output during greedy decoding, and forced the LLaMA model to decode according to the obtained decoding steps.
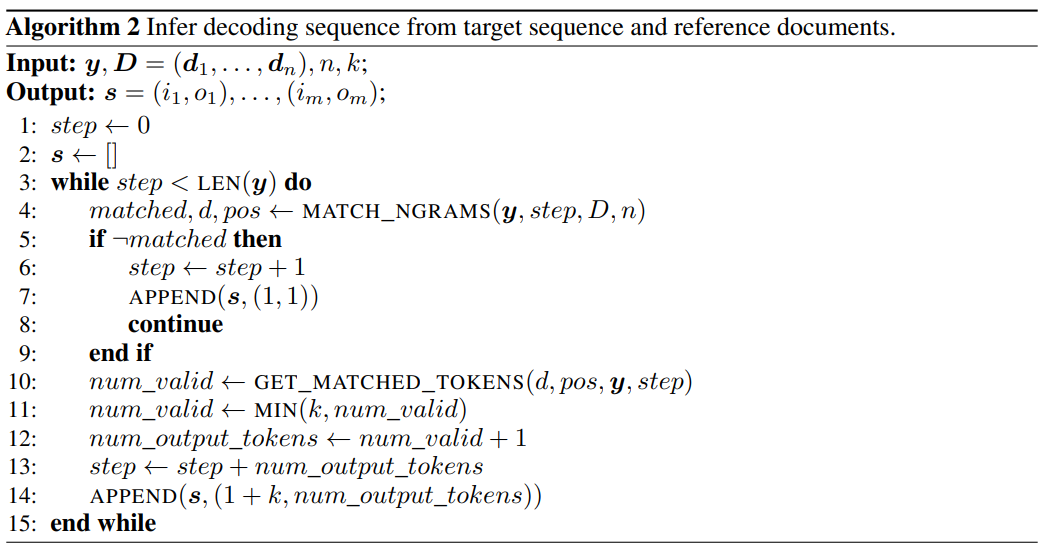
Figure 3: Using Algorithm 2 to obtain the decoding steps required to generate the target output during greedy decoding
For models with 7B and 13B parameters, the researchers conducted experiments on a single 32G NVIDIA V100 GPU; for models with 30B parameters, they conducted experiments on four identical GPUs Conduct experiments on. All experiments use half-precision floating point numbers, decoding is greedy decoding, and the batch size is 1.
Experimental results show that LLM Accelerator has achieved two to three times the performance in different model sizes (7B, 13B, 30B) and different application scenarios (retrieval enhancement, cache assistance) Speedup ratio.
Further experimental analysis found that LLM Accelertator can significantly reduce the required decoding steps, and the acceleration ratio is positively correlated with the reduction ratio of decoding steps.
Fewer decoding steps, on the one hand, means that each decoding step generates more output words, which can improve the computational efficiency of GPU computing; on the other hand, for applications that require multi-card parallelism The 30B model means less multi-card synchronization, resulting in faster speed improvements.
In the ablation experiment, the results of analyzing the hyperparameters of LLM Accelertator on the development set showed that when a single word is matched (that is, the copy mechanism is triggered), 15 to 20 are copied at a time. The speedup ratio can reach the maximum when using words (shown in Figure 4).
In Figure 5, we can see that the number of matching words is 1, which can trigger the copy mechanism more, and as the copy length increases, the output words accepted by each decoding step increase, and the decoding steps decrease. Thus achieving a higher acceleration ratio.
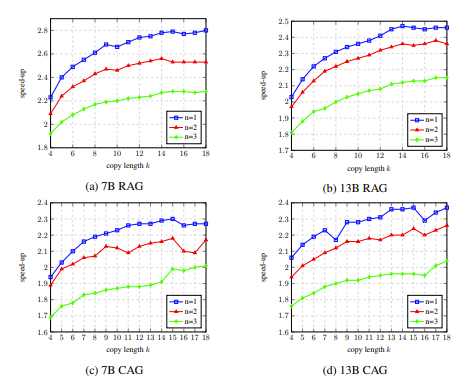
Figure 4: In the ablation experiment, the analysis results of the hyperparameters of LLM Accelertator on the development set
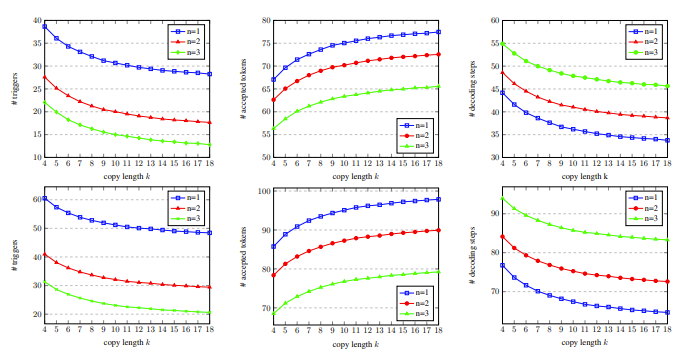
Figure 5: On the development set, with different number of matching words n and copy words Statistical data of several k decoding steps
LLM Accelertator is part of the Microsoft Research Asia Natural Language Computing Group’s series of work on large language model acceleration. In the future, researchers will continue to related issues for more in-depth exploration.
The above is the detailed content of LLM inference is 3 times faster! Microsoft releases LLM Accelerator: using reference text to achieve lossless acceleration. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 Microsoft bing international version entrance address (bing search engine entrance)
Mar 14, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Microsoft bing international version entrance address (bing search engine entrance)
Mar 14, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Bing is an online search engine launched by Microsoft. The search function is very powerful and has two entrances: the domestic version and the international version. Where are the entrances to these two versions? How to access the international version? Let’s take a look at the details below. Bing Chinese version website entrance: https://cn.bing.com/ Bing international version website entrance: https://global.bing.com/ How to access Bing international version? 1. First enter the URL to open Bing: https://www.bing.com/ 2. You can see that there are options for domestic and international versions. We only need to select the international version and enter keywords.
 Microsoft releases Win11 August cumulative update: improving security, optimizing lock screen, etc.
Aug 14, 2024 am 10:39 AM
Microsoft releases Win11 August cumulative update: improving security, optimizing lock screen, etc.
Aug 14, 2024 am 10:39 AM
According to news from this site on August 14, during today’s August Patch Tuesday event day, Microsoft released cumulative updates for Windows 11 systems, including the KB5041585 update for 22H2 and 23H2, and the KB5041592 update for 21H2. After the above-mentioned equipment is installed with the August cumulative update, the version number changes attached to this site are as follows: After the installation of the 21H2 equipment, the version number increased to Build22000.314722H2. After the installation of the equipment, the version number increased to Build22621.403723H2. After the installation of the equipment, the version number increased to Build22631.4037. The main contents of the KB5041585 update for Windows 1121H2 are as follows: Improvement: Improved
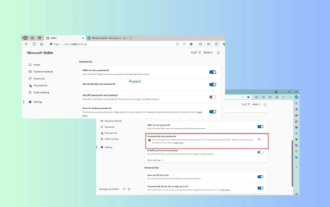 Microsoft Edge upgrade: Automatic password saving function banned? ! Users were shocked!
Apr 19, 2024 am 08:13 AM
Microsoft Edge upgrade: Automatic password saving function banned? ! Users were shocked!
Apr 19, 2024 am 08:13 AM
News on April 18th: Recently, some users of the Microsoft Edge browser using the Canary channel reported that after upgrading to the latest version, they found that the option to automatically save passwords was disabled. After investigation, it was found that this was a minor adjustment after the browser upgrade, rather than a cancellation of functionality. Before using the Edge browser to access a website, users reported that the browser would pop up a window asking if they wanted to save the login password for the website. After choosing to save, Edge will automatically fill in the saved account number and password the next time you log in, providing users with great convenience. But the latest update resembles a tweak, changing the default settings. Users need to choose to save the password and then manually turn on automatic filling of the saved account and password in the settings.
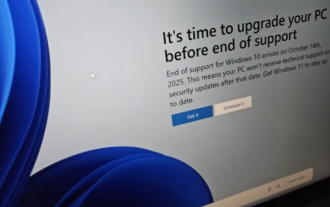 Microsoft's full-screen pop-up urges Windows 10 users to hurry up and upgrade to Windows 11
Jun 06, 2024 am 11:35 AM
Microsoft's full-screen pop-up urges Windows 10 users to hurry up and upgrade to Windows 11
Jun 06, 2024 am 11:35 AM
According to news on June 3, Microsoft is actively sending full-screen notifications to all Windows 10 users to encourage them to upgrade to the Windows 11 operating system. This move involves devices whose hardware configurations do not support the new system. Since 2015, Windows 10 has occupied nearly 70% of the market share, firmly establishing its dominance as the Windows operating system. However, the market share far exceeds the 82% market share, and the market share far exceeds that of Windows 11, which will be released in 2021. Although Windows 11 has been launched for nearly three years, its market penetration is still slow. Microsoft has announced that it will terminate technical support for Windows 10 after October 14, 2025 in order to focus more on
 Microsoft Win11's function of compressing 7z and TAR files has been downgraded from 24H2 to 23H2/22H2 versions
Apr 28, 2024 am 09:19 AM
Microsoft Win11's function of compressing 7z and TAR files has been downgraded from 24H2 to 23H2/22H2 versions
Apr 28, 2024 am 09:19 AM
According to news from this site on April 27, Microsoft released the Windows 11 Build 26100 preview version update to the Canary and Dev channels earlier this month, which is expected to become a candidate RTM version of the Windows 1124H2 update. The main changes in the new version are the file explorer, Copilot integration, editing PNG file metadata, creating TAR and 7z compressed files, etc. @PhantomOfEarth discovered that Microsoft has devolved some functions of the 24H2 version (Germanium) to the 23H2/22H2 (Nickel) version, such as creating TAR and 7z compressed files. As shown in the diagram, Windows 11 will support native creation of TAR
 Microsoft Edge browser update: Added "zoom in image" function to improve user experience
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:40 PM
Microsoft Edge browser update: Added "zoom in image" function to improve user experience
Mar 21, 2024 pm 01:40 PM
According to news on March 21, Microsoft recently updated its Microsoft Edge browser and added a practical "enlarge image" function. Now, when using the Edge browser, users can easily find this new feature in the pop-up menu by simply right-clicking on the image. What’s more convenient is that users can also hover the cursor over the image and then double-click the Ctrl key to quickly invoke the function of zooming in on the image. According to the editor's understanding, the newly released Microsoft Edge browser has been tested for new features in the Canary channel. The stable version of the browser has also officially launched the practical "enlarge image" function, providing users with a more convenient image browsing experience. Foreign science and technology media also paid attention to this
 Microsoft plans to phase out NTLM in Windows 11 in the second half of 2024 and fully shift to Kerberos authentication
Jun 09, 2024 pm 04:17 PM
Microsoft plans to phase out NTLM in Windows 11 in the second half of 2024 and fully shift to Kerberos authentication
Jun 09, 2024 pm 04:17 PM
In the second half of 2024, the official Microsoft Security Blog published a message in response to the call from the security community. The company plans to eliminate the NTLAN Manager (NTLM) authentication protocol in Windows 11, released in the second half of 2024, to improve security. According to previous explanations, Microsoft has already made similar moves before. On October 12 last year, Microsoft proposed a transition plan in an official press release aimed at phasing out NTLM authentication methods and pushing more enterprises and users to switch to Kerberos. To help enterprises that may be experiencing issues with hardwired applications and services after turning off NTLM authentication, Microsoft provides IAKerb and
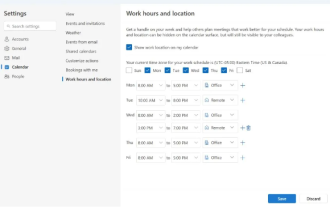 Microsoft launches new version of Outlook for Windows: comprehensive upgrade of calendar functions
Apr 27, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
Microsoft launches new version of Outlook for Windows: comprehensive upgrade of calendar functions
Apr 27, 2024 pm 03:44 PM
In news on April 27, Microsoft announced that it will soon release a test of a new version of Outlook for Windows client. This update mainly focuses on optimizing the calendar function, aiming to improve users’ work efficiency and further simplify daily workflow. The improvement of the new version of Outlook for Windows client lies in its more powerful calendar management function. Now, users can more easily share personal working time and location information, making meeting planning more efficient. In addition, Outlook has also added user-friendly settings, allowing users to set meetings to automatically end early or start later, providing users with more flexibility, whether they want to change meeting rooms, take a break or enjoy a cup of coffee. arrange. according to



